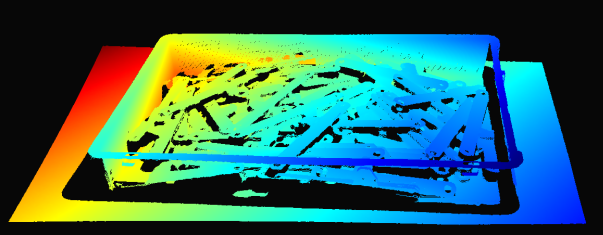
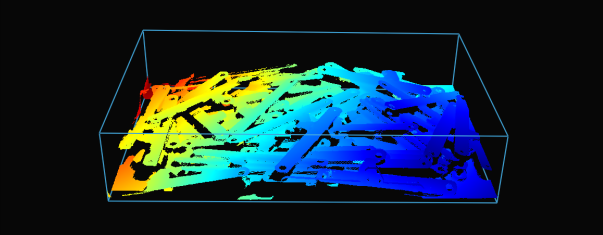
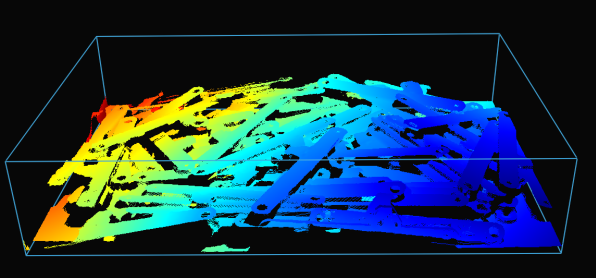
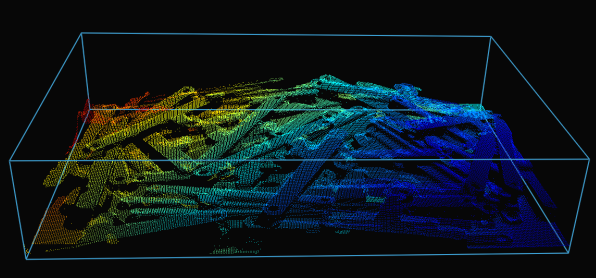
Production Preparation Processes
Zivid SDK에는 시스템을 설정하고 생산을 준비하는 데 도움이 되는 여러 프로세스와 도구가 있습니다. 생산을 시작하기 전에 권장하는 필수 항목은 다음과 같습니다.
warm-up
infield correction
hand-eye calibration
이러한 프로세스를 사용하여 작업 온도, 거리 및 FOV 등 작업 조건에 맞춰 카메라를 생산 환경에 최대한 최적화 합니다. 생산 중 처리 시간을 줄여 피킹 속도를 최대화하는 데 도움이 되는 다른 도구는 다음과 같습니다.
transforming 및 ROI 상자 필터링
다운샘플링
Robot Calibration
생산을 시작하기 전에 로봇이 잘 보정되어 위치 정확도가 좋은지 확인해야 합니다. 로봇 운동학적 교정 및 로봇 마스터링/영점 조정에 대한 자세한 내용은 로봇 공급업체에 문의하십시오.
Warm-up
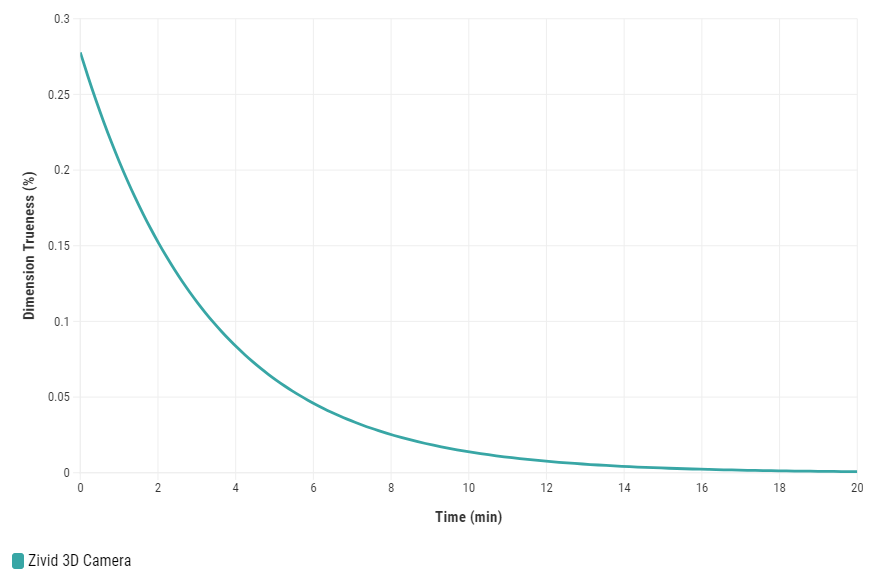
Zivid 3D 카메라가 예열되고 열 평형에 도달하도록 허용하면 애플리케이션의 전반적인 정확성과 성공을 향상시킬 수 있습니다. 애플리케이션이 엄격한 허용 오차를 요구하는 경우(예: 카메라에서 미터 거리당 허용 오차가 5mm 미만인 애플리케이션 선택)에 권장됩니다. 예열된 카메라는 Infield Correction과 Hand-Eye Calibration 결과를 모두 개선합니다.
카메라를 예열하기 위해 사이클 타임과 카메라 설정 경로를 사용하여 코드 샘플을 실행 할 수 있습니다.
Sample: warmup.py
python /path/to/warmup.py --settings-path /path/to/settings.yml --capture-cycle 6.0
Warmup이 필요한 이유와 SDK로 워밍업을 수행하는 방법을 더 잘 이해하려면 Warm-up 를 읽어보십시오.
팁
카메라가 10분 이상 사진을 찍지 못하는 시간이 길어지는 경우, Thermal Stabilization 기능을 활성화해 놓는 것이 매우 좋습니다.
Infield Correction
Infield correction은 Zivid 카메라의 Dimension Trueness을 확인하고 수정하도록 설계된 유지 관리 도구입니다. 사용자는 시야각(FOV)의 여러 지점에서 포인트 클라우드의 Dimension Trueness을 확인하고 해당 애플리케이션에 적합한지 결정할 수 있습니다. 확인 결과 카메라가 애플리케이션에 대해 충분히 정확하지 않은 것으로 나타나면 포인트 클라우드의 Dimension Trueness을 높이기 위해 수정을 수행할 수 있습니다. 여러 측정의 평균 Dimension Trueness 오차는 0에 가까울 것으로 예상됩니다(<0.1%).
Why is this necessary?
당사의 카메라는 산업 작업 환경을 견딜 수 있도록 제작되었으며 계속해서 고품질 포인트 클라우드를 반환합니다. 그러나 대부분의 고정밀 전자 기기와 마찬가지로 최상의 성능을 유지하기 위해 약간의 조정이 필요할 수 있습니다. 카메라가 환경에 상당한 변화를 겪거나 무거운 취급을 받는 경우 새로운 설정에서 최적으로 작동하려면 보정이 필요할 수 있습니다.
처음 하는 경우 Infield Correction 에 대해 자세히 읽어보십시오.
Infield Verification을 실행할 때 Dimension Trueness가 빈의 상단과 하단 모두에서 양호한지 확인하십시오. 온암 애플리케이션의 경우 Infield Verification을 수행할 때 로봇을 캡처 포즈로 이동합니다. 검증 결과가 좋으면 Infield Correction을 실행할 필요가 없습니다.
Infield Correction이 필요한 경우 최적의 결과를 위해 전체 작업 볼륨을 확장합니다. 이는 Zivid calibration board 주어진 거리의 여러 위치에 배치하고 전체 보드가 FOV 에 있도록 하면서 다양한 거리에서 수행하는 것을 의미합니다. 빈 피킹에는 빈 하단 거리에서 두 곳과 빈 상단 거리에서 두 곳이면 충분합니다. 자세한 내용 Guidelines for Performing Infield Correction 을 참고하십시오.
카메라에서 Infield Verification 또는 Correction을 실행하려면 다음을 사용할 수 있습니다.
Zivid Studio
CLI 도구
SDK
팁
Infield Correction을 처음 실행하는 경우 Zivid Studio를 사용하는 것이 좋습니다.
Infield Correction 실행에 대한 단계별 가이드 Running Infield Correction 을 확인하십시오.
Hand-Eye Calibration
Picking accuracy depends on:
Camera calibration
Hand-eye calibration
Machine vision software
Robot positioning
Robots are repeatable but not inherently accurate due to the factors such as temperature, joint friction, payload, manufacturing tolerances.
Recommendations:
Perform mastering (zeroing) to teach the robot the exact zero position of each joint.
Calibrate the robot for improved pose accuracy.
Repeat hand-eye calibration if:
robot loses calibration.
camera is dismounted and remounted.
Perform regular recalibration (robot and/or hand-eye) to maintain system performance.
Recommended method
For users who want to perform hand-eye calibration without developing their own solution, Zivid recommends using the Hand-Eye GUI—a graphical tool provided as part of our Python sample library to simplify the process. It includes all essential features such as warmup, infield correction, calibration, and verification tests. While the tool supports integration with RoboDK, its use is optional; the GUI can be used independently for features with Zivid cameras.
팁
핸드-아이 칼리브레이션을 실행하기 전에 카메라를 Warm-up 하고 Infield Correction 을 실행하는 것이 좋습니다. 워밍업, Infield Correction, 핸드-아이 칼리브레이션 시 애플리케이션과 동일한 촬영 주기를 사용하세요. 온도에 따른 성능 요소의 영향을 더욱 줄이려면 Thermal Stabilization 기능을 활성화하세요.
Alternative methods
다른 워크플로나 시스템과의 긴밀한 통합을 선호하는 경우 다음과 같은 몇 가지 대안을 사용할 수 있습니다.
- UR5 + Python sample
RoboDK나 GUI 대신 UR5 드라이버를 직접 사용하려는 사용자는 UR5 Robot + Python: Generate Dataset and perform Hand-Eye Calibration 을 참조하세요.
- RoboDK + Python sample
GUI를 사용하는 것보다 RoboDK와 Python을 사용하여 스크립팅 프로세스를 선호하는 경우 다음을 참조하세요: Any Robot + RoboDK + Python: Generate Dataset and Perform Hand-Eye Calibration.
- Command-Line Tool
Python 기반이 아니거나 종속성이 최소화된 워크플로를 선호하는 사용자는 Zivid CLI Tool For Hand-Eye Calibration 을 참조하세요. 이 실험적 CLI 도구는 제공된 데이터세트에서 핸드아이 변환을 계산하고 변환 행렬과 잔차를 사용자가 지정한 파일에 저장합니다.
Custom integration
더욱 맞춤화된 통합을 선호하는 경우(예: 핸드-아이 칼리브레이션을 자체 솔루션에 직접 내장하는 경우) 아래에 설명된 단계별 프로세스를 따르고 대화형 코드 샘플을 살펴볼 수 있습니다.
핸드아이 교정 프로세스 단계:
로봇을 새로운 자세로 옮기세요
엔드 이펙터 포즈 등록
교정 객체를 이미지화합니다(포즈를 얻습니다)
1~3단계를 여러 번 반복합니다(예: 10~20)
핸드-아이이 변환 계산
솔루션에 핸드아이 보정을 통합하는 방법을 알아보려면 대화형 코드 샘플을 확인하세요.
/*
Perform Hand-Eye calibration.
*/
#include <Zivid/Application.h>
#include <Zivid/Calibration/Detector.h>
#include <Zivid/Calibration/HandEye.h>
#include <Zivid/Calibration/Pose.h>
#include <Zivid/Exception.h>
#include <Zivid/Zivid.h>
#include <clipp.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <stdexcept>
namespace
{
std::string presetPath(const Zivid::Camera &camera)
{
const std::string presetsPath = std::string(ZIVID_SAMPLE_DATA_DIR) + "/Settings";
switch(camera.info().model().value())
{
case Zivid::CameraInfo::Model::ValueType::zividTwo:
{
return presetsPath + "/Zivid_Two_M70_ManufacturingSpecular.yml";
}
case Zivid::CameraInfo::Model::ValueType::zividTwoL100:
{
return presetsPath + "/Zivid_Two_L100_ManufacturingSpecular.yml";
}
case Zivid::CameraInfo::Model::ValueType::zivid2PlusM130:
{
return presetsPath + "/Zivid_Two_Plus_M130_ConsumerGoodsQuality.yml";
}
case Zivid::CameraInfo::Model::ValueType::zivid2PlusM60:
{
return presetsPath + "/Zivid_Two_Plus_M60_ConsumerGoodsQuality.yml";
}
case Zivid::CameraInfo::Model::ValueType::zivid2PlusL110:
{
return presetsPath + "/Zivid_Two_Plus_L110_ConsumerGoodsQuality.yml";
}
case Zivid::CameraInfo::Model::ValueType::zivid2PlusMR130:
{
return presetsPath + "/Zivid_Two_Plus_MR130_ConsumerGoodsQuality.yml";
}
case Zivid::CameraInfo::Model::ValueType::zivid2PlusMR60:
{
return presetsPath + "/Zivid_Two_Plus_MR60_ConsumerGoodsQuality.yml";
}
case Zivid::CameraInfo::Model::ValueType::zivid2PlusLR110:
{
return presetsPath + "/Zivid_Two_Plus_LR110_ConsumerGoodsQuality.yml";
}
case Zivid::CameraInfo::Model::ValueType::zivid3XL250:
{
return presetsPath + "/Zivid_Three_XL250_DepalletizationQuality.yml";
}
case Zivid::CameraInfo::Model::ValueType::zividOnePlusSmall:
case Zivid::CameraInfo::Model::ValueType::zividOnePlusMedium:
case Zivid::CameraInfo::Model::ValueType::zividOnePlusLarge: break;
default: throw std::runtime_error("Unhandled enum value '" + camera.info().model().toString() + "'");
}
throw std::invalid_argument("Invalid camera model");
}
enum class CommandType
{
AddPose,
Calibrate,
Unknown
};
std::string getInput()
{
std::string command;
std::getline(std::cin, command);
return command;
}
CommandType enterCommand()
{
std::cout << "Enter command, p (to add robot pose) or c (to perform calibration): ";
const auto command = getInput();
if(command == "P" || command == "p")
{
return CommandType::AddPose;
}
if(command == "C" || command == "c")
{
return CommandType::Calibrate;
}
return CommandType::Unknown;
}
Zivid::Calibration::Pose enterRobotPose(size_t index)
{
std::cout << "Enter pose with id (a line with 16 space separated values describing 4x4 row-major matrix) : "
<< index << std::endl;
std::stringstream input(getInput());
float element{ 0 };
std::vector<float> transformElements;
for(size_t i = 0; i < 16 && input >> element; ++i)
{
transformElements.emplace_back(element);
}
const auto robotPose{ Zivid::Matrix4x4{ transformElements.cbegin(), transformElements.cend() } };
std::cout << "The following pose was entered: \n" << robotPose << std::endl;
return robotPose;
}
std::string markersToString(const std::vector<int> &markerIds)
{
std::ostringstream oss;
for(const auto &id : markerIds)
{
oss << id << " ";
}
return oss.str();
}
void handleAddPose(
size_t ¤tPoseId,
std::vector<Zivid::Calibration::HandEyeInput> &handEyeInput,
Zivid::Camera &camera,
const std::string &calibrationObject,
const Zivid::Settings &settings)
{
const auto robotPose = enterRobotPose(currentPoseId);
std::cout << "Detecting calibration object in point cloud" << std::endl;
if(calibrationObject == "c")
{
const auto frame = camera.capture2D3D(settings);
const auto detectionResult = Zivid::Calibration::detectCalibrationBoard(frame);
if(detectionResult.valid())
{
std::cout << "Calibration board detected " << std::endl;
handEyeInput.emplace_back(robotPose, detectionResult);
currentPoseId++;
}
else
{
std::cout << "Failed to detect calibration board. " << detectionResult.statusDescription() << std::endl;
}
}
else if(calibrationObject == "m")
{
const auto frame = camera.capture2D3D(settings);
auto markerDictionary = Zivid::Calibration::MarkerDictionary::aruco4x4_50;
std::vector<int> markerIds = { 1, 2, 3 };
std::cout << "Detecting arUco marker IDs " << markersToString(markerIds) << "from the dictionary "
<< markerDictionary << std::endl;
auto detectionResult = Zivid::Calibration::detectMarkers(frame, markerIds, markerDictionary);
if(detectionResult.valid())
{
std::cout << "ArUco marker(s) detected: " << detectionResult.detectedMarkers().size() << std::endl;
handEyeInput.emplace_back(robotPose, detectionResult);
currentPoseId++;
}
else
{
std::cout
<< "Failed to detect any ArUco markers, ensure that at least one ArUco marker is in the view of the camera"
<< std::endl;
}
}
}
std::vector<Zivid::Calibration::HandEyeInput> readHandEyeInputs(
Zivid::Camera &camera,
const Zivid::Settings &settings)
{
size_t currentPoseId{ 0 };
bool calibrate{ false };
std::string calibrationObject;
while(true)
{
std::cout
<< "Enter calibration object you are using, m (for ArUco marker(s)) or c (for Zivid checkerboard): "
<< std::endl;
calibrationObject = getInput();
if(calibrationObject == "m" || calibrationObject == "c")
{
break;
}
}
std::cout << "Zivid primarily operates with a (4x4) transformation matrix. To convert" << std::endl;
std::cout << "from axis-angle, rotation vector, roll-pitch-yaw, or quaternion, check out" << std::endl;
std::cout << "our PoseConversions sample." << std::endl;
std::vector<Zivid::Calibration::HandEyeInput> handEyeInput;
do
{
switch(enterCommand())
{
case CommandType::AddPose:
{
try
{
handleAddPose(currentPoseId, handEyeInput, camera, calibrationObject, settings);
}
catch(const std::exception &e)
{
std::cout << "Error: " << Zivid::toString(e) << std::endl;
continue;
}
break;
}
case CommandType::Calibrate:
{
calibrate = true;
break;
}
case CommandType::Unknown:
{
std::cout << "Error: Unknown command" << std::endl;
break;
}
default: throw std::runtime_error{ "Unhandled command type" };
}
} while(!calibrate);
return handEyeInput;
}
Zivid::Calibration::HandEyeOutput performCalibration(
const std::vector<Zivid::Calibration::HandEyeInput> &handEyeInput)
{
while(true)
{
std::cout << "Enter type of calibration, eth (for eye-to-hand) or eih (for eye-in-hand): ";
const auto calibrationType = getInput();
if(calibrationType == "eth" || calibrationType == "ETH")
{
std::cout << "Performing eye-to-hand calibration with " << handEyeInput.size() << " dataset pairs"
<< std::endl;
std::cout << "The resulting transform is the camera pose in robot base frame" << std::endl;
return Zivid::Calibration::calibrateEyeToHand(handEyeInput);
}
if(calibrationType == "eih" || calibrationType == "EIH")
{
std::cout << "Performing eye-in-hand calibration with " << handEyeInput.size() << " dataset pairs"
<< std::endl;
std::cout << "The resulting transform is the camera pose in flange (end-effector) frame" << std::endl;
return Zivid::Calibration::calibrateEyeInHand(handEyeInput);
}
std::cout << "Entered uknown method" << std::endl;
}
}
} // namespace
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
try
{
std::string settingsPath;
bool showHelp = false;
auto cli =
(clipp::option("-h", "--help").set(showHelp) % "Show help message",
clipp::option("--settings-path")
& clipp::value("path", settingsPath) % "Path to the camera settings YML file");
if(!clipp::parse(argc, argv, cli) || showHelp)
{
auto fmt = clipp::doc_formatting{}.alternatives_min_split_size(1).surround_labels("\"", "\"");
std::cout << "USAGE:" << std::endl;
std::cout << clipp::usage_lines(cli, argv[0], fmt) << std::endl;
std::cout << "OPTIONS:" << std::endl;
std::cout << clipp::documentation(cli) << std::endl;
return showHelp ? EXIT_SUCCESS : EXIT_FAILURE;
}
Zivid::Application zivid;
std::cout << "Connecting to camera" << std::endl;
auto camera{ zivid.connectCamera() };
if(settingsPath.empty())
{
settingsPath = presetPath(camera);
}
const auto settings = Zivid::Settings(settingsPath);
const auto handEyeInput{ readHandEyeInputs(camera, settings) };
const auto calibrationResult{ performCalibration(handEyeInput) };
std::cout << "Zivid primarily operates with a (4x4) transformation matrix. To convert" << std::endl;
std::cout << "to axis-angle, rotation vector, roll-pitch-yaw, or quaternion, check out" << std::endl;
std::cout << "our PoseConversions sample." << std::endl;
if(calibrationResult.valid())
{
std::cout << "Hand-Eye calibration OK\n"
<< "Result:\n"
<< calibrationResult << std::endl;
}
else
{
std::cout << "Hand-Eye calibration FAILED" << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
}
catch(const std::exception &e)
{
std::cerr << "\nError: " << Zivid::toString(e) << std::endl;
std::cout << "Press enter to exit." << std::endl;
std::cin.get();
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
/*
Perform Hand-Eye calibration.
*/
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using Zivid.NET.Calibration;
using Duration = Zivid.NET.Duration;
class Program
{
static int Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
var userOptions = ParseOptions(args);
if (userOptions.ShowHelp)
{
ShowHelp();
return 0;
}
var zivid = new Zivid.NET.Application();
Console.WriteLine("Connecting to camera");
var camera = zivid.ConnectCamera();
var settingsPath = userOptions.SettingsPath;
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(settingsPath))
{
settingsPath = PresetPath(camera);
}
var settings = new Zivid.NET.Settings(settingsPath);
var handEyeInput = readHandEyeInputs(camera, settings);
var calibrationResult = performCalibration(handEyeInput);
Console.WriteLine("Zivid primarily operates with a (4x4) transformation matrix. To convert");
Console.WriteLine("to axis-angle, rotation vector, roll-pitch-yaw, or quaternion, check out");
Console.WriteLine("our PoseConversions sample.");
if (calibrationResult.Valid())
{
Console.WriteLine("{0}\n{1}\n{2}", "Hand-Eye calibration OK", "Result: ", calibrationResult);
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Hand-Eye calibration FAILED");
return 1;
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine("Error: {0}", ex.ToString());
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
static (string SettingsPath, bool ShowHelp) ParseOptions(string[] args)
{
string settingsPath = "";
bool showHelp = false;
foreach (var arg in args)
{
if (arg.StartsWith("--settings-path="))
{
settingsPath = arg.Substring("--settings-path=".Length);
}
else if (arg.StartsWith("-h") || arg.StartsWith("--help"))
{
showHelp = true;
}
}
return (settingsPath, showHelp);
}
static List<HandEyeInput> readHandEyeInputs(Zivid.NET.Camera camera, Zivid.NET.Settings settings)
{
var handEyeInput = new List<HandEyeInput>();
var currentPoseId = 0U;
var beingInput = true;
var calibrationObject = "";
while (true)
{
Console.WriteLine("Enter calibration object you are using, m (for ArUco marker(s)) or c (for Zivid checkerboard): ");
calibrationObject = Console.ReadLine();
if (calibrationObject.Equals("m", StringComparison.CurrentCultureIgnoreCase) ||
calibrationObject.Equals("c", StringComparison.CurrentCultureIgnoreCase))
{
break;
}
}
Interaction.ExtendInputBuffer(2048);
Console.WriteLine("Zivid primarily operates with a (4x4) transformation matrix. To convert");
Console.WriteLine("from axis-angle, rotation vector, roll-pitch-yaw, or quaternion, check out");
Console.WriteLine("our PoseConversions sample.");
do
{
switch (Interaction.EnterCommand())
{
case CommandType.AddPose:
try
{
HandleAddPose(ref currentPoseId, ref handEyeInput, camera, calibrationObject, settings);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine("Error: {0}", ex.ToString());
continue;
}
break;
case CommandType.Calibrate: beingInput = false; break;
case CommandType.Unknown: Console.WriteLine("Error: Unknown command"); break;
}
} while (beingInput);
return handEyeInput;
}
public static void HandleAddPose(ref uint currentPoseId, ref List<HandEyeInput> handEyeInput, Zivid.NET.Camera camera, string calibrationObject, Zivid.NET.Settings settings)
{
var robotPose = Interaction.EnterRobotPose(currentPoseId);
Console.Write("Detecting calibration object in point cloud");
if (calibrationObject.Equals("c", StringComparison.CurrentCultureIgnoreCase))
{
using (var frame = camera.Capture2D3D(settings))
{
var detectionResult = Detector.DetectCalibrationBoard(frame);
if (detectionResult.Valid())
{
Console.WriteLine("Calibration board detected");
handEyeInput.Add(new HandEyeInput(robotPose, detectionResult));
++currentPoseId;
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Failed to detect calibration board, ensure that the entire board is in the view of the camera");
}
}
}
else if (calibrationObject.Equals("m", StringComparison.CurrentCultureIgnoreCase))
{
using (var frame = camera.Capture2D3D(settings))
{
var markerDictionary = Zivid.NET.MarkerDictionary.Aruco4x4_50;
var markerIds = new List<int> { 1, 2, 3 };
Console.WriteLine("Detecting arUco marker IDs " + string.Join(", ", markerIds));
var detectionResult = Detector.DetectMarkers(frame, markerIds, markerDictionary);
if (detectionResult.Valid())
{
Console.WriteLine("ArUco marker(s) detected: " + detectionResult.DetectedMarkers().Length);
handEyeInput.Add(new HandEyeInput(robotPose, detectionResult));
++currentPoseId;
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Failed to detect any ArUco markers, ensure that at least one ArUco marker is in the view of the camera");
}
}
}
}
static string PresetPath(Zivid.NET.Camera camera)
{
var presetsPath = Environment.GetFolderPath(Environment.SpecialFolder.CommonApplicationData)
+ "/Zivid/Settings/";
switch (camera.Info.Model)
{
case Zivid.NET.CameraInfo.ModelOption.ZividTwo:
{
return presetsPath + "Zivid_Two_M70_ManufacturingSpecular.yml";
}
case Zivid.NET.CameraInfo.ModelOption.ZividTwoL100:
{
return presetsPath + "Zivid_Two_L100_ManufacturingSpecular.yml";
}
case Zivid.NET.CameraInfo.ModelOption.Zivid2PlusM130:
{
return presetsPath + "Zivid_Two_Plus_M130_ConsumerGoodsQuality.yml";
}
case Zivid.NET.CameraInfo.ModelOption.Zivid2PlusM60:
{
return presetsPath + "Zivid_Two_Plus_M60_ConsumerGoodsQuality.yml";
}
case Zivid.NET.CameraInfo.ModelOption.Zivid2PlusL110:
{
return presetsPath + "Zivid_Two_Plus_L110_ConsumerGoodsQuality.yml";
}
case Zivid.NET.CameraInfo.ModelOption.Zivid2PlusMR130:
{
return presetsPath + "Zivid_Two_Plus_MR130_ConsumerGoodsQuality.yml";
}
case Zivid.NET.CameraInfo.ModelOption.Zivid2PlusMR60:
{
return presetsPath + "Zivid_Two_Plus_MR60_ConsumerGoodsQuality.yml";
}
case Zivid.NET.CameraInfo.ModelOption.Zivid2PlusLR110:
{
return presetsPath + "Zivid_Two_Plus_LR110_ConsumerGoodsQuality.yml";
}
case Zivid.NET.CameraInfo.ModelOption.Zivid3XL250:
{
return presetsPath + "Zivid_Three_XL250_DepalletizationQuality.yml";
}
default: throw new System.InvalidOperationException("Unhandled camera model: " + camera.Info.Model.ToString());
}
throw new System.InvalidOperationException("Invalid camera model");
}
static Zivid.NET.Calibration.HandEyeOutput performCalibration(List<HandEyeInput> handEyeInput)
{
while (true)
{
Console.WriteLine("Enter type of calibration, eth (for eye-to-hand) or eih (for eye-in-hand): ");
var calibrationType = Console.ReadLine();
if (calibrationType.Equals("eth", StringComparison.CurrentCultureIgnoreCase))
{
Console.WriteLine("Performing eye-to-hand calibration with " + handEyeInput.Count + " dataset pairs");
Console.WriteLine("The resulting transform is the camera pose in robot base frame");
return Calibrator.CalibrateEyeToHand(handEyeInput);
}
if (calibrationType.Equals("eih", StringComparison.CurrentCultureIgnoreCase))
{
Console.WriteLine("Performing eye-in-hand calibration with " + handEyeInput.Count + " dataset pairs");
Console.WriteLine("The resulting transform is the camera pose in flange (end-effector) frame");
return Calibrator.CalibrateEyeInHand(handEyeInput);
}
Console.WriteLine("Entered unknown method");
}
}
static void ShowHelp()
{
Console.WriteLine("Usage: HandEyeCalibration.exe [options]");
Console.WriteLine("Options:");
Console.WriteLine(" --settings-path=<path> Path to the camera settings YML file (default: based on camera model)");
Console.WriteLine(" -h, --help Show this help message");
}
}
enum CommandType
{
AddPose,
Calibrate,
Unknown
}
class Interaction
{
// Console.ReadLine only supports reading 256 characters, by default. This limit is modified
// by calling ExtendInputBuffer with the maximum length of characters to be read.
public static void ExtendInputBuffer(int size)
{
Console.SetIn(new StreamReader(Console.OpenStandardInput(), Console.InputEncoding, false, size));
}
public static CommandType EnterCommand()
{
Console.Write("Enter command, p (to add robot pose) or c (to perform calibration): ");
var command = Console.ReadLine().ToLower();
switch (command)
{
case "p": return CommandType.AddPose;
case "c": return CommandType.Calibrate;
default: return CommandType.Unknown;
}
}
public static Pose EnterRobotPose(ulong index)
{
var elementCount = 16;
Console.WriteLine(
"Enter pose with id (a line with {0} space separated values describing 4x4 row-major matrix) : {1}",
elementCount,
index);
var input = Console.ReadLine();
var elements = input.Split().Where(x => !string.IsNullOrEmpty(x.Trim())).Select(x => float.Parse(x)).ToArray();
var robotPose = new Pose(elements); Console.WriteLine("The following pose was entered: \n{0}", robotPose);
return robotPose;
}
}
"""
Perform Hand-Eye calibration.
"""
import argparse
from pathlib import Path
from typing import List, Tuple
import numpy as np
import zivid
from zividsamples.paths import get_sample_data_path
from zividsamples.save_load_matrix import assert_affine_matrix_and_save
def _options() -> argparse.Namespace:
"""Function to read user arguments.
Returns:
Arguments from user
"""
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description=__doc__)
parser.add_argument(
"--settings-path",
required=False,
type=Path,
help="Path to the camera settings YML file",
)
return parser.parse_args()
def _preset_path(camera: zivid.Camera) -> Path:
"""Get path to preset settings YML file, depending on camera model.
Args:
camera: Zivid camera
Raises:
ValueError: If unsupported camera model for this code sample
Returns:
Path: Zivid 2D and 3D settings YML path
"""
presets_path = get_sample_data_path() / "Settings"
if camera.info.model == zivid.CameraInfo.Model.zivid3XL250:
return presets_path / "Zivid_Three_XL250_DepalletizationQuality.yml"
if camera.info.model == zivid.CameraInfo.Model.zivid2PlusMR60:
return presets_path / "Zivid_Two_Plus_MR60_ConsumerGoodsQuality.yml"
if camera.info.model == zivid.CameraInfo.Model.zivid2PlusMR130:
return presets_path / "Zivid_Two_Plus_MR130_ConsumerGoodsQuality.yml"
if camera.info.model == zivid.CameraInfo.Model.zivid2PlusLR110:
return presets_path / "Zivid_Two_Plus_LR110_ConsumerGoodsQuality.yml"
if camera.info.model == zivid.CameraInfo.Model.zivid2PlusM60:
return presets_path / "Zivid_Two_Plus_M60_ConsumerGoodsQuality.yml"
if camera.info.model == zivid.CameraInfo.Model.zivid2PlusM130:
return presets_path / "Zivid_Two_Plus_M130_ConsumerGoodsQuality.yml"
if camera.info.model == zivid.CameraInfo.Model.zivid2PlusL110:
return presets_path / "Zivid_Two_Plus_L110_ConsumerGoodsQuality.yml"
if camera.info.model == zivid.CameraInfo.Model.zividTwo:
return presets_path / "Zivid_Two_M70_ManufacturingSpecular.yml"
if camera.info.model == zivid.CameraInfo.Model.zividTwoL100:
return presets_path / "Zivid_Two_L100_ManufacturingSpecular.yml"
raise ValueError("Invalid camera model")
def _enter_robot_pose(index: int) -> zivid.calibration.Pose:
"""Robot pose user input.
Args:
index: Robot pose ID
Returns:
robot_pose: Robot pose
"""
inputted = input(
f"Enter pose with id={index} (a line with 16 space separated values describing 4x4 row-major matrix): "
)
elements = inputted.split(maxsplit=15)
data = np.array(elements, dtype=np.float64).reshape((4, 4))
robot_pose = zivid.calibration.Pose(data)
print(f"The following pose was entered:\n{robot_pose}")
return robot_pose
def _perform_calibration(hand_eye_input: List[zivid.calibration.HandEyeInput]) -> zivid.calibration.HandEyeOutput:
"""Hand-Eye calibration type user input.
Args:
hand_eye_input: Hand-Eye calibration input
Returns:
hand_eye_output: Hand-Eye calibration result
"""
while True:
calibration_type = input("Enter type of calibration, eth (for eye-to-hand) or eih (for eye-in-hand): ").strip()
if calibration_type.lower() == "eth":
print(f"Performing eye-to-hand calibration with {len(hand_eye_input)} dataset pairs")
print("The resulting transform is the camera pose in robot base frame")
hand_eye_output = zivid.calibration.calibrate_eye_to_hand(hand_eye_input)
return hand_eye_output
if calibration_type.lower() == "eih":
print(f"Performing eye-in-hand calibration with {len(hand_eye_input)} dataset pairs")
print("The resulting transform is the camera pose in flange (end-effector) frame")
hand_eye_output = zivid.calibration.calibrate_eye_in_hand(hand_eye_input)
return hand_eye_output
print(f"Unknown calibration type: '{calibration_type}'")
def _handle_add_pose(
current_pose_id: int,
hand_eye_input: List,
camera: zivid.Camera,
calibration_object: str,
settings: zivid.Settings,
) -> Tuple[int, List]:
"""Acquire frame and keeps track of the robot's pose id.
Args:
current_pose_id: Counter of the current pose in the hand-eye calibration dataset
hand_eye_input: List of hand-eye calibration dataset pairs (poses and point clouds)
camera: Zivid camera
calibration_object: m (for ArUco marker(s)) or c (for Zivid checkerboard)
settings: Zivid camera settings
Returns:
Tuple[int, List]: Updated current_pose_id and hand_eye_input
"""
robot_pose = _enter_robot_pose(current_pose_id)
print("Detecting calibration object in point cloud")
if calibration_object == "c":
frame = zivid.calibration.capture_calibration_board(camera)
detection_result = zivid.calibration.detect_calibration_board(frame)
if detection_result.valid():
print("Calibration board detected")
hand_eye_input.append(zivid.calibration.HandEyeInput(robot_pose, detection_result))
current_pose_id += 1
else:
print(f"Failed to detect calibration board. {detection_result.status_description()}")
elif calibration_object == "m":
frame = camera.capture_2d_3d(settings)
marker_dictionary = zivid.calibration.MarkerDictionary.aruco4x4_50
marker_ids = [1, 2, 3]
print(f"Detecting arUco marker IDs {marker_ids} from the dictionary {marker_dictionary}")
detection_result = zivid.calibration.detect_markers(frame, marker_ids, marker_dictionary)
if detection_result.valid():
print(f"ArUco marker(s) detected: {len(detection_result.detected_markers())}")
hand_eye_input.append(zivid.calibration.HandEyeInput(robot_pose, detection_result))
current_pose_id += 1
else:
print(
"Failed to detect any ArUco markers, ensure that at least one ArUco marker is in the view of the camera"
)
return current_pose_id, hand_eye_input
def _main() -> None:
user_options = _options()
app = zivid.Application()
print("Connecting to camera")
camera = app.connect_camera()
if user_options.settings_path is None:
user_options.settings_path = _preset_path(camera)
settings = zivid.Settings.load(user_options.settings_path)
current_pose_id = 0
hand_eye_input = []
calibrate = False
while True:
calibration_object = input(
"Enter calibration object you are using, m (for ArUco marker(s)) or c (for Zivid checkerboard): "
).strip()
if calibration_object.lower() == "m" or calibration_object.lower() == "c":
break
print(
"Zivid primarily operates with a (4x4) transformation matrix. To convert\n"
"from axis-angle, rotation vector, roll-pitch-yaw, or quaternion, check out\n"
"our pose_conversions sample."
)
while not calibrate:
command = input("Enter command, p (to add robot pose) or c (to perform calibration): ").strip()
if command == "p":
try:
current_pose_id, hand_eye_input = _handle_add_pose(
current_pose_id, hand_eye_input, camera, calibration_object, settings
)
except ValueError as ex:
print(ex)
elif command == "c":
calibrate = True
else:
print(f"Unknown command '{command}'")
calibration_result = _perform_calibration(hand_eye_input)
transform = calibration_result.transform()
transform_file_path = Path(Path(__file__).parent / "transform.yaml")
assert_affine_matrix_and_save(transform, transform_file_path)
print(
"Zivid primarily operates with a (4x4) transformation matrix. To convert\n"
"to axis-angle, rotation vector, roll-pitch-yaw, or quaternion, check out\n"
"our pose_conversions sample."
)
if calibration_result.valid():
print("Hand-Eye calibration OK")
print(f"Result:\n{calibration_result}")
else:
print("Hand-Eye calibration FAILED")
if __name__ == "__main__":
_main()
Hand-Eye Calibration을 완료한 후 결과 변환 매트릭스가 정확하고 정확도 요구 사항 내에 있는지 확인할 수 있습니다. 우리는 두 가지 옵션을 제공합니다:
이 주제에 대해 자세히 알아보려면 Hand-Eye Calibration 을 확인하십시오.
ROI Box Filtering
카메라 시야는 종종 관심 영역 Region of Interest (ROI)보다 큽니다 예를 들어, 빈 (bin)이 있습니다. 데이터 처리를 최적화하기 위해 빈 주변에 ROI 상자를 설정하고 포인트 클라우드를 적절히 잘라 빈의 내용만 캡처할 수 있습니다. ROI 상자 필터링은 캡처 시간을 단축할 뿐만 아니라 알고리즘에서 사용하는 데이터 포인트 수를 줄여 알고리즘의 속도와 효율성을 향상시킵니다.
팁
작은 포인트 클라우드는 캡처 속도가 빠르고, 감지 속도도 빨라지고 전체 피킹 주기도 짧아집니다.
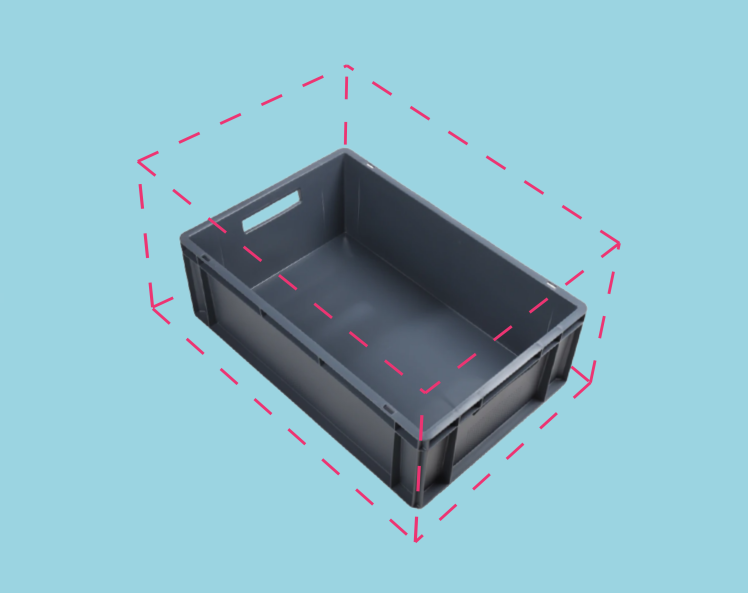
구현 예제는 ROI Box via Checkerboard 를 확인하십시오. 이 튜토리얼은 체커보드에 상대적으로 주어진 ROI 상자를 기반으로 Zivid calibration board 사용하여 포인트 클라우드를 필터링하는 방법을 보여줍니다.
Example and Performance
다음은 ROI 박스 필터링이 유용한 저사양 PC(Intel Iris Xe 통합 노트북 GPU 및 1G 네트워크 카드)를 사용하여 대규모 포인트 클라우드를 처리하는 예입니다.
고정형 Zivid 2+ MR130 카메라를 장착한 로봇이 600 x 400 x 300mm 크기의 통에서 물건을 집어 올리는 모습을 상상해 보세요. 로봇과의 충분한 간격을 확보하기 위해 카메라는 통 상단에서 1700mm 거리에 설치되어 약 1000 x 800mm의 시야각(FOV)을 제공합니다. 이 거리에 카메라를 설치하면 시야각(FOV)의 상당 부분이 ROI(관심 영역) 밖에 위치하게 되어 각 면에서 픽셀 열/행의 약 20/25%를 잘라낼 수 있습니다. 아래 표에서 볼 수 있듯이 ROI 박스 필터링을 사용하면 캡처 시간을 크게 단축할 수 있습니다.
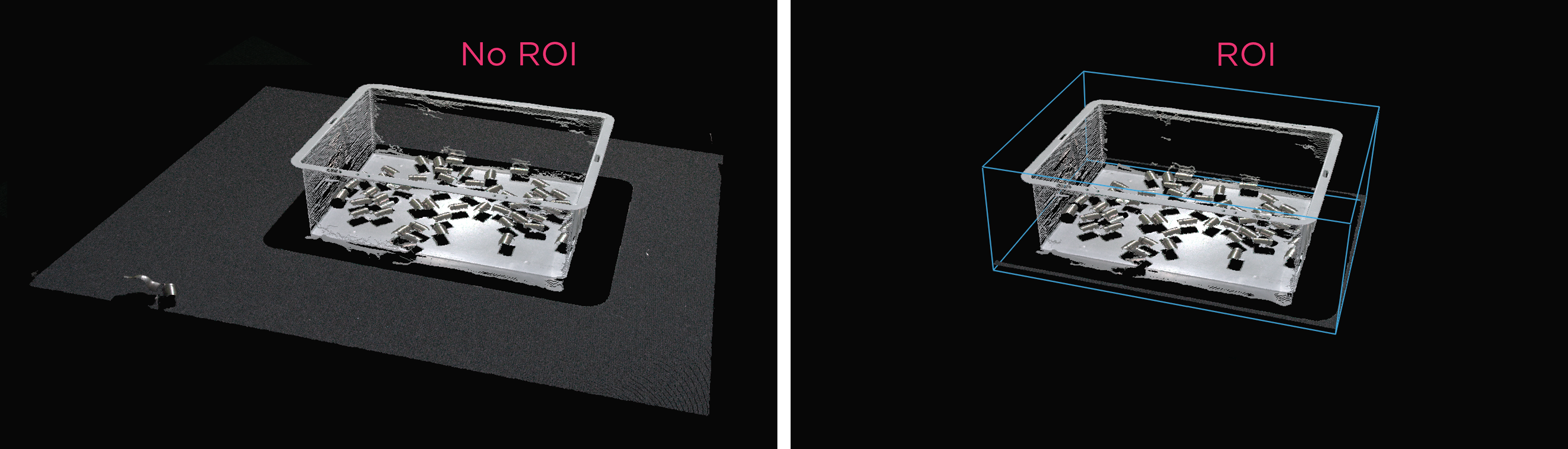
Presets |
Acquisition Time |
Capture Time |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
No ROI |
ROI |
No ROI |
ROI |
|
Manufacturing Specular |
0.64 초 |
0.64 초 |
2.1 초 |
1.0 초 |
Downsampling
참고
프리셋 선택에는 다운샘플링 선택도 포함됩니다. 하지만 이것이 무엇을 의미하는지 이해하려면 Sampling (3D) 을 참조하세요. 또한 이 글은 프리셋을 선택하지 않았을 때 어떤 다운샘플링 설정을 사용해야 하는지 이해하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
일부 애플리케이션에는 고밀도 포인트 클라우드 데이터가 필요하지 않습니다. 예를 들어 상자 표면에 평면을 맞추는 상자 감지와 물체가 뚜렷하고 쉽게 식별할 수 있는 기능이 있는 CAD 일치가 있습니다. 또한 이 데이터 양은 머신 비전 알고리즘이 애플리케이션에 필요한 속도로 처리하기에는 너무 큰 경우가 많습니다. 포인트 클라우드 다운샘플링이 작동하는 애플리케이션입니다.
포인트 클라우드 컨텍스트에서 다운샘플링은 동일한 3D 표현을 유지하면서 공간 해상도를 줄이는 것입니다. 일반적으로 데이터를 보다 관리하기 쉬운 크기로 변환하여 저장 및 처리 요구 사항을 줄이는 데 사용됩니다.
Zivid SDK를 사용하여 포인트 클라우드를 다운샘플링하는 방법에는 두 가지가 있습니다.
Settings::Processing::Resampling( Resampling ) 설정을 통해 제어됩니다. 즉, 캡처 설정을 통해 제어됩니다.API
PointCloud::downsample통해 제어됩니다.
두 경우 모두 포인트 클라우드에 동일한 작업이 적용됩니다. API 버전을 통해 그 자리에서 다운샘플링하거나 다운샘플링된 데이터를 사용하여 새로운 포인트 클라우드 인스턴스를 생성할 수 있습니다.
현재 포인트 클라우드를 수정하는 다운샘플링을 내부에서 수행할 수 있습니다.
다운샘플링된 포인트 클라우드를 기존 포인트 클라우드를 변경하지 않는 새로운 포인트 클라우드 인스턴스로 가져올 수도 있습니다.
Zivid SDK는 다음과 같은 다운샘플링 비율을 지원합니다: by2x2, by3x3 및 by4x4, 다운샘플링을 여러 번 수행할 수 있습니다.
포인트 클라우드를 다운샘플링하려면 코드 샘플을 실행하거나 튜토리얼의 다음 단계를 수행합니다.
Sample: downsample.py
python /path/to/downsample.py --zdf-path /path/to/file.zdf
ZDF 파일이 없는 경우 다음 코드 샘플을 실행할 수 있습니다. 설정으로 캡처한 Zivid 포인트 클라우드를 파일에 저장합니다.
Sample: capture_with_settings_from_yml
python /path/to/capture_with_settings_from_yml.py --settings-path /path/to/settings.yml
다운샘플링에 대한 자세한 내용은 Downsample 을 참조해주십시오.
축하드립니다! 빈 피킹 시스템을 생산에 투입할 준비를 위해 Zivid가 제공하는 모든 기능을 확인하셨습니다. 다음 섹션은 Maintenance 로, 빈 피킹 셀의 다운타임을 최소화하면서 안정적으로 유지되도록 수행하는 부분에 관련된 내용입니다.
Version History
SDK |
Changes |
|---|---|
2.12.0 |
ROI 박스 필터링이 캡처 시간을 단축하는 방법을 보여주는 섹션을 추가했습니다. 이제 |
2.10.0 |
Monochrome Capture 는 Downsampling 을 대체할 수 있는 보다 빠른 대안을 제공합니다. |