Warm-up
카메라를 예열하고 열 평형 상태에 도달하도록 하면 애플리케이션의 전반적인 정확도와 성공률을 향상시킬 수 있습니다. 이 글에서는 Zivid 카메라를 예열하는 이유와 방법을 설명합니다.
Why warm-up is needed
Zivid 카메라에는 사용 시 열을 발생시키는 능동형 전자 부품(예: 프로젝터)이 있습니다. 내부 발열로 인해 부품의 본체 온도가 변하면 기계적 변형이 발생합니다.
이러한 기계적 변화는 포인트 클라우드에서 포인트의 위치를 계산할 때 삼각 측량 정확도에 영향을 미치는 필수 광학 구성 요소의 작은 변위를 유발합니다. 카메라의 3D 보정은 warming(가열) 또는 cooling(냉각) 단계에서 정확도가 떨어지는데, 이는 각 내부 구성 요소에서 발생할 수 있는 많은 알 수 없는 온도 상태 때문입니다. 우리는 이 현상을 warm-up drift 라고 부릅니다.
카메라 온도를 제어하고 모든 구성 요소가 일정한 온도(열 평형)에 도달할 수 있도록 충분한 시간을 허용하는 것이 좋습니다. 결과적으로 Zivid 3D 보정은 카메라의 물리적 상태를 인식하고 정확하게 예측하여 정확한 포인트 클라우드를 생성할 수 있습니다.
참고
Zivid 카메라는 Thermal Stabilization 을 사용하여 안정적인 온도를 유지하고 Warm-up 필요성을 줄입니다.
Temperature change - camera vs. environment
Warm-up 테스트 결과, Zivid 카메라의 내부 온도는 가장 빠른 촬영 주기(실시간 모드)에서 분당 최대 1.5°C(10분 동안 15°C)까지 일시적으로 변할 수 있습니다. 일반적인 촬영 주기, 예를 들어 5초마다 촬영하는 경우, 내부 온도 변화는 분당 0.5~1°C로 2~3배 더 느립니다.
반면에 일별 기온은 최대 0.03 °C/min(예: 6시간에 10 °C)까지 변합니다. 이것은 워밍업 중 카메라의 일시적인 온도 변화보다 100배 더 느립니다.
Zivid 카메라는 주변 온도 변화를 보상하는 유동 보정 기능을 갖추고 있어 권장 온도 범위에서 안정성을 보장합니다. Warm-up 후 올바르게 사용하는 카메라는 지정된 주변 온도 범위 전체에서 안정적인 성능을 발휘합니다.
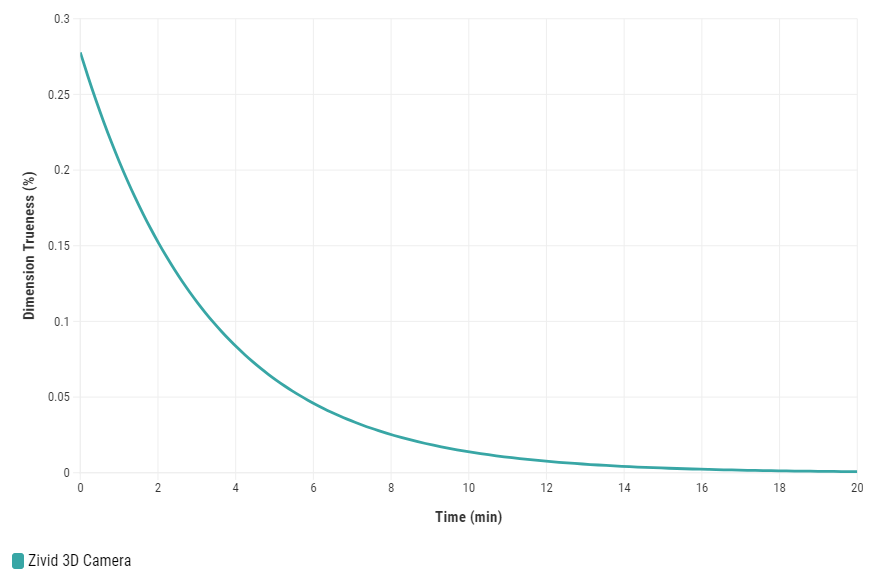
When to perform warm-up
다음 조건에서 카메라를 Warm-up하는 것이 좋습니다.
애플리케이션에는 다음과 같은 엄격한 허용 오차가 필요합니다.
카메라에서 미터당 거리가 5mm 미만인 피킹 애플리케이션.
< 0.5%의 진위 오차 요건을 갖춘 검사 애플리케이션입니다.
응용 프로그램에서 적당한 캡처 주기(10초마다 한 번 이상의 캡쳐)를 요구할 경우.
Infield Correction 전.
Hand-eye calibration 전.
생산을 실행하기 전에.
카메라를 전원에 연결하지 않은 경우(예: 카메라를 기계적으로 설치한 후).
카메라 전원이 켜져 있지만 지난 20분 동안 포인트 클라우드를 캡처하지 않은 경우(예: 아침에 생산을 시작할 때).
How to perform warm-up
카메라를 예열하려면 고정된 캡처 주기를 사용하여 10분 동안 포인트 클라우드를 캡처합니다.
Connect
첫 번째 단계는 카메라에 연결하는 것입니다.
Set Capture cycle and settings
Warm-up 동안 캡처 주기는 애플리케이션의 캡처 주기와 최대한 유사해야 합니다(빈 피킹, 팔레트 제거 등).
배포된 카메라가 예를 들어 5초마다 한 번씩 캡처하는 경우 Warm-up 단계에서 동일한 간격으로 캡처해야 합니다. 카메라에 안정적인 캡처 주기가 없는 경우 Warm-up 단계 중 캡처 주기는 극한 값 사이여야 합니다. 예를 들어 애플리케이션에서 5~11초에 한 번 캡처하는 경우 Warm-up 중에 8초에 한 번 캡처해야 합니다. 응용 프로그램에서 캡처 사이의 지연이 10초보다 길면 카메라를 예열할 필요가 없습니다.
워밍업 중에 사용하는 카메라 설정은 애플리케이션의 설정(사전 구성, YML 파일에서 로드 또는 캡처 어시스턴트)과 가능한 한 유사해야 합니다.
const auto warmupTime = std::chrono::minutes(10);
const auto captureCycle = std::chrono::seconds{ captureCycleSeconds };
const auto settings = loadOrDefaultSettings(settingsPath);
Load or suggest settings
Zivid::Settings loadOrDefaultSettings(const std::string &settingsPath)
{
if(!settingsPath.empty())
{
std::cout << "Loading settings from file" << std::endl;
return Zivid::Settings(settingsPath);
}
std::cout << "Using default 3D settings" << std::endl;
auto settings = Zivid::Settings{ Zivid::Settings::Acquisitions{ Zivid::Settings::Acquisition{} } };
return settings;
static Zivid.NET.Settings LoadOrDefaultSettings(string settingsPath)
{
if (settingsPath != null)
{
Console.WriteLine("Loading settings from file");
return new Zivid.NET.Settings(settingsPath);
}
Console.WriteLine("Using default 3D settings");
var settings = new Zivid.NET.Settings
{
Acquisitions = { new Zivid.NET.Settings.Acquisition { } }
};
return settings;
}
def _load_or_default_settings(settings_path: str) -> zivid.Settings:
"""Load settings from YML file or use default settings.
Args:
settings_path: Path to the YML file that contains camera settings
Returns:
Camera Settings
"""
if settings_path:
print("Loading settings from file")
return zivid.Settings.load(Path(settings_path))
print("Using default 3D settings")
settings = zivid.Settings(acquisitions=[zivid.Settings.Acquisition()])
return settings
참고
이 Warm-up 방식은 프로젝터를 발열체로 사용하여 안정적인 촬영 주기 동안 카메라를 예열합니다. 프로젝터가 켜진 시간과 전체 촬영 주기 시간의 비율을 듀티 사이클이라고 합니다. 듀티 사이클은 카메라가 예열되는 속도뿐만 아니라 예열 단계 후 카메라의 최종 정상 온도에도 영향을 미칩니다.
Warm up the camera
카메라를 Warm-up하려면 온도가 안정화될 때까지 10분 동안 계속해서 3D 포인트 클라우드를 캡처합니다.
std::cout << "Starting warm up for: " << warmupTime.count() << " minutes" << std::endl;
const auto beforeWarmup = SteadyClock::now();
while(SteadyClock::now() - beforeWarmup < warmupTime)
{
const auto beforeCapture = SteadyClock::now();
// Use the same capture method as you would use in production
// to get the most accurate results from warmup
camera.capture3D(settings);
const auto afterCapture = SteadyClock::now();
const auto captureTime = afterCapture - beforeCapture;
if(captureTime < captureCycle)
{
std::this_thread::sleep_for(captureCycle - captureTime);
}
else
{
std::cout << "Your capture time is longer than your desired capture cycle."
<< "Please increase the desired capture cycle." << std::endl;
}
const auto remainingTime = warmupTime - (SteadyClock::now() - beforeWarmup);
const auto remainingTimeMinutes = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::minutes>(remainingTime);
const auto remainingTimeSeconds =
std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::seconds>(remainingTime - remainingTimeMinutes);
std::cout << "Remaining time: " << remainingTimeMinutes.count() << " minutes, "
<< remainingTimeSeconds.count() << " seconds." << std::endl;
}
std::cout << "Warm up completed" << std::endl;
DateTime beforeWarmup = DateTime.Now;
Console.WriteLine("Starting warm up for: {0} minutes", warmupTime.Minutes);
while (DateTime.Now.Subtract(beforeWarmup) < warmupTime)
{
var beforeCapture = DateTime.Now;
// Use the same capture method as you would use in production
// to get the most accurate results from warmup
using (camera.Capture3D(settings)) { }
var afterCapture = DateTime.Now;
var captureTime = afterCapture.Subtract(beforeCapture);
if (captureTime < captureCycle)
{
Thread.Sleep(captureCycle.Subtract(captureTime));
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine(
"Your capture time is longer than your desired capture cycle. Please increase the desired capture cycle.");
}
var remainingTime = warmupTime.Subtract(DateTime.Now.Subtract(beforeWarmup));
var remainingMinutes = Math.Floor(remainingTime.TotalMinutes);
var remainingSeconds = Math.Floor(remainingTime.TotalSeconds) % 60;
Console.WriteLine("Remaining time: {0} minutes, {1} seconds.", remainingMinutes, remainingSeconds);
}
Console.WriteLine("Warm up completed");
before_warmup = datetime.now()
print(f"Starting warmup for {warmup_time} minutes")
while (datetime.now() - before_warmup) < warmup_time:
before_capture = datetime.now()
# Use the same capture method as you would use in production
# to get the most accurate results from warmup
camera.capture_3d(settings)
after_capture = datetime.now()
duration = after_capture - before_capture
if duration.seconds <= capture_cycle.seconds:
sleep(capture_cycle.seconds - duration.seconds)
else:
print(
"Your capture time is longer than your desired capture cycle. \
Please increase the desired capture cycle."
)
remaining_time = warmup_time - (datetime.now() - before_warmup)
remaining_time_minutes = remaining_time.seconds // 60
remaining_time_seconds = remaining_time.seconds % 60
print(f"Remaining time: {remaining_time_minutes} minutes, {remaining_time_seconds} seconds.")
print("Warmup completed")
구현 예는 아래의 전체 Warm-up 코드 샘플을 참조하세요.
/*
Short example of a basic way to warm up the camera with specified time and capture cycle.
*/
#include <Zivid/Zivid.h>
#include <clipp.h>
#include <chrono>
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
using SteadyClock = std::chrono::steady_clock;
using Duration = std::chrono::nanoseconds;
namespace
{
Zivid::Settings loadOrDefaultSettings(const std::string &settingsPath)
{
if(!settingsPath.empty())
{
std::cout << "Loading settings from file" << std::endl;
return Zivid::Settings(settingsPath);
}
std::cout << "Using default 3D settings" << std::endl;
auto settings = Zivid::Settings{ Zivid::Settings::Acquisitions{ Zivid::Settings::Acquisition{} } };
return settings;
}
} // namespace
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
try
{
std::string settingsPath;
size_t captureCycleSeconds = 5;
auto settingsOption = clipp::option("--settings-path")
& clipp::value("Path to the YML file that contains camera settings", settingsPath);
auto captureCycleOption =
clipp::option("--capture-cycle") & clipp::value("Capture cycle in seconds", captureCycleSeconds);
auto cli = (settingsOption, captureCycleOption);
if(!parse(argc, argv, cli))
{
auto fmt = clipp::doc_formatting{}.alternatives_min_split_size(1).surround_labels("\"", "\"");
std::cout << clipp::usage_lines(cli, "Warmup", fmt) << std::endl;
throw std::runtime_error{ "Invalid usage" };
}
Zivid::Application zivid;
std::cout << "Connecting to camera" << std::endl;
auto camera = zivid.connectCamera();
const auto warmupTime = std::chrono::minutes(10);
const auto captureCycle = std::chrono::seconds{ captureCycleSeconds };
const auto settings = loadOrDefaultSettings(settingsPath);
std::cout << "Starting warm up for: " << warmupTime.count() << " minutes" << std::endl;
const auto beforeWarmup = SteadyClock::now();
while(SteadyClock::now() - beforeWarmup < warmupTime)
{
const auto beforeCapture = SteadyClock::now();
// Use the same capture method as you would use in production
// to get the most accurate results from warmup
camera.capture3D(settings);
const auto afterCapture = SteadyClock::now();
const auto captureTime = afterCapture - beforeCapture;
if(captureTime < captureCycle)
{
std::this_thread::sleep_for(captureCycle - captureTime);
}
else
{
std::cout << "Your capture time is longer than your desired capture cycle."
<< "Please increase the desired capture cycle." << std::endl;
}
const auto remainingTime = warmupTime - (SteadyClock::now() - beforeWarmup);
const auto remainingTimeMinutes = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::minutes>(remainingTime);
const auto remainingTimeSeconds =
std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::seconds>(remainingTime - remainingTimeMinutes);
std::cout << "Remaining time: " << remainingTimeMinutes.count() << " minutes, "
<< remainingTimeSeconds.count() << " seconds." << std::endl;
}
std::cout << "Warm up completed" << std::endl;
}
catch(const std::exception &e)
{
std::cerr << "Error: " << Zivid::toString(e) << std::endl;
std::cout << "Press enter to exit." << std::endl;
std::cin.get();
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine("Error: " + ex.ToString());
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
static Zivid.NET.Settings LoadOrDefaultSettings(string settingsPath)
{
if (settingsPath != null)
{
Console.WriteLine("Loading settings from file");
return new Zivid.NET.Settings(settingsPath);
}
Console.WriteLine("Using default 3D settings");
var settings = new Zivid.NET.Settings
{
Acquisitions = { new Zivid.NET.Settings.Acquisition { } }
};
return settings;
}
/*
Short example of a basic way to warm up the camera with specified time and capture cycle.
*/
using CommandLine;
using System;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
using System.Threading;
using Duration = Zivid.NET.Duration;
class Program
{
public class Options
{
[Option('s', "settings-path", Required = false, HelpText = "Path to the YML file that contains camera settings.")]
public string SettingsPath { get; set; }
[Option('c', "capture-cycle", Required = false, HelpText = "Capture cycle in seconds.")]
public int? CaptureCycle { get; set; }
}
static int Main(string[] args)
{
return Parser.Default.ParseArguments<Options>(args)
.MapResult(
(Options opts) => RunWarmupWithOptionsAndReturnExitCode(opts),
errs => 1);
}
static int RunWarmupWithOptionsAndReturnExitCode(Options opts)
{
try
{
var zivid = new Zivid.NET.Application();
Console.WriteLine("Connecting to camera");
var camera = zivid.ConnectCamera();
var warmupTime = TimeSpan.FromMinutes(10);
var captureCycle = opts.CaptureCycle.HasValue ? TimeSpan.FromSeconds(opts.CaptureCycle.Value) : TimeSpan.FromSeconds(5);
var settings = LoadOrDefaultSettings(opts.SettingsPath);
DateTime beforeWarmup = DateTime.Now;
Console.WriteLine("Starting warm up for: {0} minutes", warmupTime.Minutes);
while (DateTime.Now.Subtract(beforeWarmup) < warmupTime)
{
var beforeCapture = DateTime.Now;
// Use the same capture method as you would use in production
// to get the most accurate results from warmup
using (camera.Capture3D(settings)) { }
var afterCapture = DateTime.Now;
var captureTime = afterCapture.Subtract(beforeCapture);
if (captureTime < captureCycle)
{
Thread.Sleep(captureCycle.Subtract(captureTime));
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine(
"Your capture time is longer than your desired capture cycle. Please increase the desired capture cycle.");
}
var remainingTime = warmupTime.Subtract(DateTime.Now.Subtract(beforeWarmup));
var remainingMinutes = Math.Floor(remainingTime.TotalMinutes);
var remainingSeconds = Math.Floor(remainingTime.TotalSeconds) % 60;
Console.WriteLine("Remaining time: {0} minutes, {1} seconds.", remainingMinutes, remainingSeconds);
}
Console.WriteLine("Warm up completed");
}
"""
Short example of a basic way to warm up the camera with specified time and capture cycle.
"""
import argparse
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
from pathlib import Path
from time import sleep
import zivid
def _options() -> argparse.Namespace:
"""Function to read user arguments.
Returns:
Arguments from user
"""
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description=__doc__)
parser.add_argument(
"--settings-path",
required=False,
help="Path to the YML file that contains camera settings",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--capture-cycle",
required=False,
type=float,
default=5.0,
help="Capture cycle in seconds",
)
return parser.parse_args()
def _load_or_default_settings(settings_path: str) -> zivid.Settings:
"""Load settings from YML file or use default settings.
Args:
settings_path: Path to the YML file that contains camera settings
Returns:
Camera Settings
"""
if settings_path:
print("Loading settings from file")
return zivid.Settings.load(Path(settings_path))
print("Using default 3D settings")
settings = zivid.Settings(acquisitions=[zivid.Settings.Acquisition()])
return settings
def _main() -> None:
user_options = _options()
app = zivid.Application()
print("Connecting to camera")
camera = app.connect_camera()
warmup_time = timedelta(minutes=10)
capture_cycle = timedelta(seconds=user_options.capture_cycle)
settings = _load_or_default_settings(user_options.settings_path)
before_warmup = datetime.now()
print(f"Starting warmup for {warmup_time} minutes")
while (datetime.now() - before_warmup) < warmup_time:
before_capture = datetime.now()
# Use the same capture method as you would use in production
# to get the most accurate results from warmup
camera.capture_3d(settings)
after_capture = datetime.now()
duration = after_capture - before_capture
if duration.seconds <= capture_cycle.seconds:
sleep(capture_cycle.seconds - duration.seconds)
else:
print(
"Your capture time is longer than your desired capture cycle. \
Please increase the desired capture cycle."
)
remaining_time = warmup_time - (datetime.now() - before_warmup)
remaining_time_minutes = remaining_time.seconds // 60
remaining_time_seconds = remaining_time.seconds % 60
print(f"Remaining time: {remaining_time_minutes} minutes, {remaining_time_seconds} seconds.")
print("Warmup completed")
if __name__ == "__main__":
_main()
카메라를 예열하기 위해 사이클 타임과 카메라 설정 경로를 사용하여 코드 샘플을 실행할 수 있습니다.
Sample: warmup.py
python /path/to/warmup.py --settings-path /path/to/settings.yml --capture-cycle 6.0