生产准备过程
我们在Zivid SDK中有多个流程和工具可帮助您设置好系统并为生产做好准备。我们建议在部署之前进行的必要的操作包括:
预热
现场标定
手眼标定
我们可以通过执行这些流程模仿生产条件来优化相机的工作温度、距离和 FOV 。其它可能帮助您减少生产过程中的处理时间从而最大限度地提高抓取率的工具包括:
下采样
坐标系转换和ROI盒过滤
机器人标定
在开始生产之前,您应该确保您的机器人经过良好校正,并展现出良好的定位精度。关于何如进行机器人运动学校正和机器人校正零点的信息,请联系您的机器人供应商。
预热
对Zivid 3D相机进行预热并达到热平衡,可以提高应用的整体准确性和成功率。如果应用有着严格的公差要求,则建议使用此方法,例如,距离相机每米距离的公差<5毫米的3D抓取应用。使用预热过的相机进行现场标定和手眼标定能够获得更好的结果。
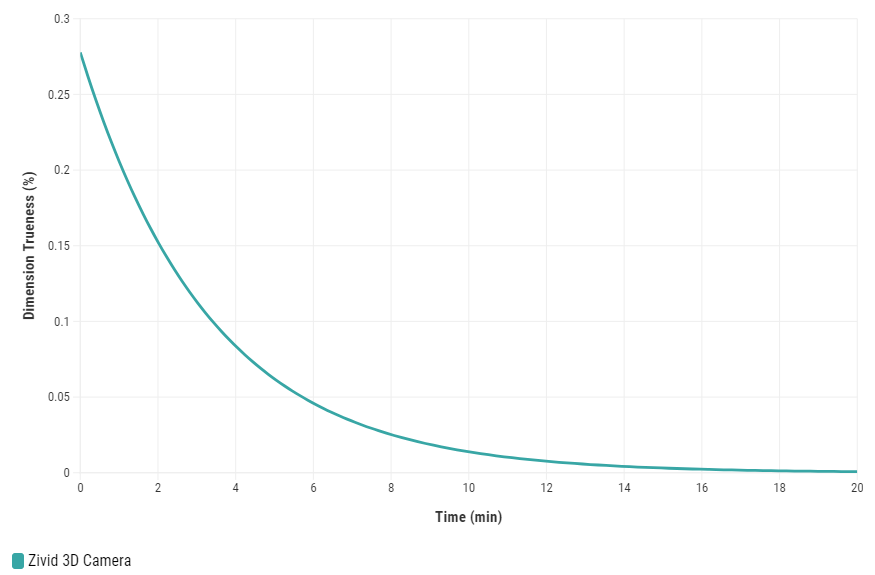
如需对您的相机进行预热,您可以运行我们的代码示例,您需要输入循环时间和相机设置路径。
示例: warmup.py
python /path/to/warmup.py --settings-path /path/to/settings.yml --capture-cycle 6.0
如需了解为什么需要预热以及如何使用SDK进行预热,请阅读 预热 。
小技巧
如果您的相机长时间不触发拍照(持续时间超过 10 分钟),则保持 Thermal Stabilization(热稳定功能) 处于启用状态非常有益。
现场标定
现场标定是一个维护工具,可用于验证和校正Zivid相机的尺寸准确度。用户可以检查视场 (FOV) 中不同区域的点云的尺寸准确度,并确定验证结果是否符合您的应用要求。如果发现验证结果对于应用来说不够准确,则可以执行校正以增加点云的尺寸准确度。多次测量的平均尺寸准确度误差的预期值接近于零 (<0.1%)。
为什么这是必要的?
我们的相机被设计为可以在工业工作环境中工作并持续输出高质量的点云。然而,与大多数高精密电子仪器一样,有时可能需要进行一些调整以确保它们能够一直保持最佳性能。当相机在其环境中经历重大改动或繁重的装卸时,可能需要进行校正才能在新的设置中以最佳状况执行工作。
如果您第一次进行这些操作,请阅读有关 现场标定 的更多信息。
进行现场验证时,需要确保料箱顶部和底部的尺寸准确度都是良好的。对于相机安装在手臂上的应用,在进行现场验证时,将机器人移动到捕获位姿。如果验证结果良好,则无需运行内场校正。
当需要进行现场标定时,覆盖整个工作立体区域可以获得最佳的结果。这意味着需要将 Zivid calibration board 先后放置给定距离处的多个不同位置执行校正,并在不同的拍照距离重复以上操作,在这个过程中,请确保整个标定板一直都在相机的 FOV 中。选定箱子底部的数个位置和箱子顶部的数个位置进行校正足以满足单品拣选的要求。您可以查看 进行现场标定的准则 来了解更多信息。
如需在相机上运行现场标定的验证和/或校正功能,您可以使用:
Zivid Studio
CLI工具
SDK
小技巧
如果您是第一次使用现场标定,我们建议使用Zivid Studio。
查看 运行现场标定 以获得有关运行现场校正的分步指南。
手眼标定
Picking accuracy depends on:
Camera calibration
Hand-eye calibration
Machine vision software
Robot positioning
Robots are repeatable but not inherently accurate due to the factors such as temperature, joint friction, payload, manufacturing tolerances.
Recommendations:
Perform mastering (zeroing) to teach the robot the exact zero position of each joint.
Calibrate the robot for improved pose accuracy.
Repeat hand-eye calibration if:
robot loses calibration.
camera is dismounted and remounted.
Perform regular recalibration (robot and/or hand-eye) to maintain system performance.
推荐方法
For users who want to perform hand-eye calibration without developing their own solution, Zivid recommends using the Hand-Eye GUI(手眼标定图形用户界面)—a graphical tool provided as part of our Python sample library to simplify the process. It includes all essential features such as warmup, infield correction, calibration, and verification tests. While the tool supports integration with RoboDK, its use is optional; the GUI can be used independently for features with Zivid cameras.
小技巧
建议在进行手眼标定之前先 预热 相机并运行 现场标定 。预热、现场标定和手眼标定期间的捕获周期应与您的应用相同。为了进一步降低温度相关性能因素的影响,请启用 Thermal Stabilization(热稳定功能) 。
替代方法
如果您希望采用不同的工作流程或更紧密地集成到您的系统中,则有几种可供选择的方案:
- UR5 + Python 示例
对于想要直接使用 UR5 驱动程序而不是 RoboDK 或 GUI 的用户,请参阅 UR5 Robot + Python:生成数据集并执行手眼标定 。
- RoboDK + Python 示例
对于那些喜欢使用 RoboDK 和 Python 而不是使用 GUI 编写脚本的用户,请参阅 任意机械臂 + RobotDK + Python:生成数据集并执行手眼标定 。
- 命令行工具
对于不喜欢基于 Python 或依赖性极少的工作流程的用户,请参阅 用于手眼标定的Zivid CLI工具 。此实验性 CLI 工具根据提供的数据集计算手眼变换,并将变换矩阵和残差保存到用户指定的文件中。
自定义集成
如果您更喜欢定制化程度更高的集成,例如将手眼标定直接嵌入到您自己的解决方案中,您可以按照下面概述的分步过程并探索我们的交互式代码示例。
手眼标定过程步骤:
将机器人移动到新的位姿
注册末端执行器位姿
对标定对象进行成像(获取其位姿)
重复步骤 1-3 多次,例如 10 - 20
计算手眼变换关系
要了解如何将手眼标定集成到您的解决方案中,请查看我们的交互式代码示例:
/*
Perform Hand-Eye calibration.
*/
#include <Zivid/Application.h>
#include <Zivid/Calibration/Detector.h>
#include <Zivid/Calibration/HandEye.h>
#include <Zivid/Calibration/Pose.h>
#include <Zivid/Exception.h>
#include <Zivid/Zivid.h>
#include <clipp.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <stdexcept>
namespace
{
std::string presetPath(const Zivid::Camera &camera)
{
const std::string presetsPath = std::string(ZIVID_SAMPLE_DATA_DIR) + "/Settings";
switch(camera.info().model().value())
{
case Zivid::CameraInfo::Model::ValueType::zividTwo:
{
return presetsPath + "/Zivid_Two_M70_ManufacturingSpecular.yml";
}
case Zivid::CameraInfo::Model::ValueType::zividTwoL100:
{
return presetsPath + "/Zivid_Two_L100_ManufacturingSpecular.yml";
}
case Zivid::CameraInfo::Model::ValueType::zivid2PlusM130:
{
return presetsPath + "/Zivid_Two_Plus_M130_ConsumerGoodsQuality.yml";
}
case Zivid::CameraInfo::Model::ValueType::zivid2PlusM60:
{
return presetsPath + "/Zivid_Two_Plus_M60_ConsumerGoodsQuality.yml";
}
case Zivid::CameraInfo::Model::ValueType::zivid2PlusL110:
{
return presetsPath + "/Zivid_Two_Plus_L110_ConsumerGoodsQuality.yml";
}
case Zivid::CameraInfo::Model::ValueType::zivid2PlusMR130:
{
return presetsPath + "/Zivid_Two_Plus_MR130_ConsumerGoodsQuality.yml";
}
case Zivid::CameraInfo::Model::ValueType::zivid2PlusMR60:
{
return presetsPath + "/Zivid_Two_Plus_MR60_ConsumerGoodsQuality.yml";
}
case Zivid::CameraInfo::Model::ValueType::zivid2PlusLR110:
{
return presetsPath + "/Zivid_Two_Plus_LR110_ConsumerGoodsQuality.yml";
}
case Zivid::CameraInfo::Model::ValueType::zivid3XL250:
{
return presetsPath + "/Zivid_Three_XL250_DepalletizationQuality.yml";
}
case Zivid::CameraInfo::Model::ValueType::zividOnePlusSmall:
case Zivid::CameraInfo::Model::ValueType::zividOnePlusMedium:
case Zivid::CameraInfo::Model::ValueType::zividOnePlusLarge: break;
default: throw std::runtime_error("Unhandled enum value '" + camera.info().model().toString() + "'");
}
throw std::invalid_argument("Invalid camera model");
}
enum class CommandType
{
AddPose,
Calibrate,
Unknown
};
std::string getInput()
{
std::string command;
std::getline(std::cin, command);
return command;
}
CommandType enterCommand()
{
std::cout << "Enter command, p (to add robot pose) or c (to perform calibration): ";
const auto command = getInput();
if(command == "P" || command == "p")
{
return CommandType::AddPose;
}
if(command == "C" || command == "c")
{
return CommandType::Calibrate;
}
return CommandType::Unknown;
}
Zivid::Calibration::Pose enterRobotPose(size_t index)
{
std::cout << "Enter pose with id (a line with 16 space separated values describing 4x4 row-major matrix) : "
<< index << std::endl;
std::stringstream input(getInput());
float element{ 0 };
std::vector<float> transformElements;
for(size_t i = 0; i < 16 && input >> element; ++i)
{
transformElements.emplace_back(element);
}
const auto robotPose{ Zivid::Matrix4x4{ transformElements.cbegin(), transformElements.cend() } };
std::cout << "The following pose was entered: \n" << robotPose << std::endl;
return robotPose;
}
std::string markersToString(const std::vector<int> &markerIds)
{
std::ostringstream oss;
for(const auto &id : markerIds)
{
oss << id << " ";
}
return oss.str();
}
void handleAddPose(
size_t ¤tPoseId,
std::vector<Zivid::Calibration::HandEyeInput> &handEyeInput,
Zivid::Camera &camera,
const std::string &calibrationObject,
const Zivid::Settings &settings)
{
const auto robotPose = enterRobotPose(currentPoseId);
std::cout << "Detecting calibration object in point cloud" << std::endl;
if(calibrationObject == "c")
{
const auto frame = camera.capture2D3D(settings);
const auto detectionResult = Zivid::Calibration::detectCalibrationBoard(frame);
if(detectionResult.valid())
{
std::cout << "Calibration board detected " << std::endl;
handEyeInput.emplace_back(robotPose, detectionResult);
currentPoseId++;
}
else
{
std::cout << "Failed to detect calibration board. " << detectionResult.statusDescription() << std::endl;
}
}
else if(calibrationObject == "m")
{
const auto frame = camera.capture2D3D(settings);
auto markerDictionary = Zivid::Calibration::MarkerDictionary::aruco4x4_50;
std::vector<int> markerIds = { 1, 2, 3 };
std::cout << "Detecting arUco marker IDs " << markersToString(markerIds) << "from the dictionary "
<< markerDictionary << std::endl;
auto detectionResult = Zivid::Calibration::detectMarkers(frame, markerIds, markerDictionary);
if(detectionResult.valid())
{
std::cout << "ArUco marker(s) detected: " << detectionResult.detectedMarkers().size() << std::endl;
handEyeInput.emplace_back(robotPose, detectionResult);
currentPoseId++;
}
else
{
std::cout
<< "Failed to detect any ArUco markers, ensure that at least one ArUco marker is in the view of the camera"
<< std::endl;
}
}
}
std::vector<Zivid::Calibration::HandEyeInput> readHandEyeInputs(
Zivid::Camera &camera,
const Zivid::Settings &settings)
{
size_t currentPoseId{ 0 };
bool calibrate{ false };
std::string calibrationObject;
while(true)
{
std::cout
<< "Enter calibration object you are using, m (for ArUco marker(s)) or c (for Zivid checkerboard): "
<< std::endl;
calibrationObject = getInput();
if(calibrationObject == "m" || calibrationObject == "c")
{
break;
}
}
std::cout << "Zivid primarily operates with a (4x4) transformation matrix. To convert" << std::endl;
std::cout << "from axis-angle, rotation vector, roll-pitch-yaw, or quaternion, check out" << std::endl;
std::cout << "our PoseConversions sample." << std::endl;
std::vector<Zivid::Calibration::HandEyeInput> handEyeInput;
do
{
switch(enterCommand())
{
case CommandType::AddPose:
{
try
{
handleAddPose(currentPoseId, handEyeInput, camera, calibrationObject, settings);
}
catch(const std::exception &e)
{
std::cout << "Error: " << Zivid::toString(e) << std::endl;
continue;
}
break;
}
case CommandType::Calibrate:
{
calibrate = true;
break;
}
case CommandType::Unknown:
{
std::cout << "Error: Unknown command" << std::endl;
break;
}
default: throw std::runtime_error{ "Unhandled command type" };
}
} while(!calibrate);
return handEyeInput;
}
Zivid::Calibration::HandEyeOutput performCalibration(
const std::vector<Zivid::Calibration::HandEyeInput> &handEyeInput)
{
while(true)
{
std::cout << "Enter type of calibration, eth (for eye-to-hand) or eih (for eye-in-hand): ";
const auto calibrationType = getInput();
if(calibrationType == "eth" || calibrationType == "ETH")
{
std::cout << "Performing eye-to-hand calibration with " << handEyeInput.size() << " dataset pairs"
<< std::endl;
std::cout << "The resulting transform is the camera pose in robot base frame" << std::endl;
return Zivid::Calibration::calibrateEyeToHand(handEyeInput);
}
if(calibrationType == "eih" || calibrationType == "EIH")
{
std::cout << "Performing eye-in-hand calibration with " << handEyeInput.size() << " dataset pairs"
<< std::endl;
std::cout << "The resulting transform is the camera pose in flange (end-effector) frame" << std::endl;
return Zivid::Calibration::calibrateEyeInHand(handEyeInput);
}
std::cout << "Entered uknown method" << std::endl;
}
}
} // namespace
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
try
{
std::string settingsPath;
bool showHelp = false;
auto cli =
(clipp::option("-h", "--help").set(showHelp) % "Show help message",
clipp::option("--settings-path")
& clipp::value("path", settingsPath) % "Path to the camera settings YML file");
if(!clipp::parse(argc, argv, cli) || showHelp)
{
auto fmt = clipp::doc_formatting{}.alternatives_min_split_size(1).surround_labels("\"", "\"");
std::cout << "USAGE:" << std::endl;
std::cout << clipp::usage_lines(cli, argv[0], fmt) << std::endl;
std::cout << "OPTIONS:" << std::endl;
std::cout << clipp::documentation(cli) << std::endl;
return showHelp ? EXIT_SUCCESS : EXIT_FAILURE;
}
Zivid::Application zivid;
std::cout << "Connecting to camera" << std::endl;
auto camera{ zivid.connectCamera() };
if(settingsPath.empty())
{
settingsPath = presetPath(camera);
}
const auto settings = Zivid::Settings(settingsPath);
const auto handEyeInput{ readHandEyeInputs(camera, settings) };
const auto calibrationResult{ performCalibration(handEyeInput) };
std::cout << "Zivid primarily operates with a (4x4) transformation matrix. To convert" << std::endl;
std::cout << "to axis-angle, rotation vector, roll-pitch-yaw, or quaternion, check out" << std::endl;
std::cout << "our PoseConversions sample." << std::endl;
if(calibrationResult.valid())
{
std::cout << "Hand-Eye calibration OK\n"
<< "Result:\n"
<< calibrationResult << std::endl;
}
else
{
std::cout << "Hand-Eye calibration FAILED" << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
}
catch(const std::exception &e)
{
std::cerr << "\nError: " << Zivid::toString(e) << std::endl;
std::cout << "Press enter to exit." << std::endl;
std::cin.get();
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
/*
Perform Hand-Eye calibration.
*/
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using Zivid.NET.Calibration;
using Duration = Zivid.NET.Duration;
class Program
{
static int Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
var userOptions = ParseOptions(args);
if (userOptions.ShowHelp)
{
ShowHelp();
return 0;
}
var zivid = new Zivid.NET.Application();
Console.WriteLine("Connecting to camera");
var camera = zivid.ConnectCamera();
var settingsPath = userOptions.SettingsPath;
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(settingsPath))
{
settingsPath = PresetPath(camera);
}
var settings = new Zivid.NET.Settings(settingsPath);
var handEyeInput = readHandEyeInputs(camera, settings);
var calibrationResult = performCalibration(handEyeInput);
Console.WriteLine("Zivid primarily operates with a (4x4) transformation matrix. To convert");
Console.WriteLine("to axis-angle, rotation vector, roll-pitch-yaw, or quaternion, check out");
Console.WriteLine("our PoseConversions sample.");
if (calibrationResult.Valid())
{
Console.WriteLine("{0}\n{1}\n{2}", "Hand-Eye calibration OK", "Result: ", calibrationResult);
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Hand-Eye calibration FAILED");
return 1;
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine("Error: {0}", ex.ToString());
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
static (string SettingsPath, bool ShowHelp) ParseOptions(string[] args)
{
string settingsPath = "";
bool showHelp = false;
foreach (var arg in args)
{
if (arg.StartsWith("--settings-path="))
{
settingsPath = arg.Substring("--settings-path=".Length);
}
else if (arg.StartsWith("-h") || arg.StartsWith("--help"))
{
showHelp = true;
}
}
return (settingsPath, showHelp);
}
static List<HandEyeInput> readHandEyeInputs(Zivid.NET.Camera camera, Zivid.NET.Settings settings)
{
var handEyeInput = new List<HandEyeInput>();
var currentPoseId = 0U;
var beingInput = true;
var calibrationObject = "";
while (true)
{
Console.WriteLine("Enter calibration object you are using, m (for ArUco marker(s)) or c (for Zivid checkerboard): ");
calibrationObject = Console.ReadLine();
if (calibrationObject.Equals("m", StringComparison.CurrentCultureIgnoreCase) ||
calibrationObject.Equals("c", StringComparison.CurrentCultureIgnoreCase))
{
break;
}
}
Interaction.ExtendInputBuffer(2048);
Console.WriteLine("Zivid primarily operates with a (4x4) transformation matrix. To convert");
Console.WriteLine("from axis-angle, rotation vector, roll-pitch-yaw, or quaternion, check out");
Console.WriteLine("our PoseConversions sample.");
do
{
switch (Interaction.EnterCommand())
{
case CommandType.AddPose:
try
{
HandleAddPose(ref currentPoseId, ref handEyeInput, camera, calibrationObject, settings);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine("Error: {0}", ex.ToString());
continue;
}
break;
case CommandType.Calibrate: beingInput = false; break;
case CommandType.Unknown: Console.WriteLine("Error: Unknown command"); break;
}
} while (beingInput);
return handEyeInput;
}
public static void HandleAddPose(ref uint currentPoseId, ref List<HandEyeInput> handEyeInput, Zivid.NET.Camera camera, string calibrationObject, Zivid.NET.Settings settings)
{
var robotPose = Interaction.EnterRobotPose(currentPoseId);
Console.Write("Detecting calibration object in point cloud");
if (calibrationObject.Equals("c", StringComparison.CurrentCultureIgnoreCase))
{
using (var frame = camera.Capture2D3D(settings))
{
var detectionResult = Detector.DetectCalibrationBoard(frame);
if (detectionResult.Valid())
{
Console.WriteLine("Calibration board detected");
handEyeInput.Add(new HandEyeInput(robotPose, detectionResult));
++currentPoseId;
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Failed to detect calibration board, ensure that the entire board is in the view of the camera");
}
}
}
else if (calibrationObject.Equals("m", StringComparison.CurrentCultureIgnoreCase))
{
using (var frame = camera.Capture2D3D(settings))
{
var markerDictionary = Zivid.NET.MarkerDictionary.Aruco4x4_50;
var markerIds = new List<int> { 1, 2, 3 };
Console.WriteLine("Detecting arUco marker IDs " + string.Join(", ", markerIds));
var detectionResult = Detector.DetectMarkers(frame, markerIds, markerDictionary);
if (detectionResult.Valid())
{
Console.WriteLine("ArUco marker(s) detected: " + detectionResult.DetectedMarkers().Length);
handEyeInput.Add(new HandEyeInput(robotPose, detectionResult));
++currentPoseId;
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Failed to detect any ArUco markers, ensure that at least one ArUco marker is in the view of the camera");
}
}
}
}
static string PresetPath(Zivid.NET.Camera camera)
{
var presetsPath = Environment.GetFolderPath(Environment.SpecialFolder.CommonApplicationData)
+ "/Zivid/Settings/";
switch (camera.Info.Model)
{
case Zivid.NET.CameraInfo.ModelOption.ZividTwo:
{
return presetsPath + "Zivid_Two_M70_ManufacturingSpecular.yml";
}
case Zivid.NET.CameraInfo.ModelOption.ZividTwoL100:
{
return presetsPath + "Zivid_Two_L100_ManufacturingSpecular.yml";
}
case Zivid.NET.CameraInfo.ModelOption.Zivid2PlusM130:
{
return presetsPath + "Zivid_Two_Plus_M130_ConsumerGoodsQuality.yml";
}
case Zivid.NET.CameraInfo.ModelOption.Zivid2PlusM60:
{
return presetsPath + "Zivid_Two_Plus_M60_ConsumerGoodsQuality.yml";
}
case Zivid.NET.CameraInfo.ModelOption.Zivid2PlusL110:
{
return presetsPath + "Zivid_Two_Plus_L110_ConsumerGoodsQuality.yml";
}
case Zivid.NET.CameraInfo.ModelOption.Zivid2PlusMR130:
{
return presetsPath + "Zivid_Two_Plus_MR130_ConsumerGoodsQuality.yml";
}
case Zivid.NET.CameraInfo.ModelOption.Zivid2PlusMR60:
{
return presetsPath + "Zivid_Two_Plus_MR60_ConsumerGoodsQuality.yml";
}
case Zivid.NET.CameraInfo.ModelOption.Zivid2PlusLR110:
{
return presetsPath + "Zivid_Two_Plus_LR110_ConsumerGoodsQuality.yml";
}
case Zivid.NET.CameraInfo.ModelOption.Zivid3XL250:
{
return presetsPath + "Zivid_Three_XL250_DepalletizationQuality.yml";
}
default: throw new System.InvalidOperationException("Unhandled camera model: " + camera.Info.Model.ToString());
}
throw new System.InvalidOperationException("Invalid camera model");
}
static Zivid.NET.Calibration.HandEyeOutput performCalibration(List<HandEyeInput> handEyeInput)
{
while (true)
{
Console.WriteLine("Enter type of calibration, eth (for eye-to-hand) or eih (for eye-in-hand): ");
var calibrationType = Console.ReadLine();
if (calibrationType.Equals("eth", StringComparison.CurrentCultureIgnoreCase))
{
Console.WriteLine("Performing eye-to-hand calibration with " + handEyeInput.Count + " dataset pairs");
Console.WriteLine("The resulting transform is the camera pose in robot base frame");
return Calibrator.CalibrateEyeToHand(handEyeInput);
}
if (calibrationType.Equals("eih", StringComparison.CurrentCultureIgnoreCase))
{
Console.WriteLine("Performing eye-in-hand calibration with " + handEyeInput.Count + " dataset pairs");
Console.WriteLine("The resulting transform is the camera pose in flange (end-effector) frame");
return Calibrator.CalibrateEyeInHand(handEyeInput);
}
Console.WriteLine("Entered unknown method");
}
}
static void ShowHelp()
{
Console.WriteLine("Usage: HandEyeCalibration.exe [options]");
Console.WriteLine("Options:");
Console.WriteLine(" --settings-path=<path> Path to the camera settings YML file (default: based on camera model)");
Console.WriteLine(" -h, --help Show this help message");
}
}
enum CommandType
{
AddPose,
Calibrate,
Unknown
}
class Interaction
{
// Console.ReadLine only supports reading 256 characters, by default. This limit is modified
// by calling ExtendInputBuffer with the maximum length of characters to be read.
public static void ExtendInputBuffer(int size)
{
Console.SetIn(new StreamReader(Console.OpenStandardInput(), Console.InputEncoding, false, size));
}
public static CommandType EnterCommand()
{
Console.Write("Enter command, p (to add robot pose) or c (to perform calibration): ");
var command = Console.ReadLine().ToLower();
switch (command)
{
case "p": return CommandType.AddPose;
case "c": return CommandType.Calibrate;
default: return CommandType.Unknown;
}
}
public static Pose EnterRobotPose(ulong index)
{
var elementCount = 16;
Console.WriteLine(
"Enter pose with id (a line with {0} space separated values describing 4x4 row-major matrix) : {1}",
elementCount,
index);
var input = Console.ReadLine();
var elements = input.Split().Where(x => !string.IsNullOrEmpty(x.Trim())).Select(x => float.Parse(x)).ToArray();
var robotPose = new Pose(elements); Console.WriteLine("The following pose was entered: \n{0}", robotPose);
return robotPose;
}
}
"""
Perform Hand-Eye calibration.
"""
import argparse
from pathlib import Path
from typing import List, Tuple
import numpy as np
import zivid
from zividsamples.paths import get_sample_data_path
from zividsamples.save_load_matrix import assert_affine_matrix_and_save
def _options() -> argparse.Namespace:
"""Function to read user arguments.
Returns:
Arguments from user
"""
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description=__doc__)
parser.add_argument(
"--settings-path",
required=False,
type=Path,
help="Path to the camera settings YML file",
)
return parser.parse_args()
def _preset_path(camera: zivid.Camera) -> Path:
"""Get path to preset settings YML file, depending on camera model.
Args:
camera: Zivid camera
Raises:
ValueError: If unsupported camera model for this code sample
Returns:
Path: Zivid 2D and 3D settings YML path
"""
presets_path = get_sample_data_path() / "Settings"
if camera.info.model == zivid.CameraInfo.Model.zivid3XL250:
return presets_path / "Zivid_Three_XL250_DepalletizationQuality.yml"
if camera.info.model == zivid.CameraInfo.Model.zivid2PlusMR60:
return presets_path / "Zivid_Two_Plus_MR60_ConsumerGoodsQuality.yml"
if camera.info.model == zivid.CameraInfo.Model.zivid2PlusMR130:
return presets_path / "Zivid_Two_Plus_MR130_ConsumerGoodsQuality.yml"
if camera.info.model == zivid.CameraInfo.Model.zivid2PlusLR110:
return presets_path / "Zivid_Two_Plus_LR110_ConsumerGoodsQuality.yml"
if camera.info.model == zivid.CameraInfo.Model.zivid2PlusM60:
return presets_path / "Zivid_Two_Plus_M60_ConsumerGoodsQuality.yml"
if camera.info.model == zivid.CameraInfo.Model.zivid2PlusM130:
return presets_path / "Zivid_Two_Plus_M130_ConsumerGoodsQuality.yml"
if camera.info.model == zivid.CameraInfo.Model.zivid2PlusL110:
return presets_path / "Zivid_Two_Plus_L110_ConsumerGoodsQuality.yml"
if camera.info.model == zivid.CameraInfo.Model.zividTwo:
return presets_path / "Zivid_Two_M70_ManufacturingSpecular.yml"
if camera.info.model == zivid.CameraInfo.Model.zividTwoL100:
return presets_path / "Zivid_Two_L100_ManufacturingSpecular.yml"
raise ValueError("Invalid camera model")
def _enter_robot_pose(index: int) -> zivid.calibration.Pose:
"""Robot pose user input.
Args:
index: Robot pose ID
Returns:
robot_pose: Robot pose
"""
inputted = input(
f"Enter pose with id={index} (a line with 16 space separated values describing 4x4 row-major matrix): "
)
elements = inputted.split(maxsplit=15)
data = np.array(elements, dtype=np.float64).reshape((4, 4))
robot_pose = zivid.calibration.Pose(data)
print(f"The following pose was entered:\n{robot_pose}")
return robot_pose
def _perform_calibration(hand_eye_input: List[zivid.calibration.HandEyeInput]) -> zivid.calibration.HandEyeOutput:
"""Hand-Eye calibration type user input.
Args:
hand_eye_input: Hand-Eye calibration input
Returns:
hand_eye_output: Hand-Eye calibration result
"""
while True:
calibration_type = input("Enter type of calibration, eth (for eye-to-hand) or eih (for eye-in-hand): ").strip()
if calibration_type.lower() == "eth":
print(f"Performing eye-to-hand calibration with {len(hand_eye_input)} dataset pairs")
print("The resulting transform is the camera pose in robot base frame")
hand_eye_output = zivid.calibration.calibrate_eye_to_hand(hand_eye_input)
return hand_eye_output
if calibration_type.lower() == "eih":
print(f"Performing eye-in-hand calibration with {len(hand_eye_input)} dataset pairs")
print("The resulting transform is the camera pose in flange (end-effector) frame")
hand_eye_output = zivid.calibration.calibrate_eye_in_hand(hand_eye_input)
return hand_eye_output
print(f"Unknown calibration type: '{calibration_type}'")
def _handle_add_pose(
current_pose_id: int,
hand_eye_input: List,
camera: zivid.Camera,
calibration_object: str,
settings: zivid.Settings,
) -> Tuple[int, List]:
"""Acquire frame and keeps track of the robot's pose id.
Args:
current_pose_id: Counter of the current pose in the hand-eye calibration dataset
hand_eye_input: List of hand-eye calibration dataset pairs (poses and point clouds)
camera: Zivid camera
calibration_object: m (for ArUco marker(s)) or c (for Zivid checkerboard)
settings: Zivid camera settings
Returns:
Tuple[int, List]: Updated current_pose_id and hand_eye_input
"""
robot_pose = _enter_robot_pose(current_pose_id)
print("Detecting calibration object in point cloud")
if calibration_object == "c":
frame = zivid.calibration.capture_calibration_board(camera)
detection_result = zivid.calibration.detect_calibration_board(frame)
if detection_result.valid():
print("Calibration board detected")
hand_eye_input.append(zivid.calibration.HandEyeInput(robot_pose, detection_result))
current_pose_id += 1
else:
print(f"Failed to detect calibration board. {detection_result.status_description()}")
elif calibration_object == "m":
frame = camera.capture_2d_3d(settings)
marker_dictionary = zivid.calibration.MarkerDictionary.aruco4x4_50
marker_ids = [1, 2, 3]
print(f"Detecting arUco marker IDs {marker_ids} from the dictionary {marker_dictionary}")
detection_result = zivid.calibration.detect_markers(frame, marker_ids, marker_dictionary)
if detection_result.valid():
print(f"ArUco marker(s) detected: {len(detection_result.detected_markers())}")
hand_eye_input.append(zivid.calibration.HandEyeInput(robot_pose, detection_result))
current_pose_id += 1
else:
print(
"Failed to detect any ArUco markers, ensure that at least one ArUco marker is in the view of the camera"
)
return current_pose_id, hand_eye_input
def _main() -> None:
user_options = _options()
app = zivid.Application()
print("Connecting to camera")
camera = app.connect_camera()
if user_options.settings_path is None:
user_options.settings_path = _preset_path(camera)
settings = zivid.Settings.load(user_options.settings_path)
current_pose_id = 0
hand_eye_input = []
calibrate = False
while True:
calibration_object = input(
"Enter calibration object you are using, m (for ArUco marker(s)) or c (for Zivid checkerboard): "
).strip()
if calibration_object.lower() == "m" or calibration_object.lower() == "c":
break
print(
"Zivid primarily operates with a (4x4) transformation matrix. To convert\n"
"from axis-angle, rotation vector, roll-pitch-yaw, or quaternion, check out\n"
"our pose_conversions sample."
)
while not calibrate:
command = input("Enter command, p (to add robot pose) or c (to perform calibration): ").strip()
if command == "p":
try:
current_pose_id, hand_eye_input = _handle_add_pose(
current_pose_id, hand_eye_input, camera, calibration_object, settings
)
except ValueError as ex:
print(ex)
elif command == "c":
calibrate = True
else:
print(f"Unknown command '{command}'")
calibration_result = _perform_calibration(hand_eye_input)
transform = calibration_result.transform()
transform_file_path = Path(Path(__file__).parent / "transform.yaml")
assert_affine_matrix_and_save(transform, transform_file_path)
print(
"Zivid primarily operates with a (4x4) transformation matrix. To convert\n"
"to axis-angle, rotation vector, roll-pitch-yaw, or quaternion, check out\n"
"our pose_conversions sample."
)
if calibration_result.valid():
print("Hand-Eye calibration OK")
print(f"Result:\n{calibration_result}")
else:
print("Hand-Eye calibration FAILED")
if __name__ == "__main__":
_main()
完成手眼标定后,您可能需要验证生成的变换矩阵是否正确并在精度要求内。我们提供了两种选择:
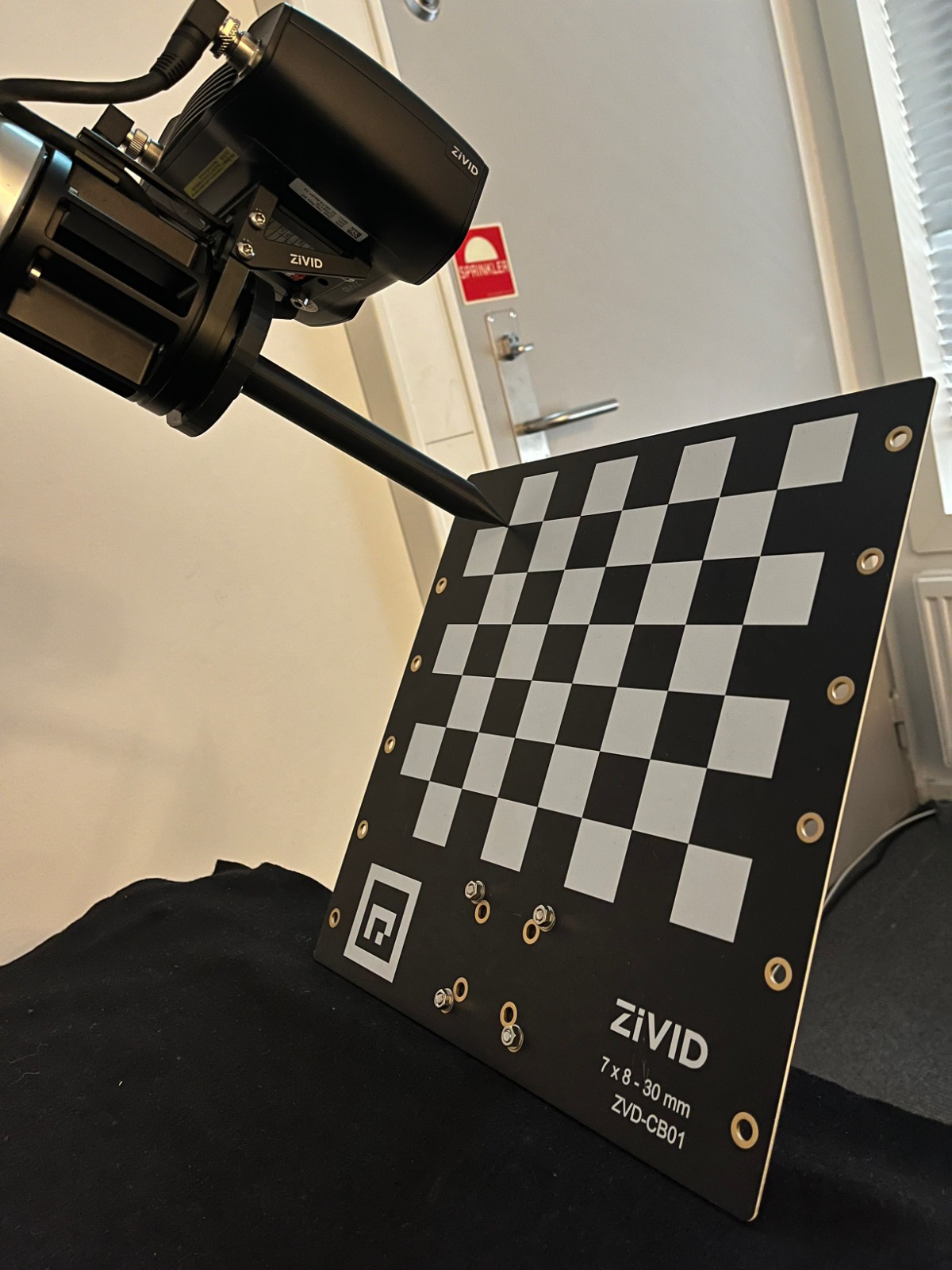
如需了解有关该主题的更多信息,请查看 手眼标定 。
色彩平衡
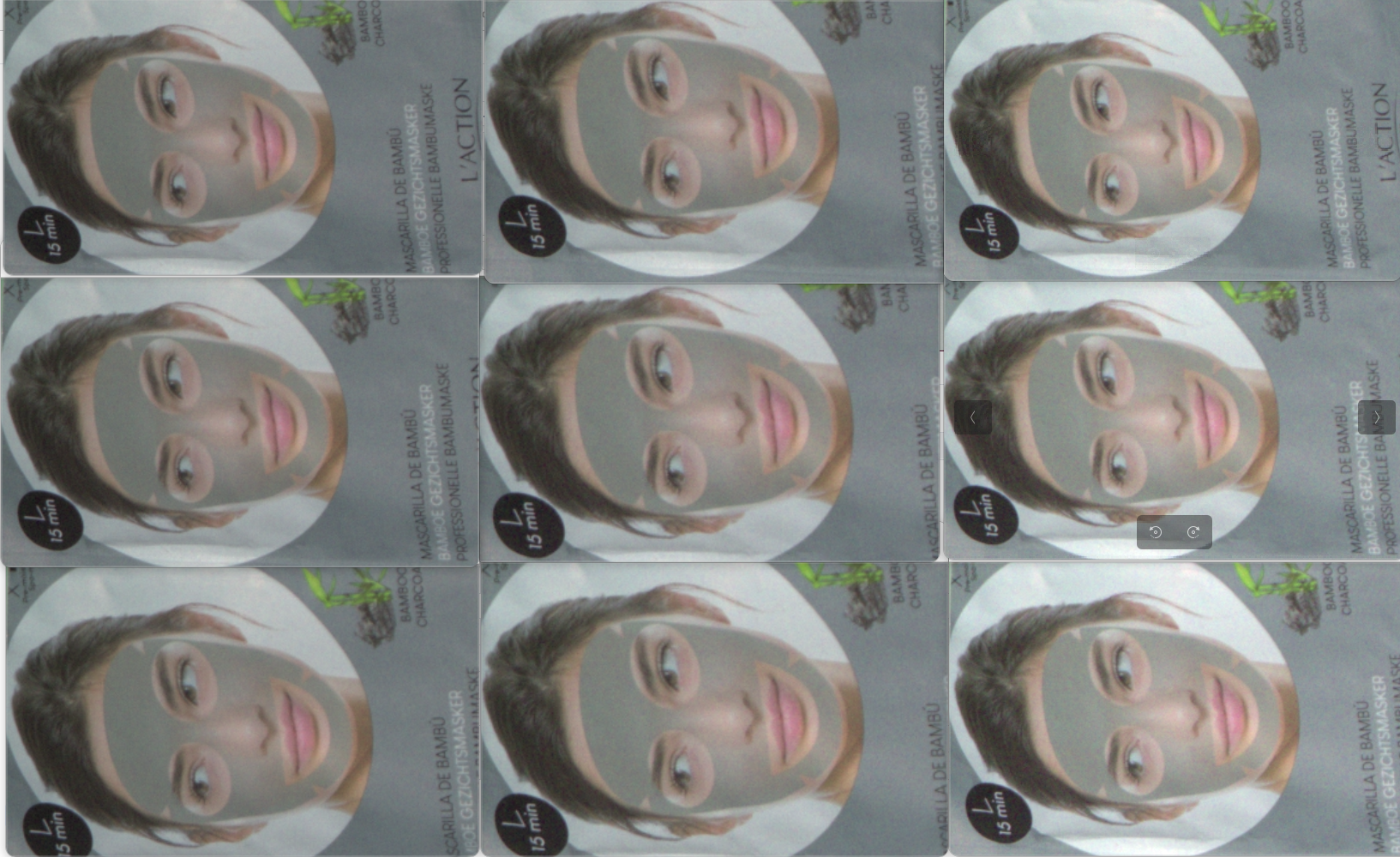
SDK 具有调整红色、绿色和蓝色通道的色彩平衡值的功能。但是,如 基于场景立体空间要求的相机选择器 所示,推荐用于单品拣选的相机具有固有的色彩平衡。即使当环境光非常强烈且不是纯白光时,对彩色图像的 RGB 值的影响仍然很小。因此,您无需在相机上运行额外的色彩平衡算法。
下图展示了在不同环境光条件下使用 Zivid 2+ MR130 拍摄的二维彩色图像的细节。
300 LUX |
1000 LUX |
2000 LUX |
|
3200K |
|
||
5000K |
|||
6500K |
|||
如果您注意到 彩色图像中以随机绿色或粉红色色调形式出现的颜色不一致 ,请选择您所在地区的电网频率预设(50 Hz 或 60 Hz)。
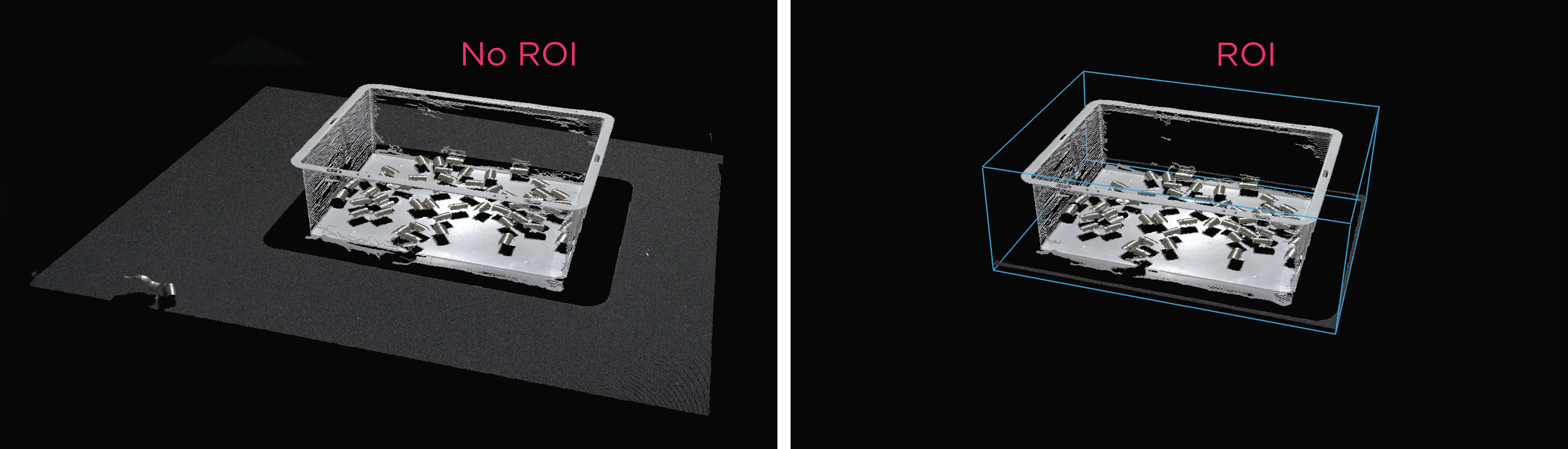
ROI盒过滤
相机视野通常比我们的 感兴趣区域 (ROI) 大,例如一个箱子。为了优化数据处理,我们可以在箱子周围设置一个 ROI 框,并相应地裁剪点云,仅捕获箱子以内的数据。ROI 框过滤不仅可以减少捕获时间,还可以减少算法使用的数据点数量,从而提高其速度和效率。
小技巧
点云越小,捕获速度越快,从而可以加快检测速度并缩短总拾取周期时间。
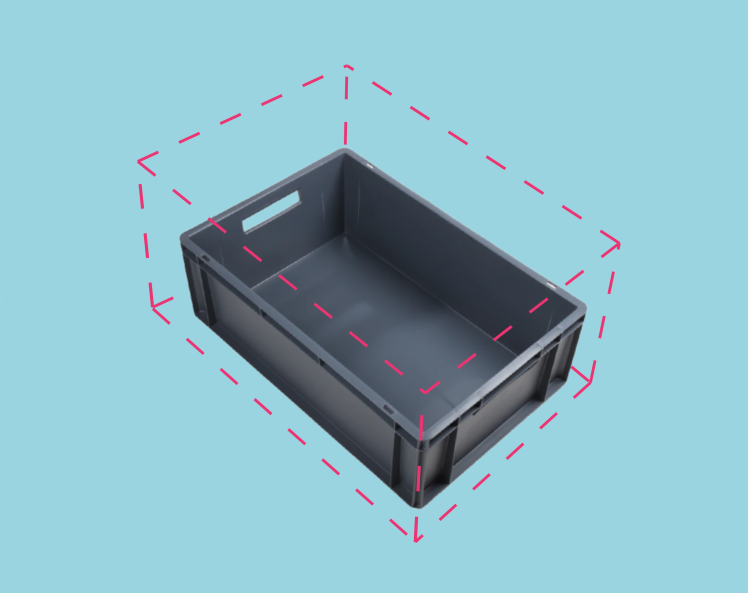
如需了解实施示例,请查看 通过棋盘格定义的ROI盒 。该教程展示了如何使用 Zivid calibration board 根据相对于棋盘格给定的ROI盒来过滤点云。
示例和表现
这是一个使用低端 PC(搭载 Intel Iris Xe 笔记本电脑集成显卡 和 1G 网卡)进行大量点云处理的示例,其中 ROI 框过滤方法对提升效率很有益处。
想象一下,一个机器人用固定安装的 Zivid 2+ MR130 相机从 600 x 400 x 300 毫米的箱子中拾取物品。为了给机器人留出足够的空间,相机安装在距离箱子顶部 1700 毫米的位置,提供大约 1000 x 800 毫米的视场。当相机安装在这个距离时,大部分视场都在 ROI 之外,因此可以从每一侧裁剪约 20/25% 的像素列/行。从下表可以看出,使用 ROI 框过滤可以显著缩短捕获时间。
预设值 |
采集时间 |
捕获时间 |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
未设置 ROI |
设置了 ROI |
未设置 ROI |
设置了 ROI |
|
Consumer Goods Quality |
0.15秒 |
0.15秒 |
0.9秒 |
0.35秒 |
下采样
备注
选择一个包含下采样选项的预设值。但是,为了理解这意味着什么,请参阅 Sampling(采样) - 3D 。
有些应用不需要高密度点云数据。例如,通过将平面拟合到盒子表面来进行盒子检测以及 CAD 匹配,其中对象具有独特且易于识别的特征。此外,对于机器视觉算法来说,这样的数据量通常太大,无法以应用程序所需的速度进行处理。点云下采样正是在此类应用中发挥作用。
在点云领域,下采样(Downsampling)是指在保持相同三维表征的前提下,降低空间分辨率。它通常用于将数据转换为更易处理的规模,从而减少存储和处理需求。
使用 Zivid SDK 对点云进行下采样有两种方法:
通过设置
Settings::Processing::Resampling( Resampling(重采样) )实现,这意味着它是通过捕获设置进行控制的。通过 API
PointCloud::downsample实现。
这两种方法都对点云应用了相同的操作。通过 API 的方法,您可以选择就地下采样或使用下采样数据获取新的点云实例。
下采样可以就地完成,该功能会修改当前的点云。
也可以将下采样点云作为新的点云实例,这样就不会改变现有的点云了。
Zivid SDK 支持以下下采样率 by2x2 、 by3x3 和 by4x4 ,支持多次执行下采样操作。
要对点云进行下采样,您可以运行我们的代码示例:
示例: downsample.py
python /path/to/downsample.py --zdf-path /path/to/file.zdf
如果您没有ZDF文件,则可以运行以下代码示例。它将使用您的设置来捕获Zivid点云,并保存到文件中。
示例: capture_with_settings_from_yml
python /path/to/capture_with_settings_from_yml.py --settings-path /path/to/settings.yml
如需阅读有关下采样的更多信息,请转到 下采样 。
祝贺您已经阅读完关于将您的单品拣选系统投入生产的准备工作中的所有与Zivid有关的内容了。接下来的章节是 维护 ,里面包含了我们建议执行的所有流程,以确保单品拣选单元能在最小停机时间的情况下保持稳定运行。
版本历史
SDK |
变更 |
|---|---|
2.12.0 |
新增了内容用于说明 ROI 框过滤如何加快数据捕获时间。现在也可以通过 |
2.10.0 |
Monochrome Capture(单色捕获) 引入了比 下采样 更快的替代方案。 |