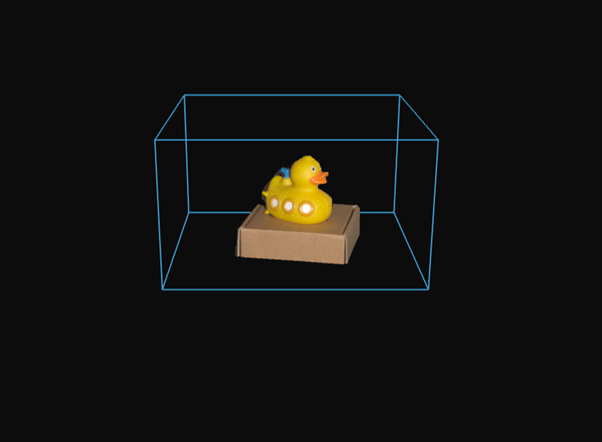
Stitching
중요
예제 스티칭 Sample Data 데이터 세트와 참조 파일을 다운로드하여 따라 하거나 샘플을 실행해 보세요.
Introduction
이 문서는 Zivid의 정리되지 않은 포인트 클라우드를 스티칭하는 방법에 대한 심층적인 튜토리얼입니다.
실제 문제를 이해하기 위해 먼저 응용 프로그램을 간략하게 살펴보겠습니다. 다른 카메라나 사람의 눈과 마찬가지로 Zivid 카메라는 물체를 관통하거나 주변을 볼 수 없으며, 한 번에 한 면만 관찰할 수 있습니다. 따라서 물체의 완전한 3D 모델을 얻으려면 물체를 회전하거나 카메라 위치를 조정하여 여러 관점에서 모델을 캡처해야 합니다.
The problem
Zivid SDK에서 반환된 포인트 클라우드는 camera coordinate system 로 표현되며, 원점은 카메라 내부에 있습니다. 여러 시점에서 촬영할 때 각 포인트 클라우드는 촬영 시점의 카메라 좌표계를 기준으로 정의됩니다. 이러한 포인트 클라우드를 변환 없이 단순히 결합하면 공간적으로 정렬되지 않고 3D 공간에서 분리되고 단절된 것처럼 보입니다. 즉, 포인트 클라우드는 스캔 대상 객체에 연결된 공통 좌표계를 공유하지 않습니다.
The Solution
여러 개의 포인트 클라우드를 단일의 공간적으로 정렬된 객체의 3D 표현으로 병합하려면 다음이 필요합니다.
모든 포인트 클라우드를 스캔 중인 객체에 첨부된 공통 좌표계로 변환합니다.
포즈 추정에서 발생하는 노이즈나 사소한 오류를 보정하기 위해 정렬을 세부화합니다.
각 카메라 좌표계에서 공통 좌표계로의 변환은 로봇 운동학, 동작 추적 시스템 또는 수동 측정 등 다양한 출처에서 발생할 수 있습니다. 그러나 이러한 변환은 완벽하지 않으며 일반적으로 작은 정렬 오류가 발생합니다. 이러한 오류를 수정하려면 Zivid::Experimental::Toolbox::localPointCloudRegistration() 을 사용할 수 있습니다. 이 API 도구는 한 점군을 다른 점군에 가장 잘 등록하는 변환 행렬을 계산하여 두 개의 겹치는 점군 간의 정렬을 개선합니다.
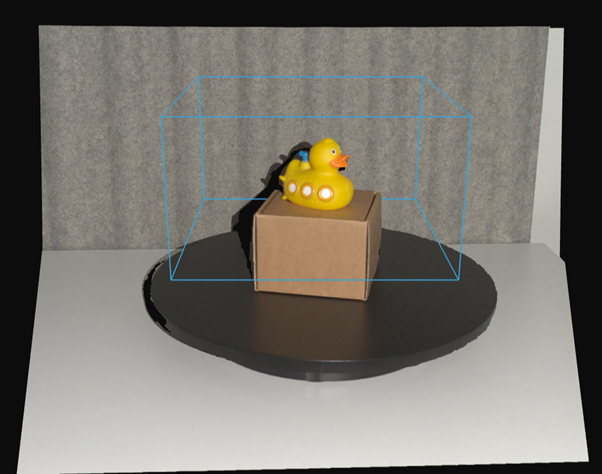
포인트 클라우드 스티칭을 시작하기 전에, 포인트 클라우드에 충분히 겹치는 특징점이 있는지 확인하는 것이 중요합니다. 또한 카메라에서 너무 멀리 떨어져 있거나 스티칭할 객체/장면에 속하지 않는 포인트 등 잘못된 스티칭을 유발할 수 있는 데이터는 삭제해야 합니다. 스티칭 전에 Zivid의 Region of Interest 를 사용하는 것이 좋습니다. 카메라가 고정된 촬영의 경우, 관심 영역을 한 번 정의하여 모든 촬영에 적용할 수 있습니다. 로봇 팔을 사용하여 카메라를 객체 주위로 이동하는 경우, 각 포인트 클라우드마다 다른 관심 영역을 설정해야 할 수 있습니다.
참고
Zivid 샘플 데이터의 모든 포인트 클라우드는 이미 ROI 필터링을 거쳤습니다.
Stitching point clouds without pre-alignment
이 섹션에서는 사전 정렬 없이 포인트 클라우드를 스티칭하는 방법을 보여줍니다. 핵심 요건은 한 포인트 클라우드에서 다른 포인트 클라우드로의 상대적인 이동이 충분히 작아서 캡처 간에 상당한 중첩이 보장되어야 한다는 것입니다. 이 예시에서는 카메라가 캡처 간에 약간씩 움직이는 동안 객체는 고정된 상태를 유지하며, Zivid::Experimental::Toolbox::localPointCloudRegistration() 를 사용하여 포인트 클라우드를 정렬합니다. 사전 포즈 정보 없이 두 포인트 클라우드를 스티칭하는 간단한 예시부터 시작하여, 회전 테이블을 사용하여 전체 객체를 스캔하는 고급 사례로 이어집니다.
Stitching two point clouds
이 간단한 예제는 사전 정렬 없이 두 개의 포인트 클라우드를 스티칭하는 방법을 보여줍니다. 이 방법을 사용하여 스티칭하려면 다음이 필요합니다.
두 개의 ZDF 파일을 로드합니다.
포인트 클라우드를 정리되지 않은 형식으로 변환합니다.
Voxel 다운샘플링을 적용합니다.
정렬을 위한 변환을 추정합니다.
포인크 클라우드를 스티칭 합니다.
최종 스티칭 결과를 다운샘플링합니다.
ZDF 파일을 로드하고 Zivid::PointCloud::toUnorganizedPointCloud() 를 사용하여 포인트 클라우드를 비정형 포맷으로 변환하는 방법은 다음과 같습니다. 정렬되지 않은 포인트 클라우드는 Zivid::UnorganizedPointCloud::extend() 를 사용하여 하나의 Zivid::UnorganizedPointCloud 객체로 결합되고 표시됩니다.
// Ensure the dataset is extracted to the correct location depending on the operating system:
// - Windows: %ProgramData%/Zivid/StitchingPointClouds/
// - Linux: /usr/share/Zivid/data/StitchingPointClouds/
// StitchingPointClouds/
// └── BlueObject/
std::cout << "Reading point clouds from ZDF files" << std::endl;
const auto directory = std::filesystem::path(ZIVID_SAMPLE_DATA_DIR) / "StitchingPointClouds" / "BlueObject";
if(!std::filesystem::exists(directory))
{
std::ostringstream oss;
oss << "Missing dataset folders.\n"
<< "Make sure 'StitchingPointClouds/BlueObject/' exist at " << ZIVID_SAMPLE_DATA_DIR << ".\n\n"
<< "You can download the dataset (StitchingPointClouds.zip) from:\n"
<< "https://support.zivid.com/en/latest/api-reference/samples/sample-data.html";
throw std::runtime_error(oss.str());
}
const auto frame1 = Zivid::Frame((directory / "BlueObject.zdf").string());
const auto frame2 = Zivid::Frame((directory / "BlueObjectSlightlyMoved.zdf").string());
std::cout << "Converting organized point clouds to unorganized point clouds and voxel downsampling"
<< std::endl;
const auto unorganizedPointCloud1 = frame1.pointCloud().toUnorganizedPointCloud();
const auto unorganizedPointCloud2 = frame2.pointCloud().toUnorganizedPointCloud();
std::cout << "Displaying point clouds before stitching" << std::endl;
Zivid::UnorganizedPointCloud unorganizedNotStitchedPointCloud;
unorganizedNotStitchedPointCloud.extend(unorganizedPointCloud1);
unorganizedNotStitchedPointCloud.extend(unorganizedPointCloud2);
visualizePointCloud(unorganizedNotStitchedPointCloud);
// Ensure the dataset is extracted to the correct location depending on the operating system:
// - Windows: %ProgramData%/Zivid/StitchingPointClouds/
// - Linux: /usr/share/Zivid/data/StitchingPointClouds/
// StitchingPointClouds/
// └── BlueObject/
var sampleDataDir = Environment.GetFolderPath(Environment.SpecialFolder.CommonApplicationData) + "/Zivid";
var directory = Path.Combine(sampleDataDir, "StitchingPointClouds", "BlueObject");
Console.WriteLine("Reading point clouds from ZDF files");
if (!Directory.Exists(directory))
{
Console.WriteLine("Missing dataset folders.");
Console.WriteLine("Make sure 'StitchingPointClouds/BlueObject/' exists at " + sampleDataDir);
Console.WriteLine("You can download the dataset (StitchingPointClouds.zip) from:");
Console.WriteLine("https://support.zivid.com/en/latest/api-reference/samples/sample-data.html");
return 1;
}
var frame1 = new Zivid.NET.Frame(Path.Combine(directory, "BlueObject.zdf"));
var frame2 = new Zivid.NET.Frame(Path.Combine(directory, "BlueObjectSlightlyMoved.zdf"));
Console.WriteLine("Converting organized point clouds to unorganized point clouds and voxel downsampling");
var unorganizedPointCloud1 = frame1.PointCloud.ToUnorganizedPointCloud();
var unorganizedPointCloud2 = frame2.PointCloud.ToUnorganizedPointCloud();
Console.WriteLine("Displaying point clouds before stitching");
var unorganizedNotStitchedPointCloud = new Zivid.NET.UnorganizedPointCloud();
unorganizedNotStitchedPointCloud.Extend(unorganizedPointCloud1);
unorganizedNotStitchedPointCloud.Extend(unorganizedPointCloud2);
VisualizePointCloud(unorganizedNotStitchedPointCloud);
# Ensure the dataset is extracted to the correct location depending on the operating system:
# • Windows: %ProgramData%\\Zivid\\StitchingPointClouds\\
# • Linux: /usr/share/Zivid/data/StitchingPointClouds/
# The folder must contain:
# StitchingPointClouds/
# └── BlueObject/
print("Reading point clouds from files")
directory = get_sample_data_path() / "StitchingPointClouds" / "BlueObject"
if not directory.exists() or not directory.exists():
raise FileNotFoundError(
f"Missing dataset folders.\n"
f"Make sure 'StitchingPointClouds/BlueObject' exist at {get_sample_data_path()}.\n\n"
f"You can download the dataset (StitchingPointClouds.zip) from:\n"
f"https://support.zivid.com/en/latest/api-reference/samples/sample-data.html"
)
frame_1 = zivid.Frame(directory / "BlueObject.zdf")
frame_2 = zivid.Frame(directory / "BlueObjectSlightlyMoved.zdf")
print("Converting organized point clouds to unorganized point clouds and voxel downsampling")
unorganized_point_cloud_1 = frame_1.point_cloud().to_unorganized_point_cloud()
unorganized_point_cloud_2 = frame_2.point_cloud().to_unorganized_point_cloud()
print("Displaying point clouds before stitching")
unorganized_not_stitched_point_cloud = zivid.UnorganizedPointCloud()
unorganized_not_stitched_point_cloud.extend(unorganized_point_cloud_1)
unorganized_not_stitched_point_cloud.extend(unorganized_point_cloud_2)
display_pointcloud(unorganized_not_stitched_point_cloud)
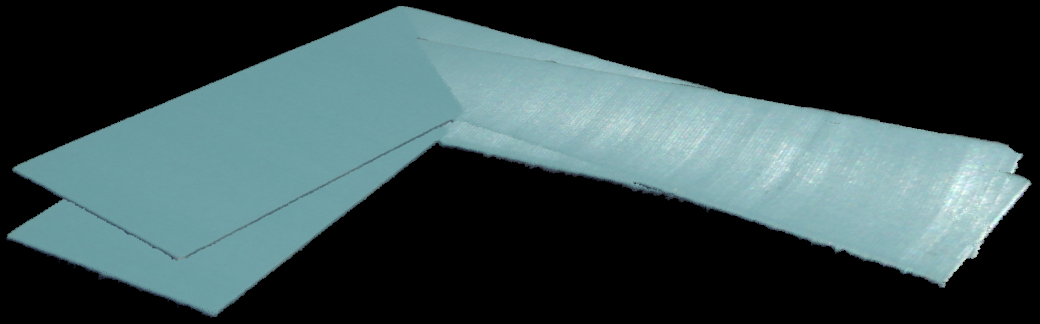
더 빠른 등록을 위해 점 수를 줄이기 위해 Voxel 다운샘플링을 적용합니다. 그런 다음 Zivid::Experimental::Toolbox::localPointCloudRegistration() 를 사용하여 두 포인트 클라우드 사이의 변환 행렬을 계산합니다. 두 번째 포인트 클라우드은 결과 변환을 사용하여 변환되고 최종 포인트 클라우드(첫 번째 포인트 클라우드을 포함하는 Zivid::UnorganizedPointCloud 객체)에 추가됩니다. 스티칭을 완료하기 위해 스티칭된 포인트 클라우드에 복셀 다운샘플링을 적용하고 결과를 표시합니다.
std::cout << "Estimating transformation between point clouds" << std::endl;
const auto unorganizedPointCloud1LPCR = unorganizedPointCloud1.voxelDownsampled(1.0, 3);
const auto unorganizedPointCloud2LPCR = unorganizedPointCloud2.voxelDownsampled(1.0, 3);
const auto registrationParams = Zivid::Experimental::LocalPointCloudRegistrationParameters{};
const auto localPointCloudRegistrationResult = Zivid::Experimental::Toolbox::localPointCloudRegistration(
unorganizedPointCloud1LPCR, unorganizedPointCloud2LPCR, registrationParams);
if(!localPointCloudRegistrationResult.converged())
{
throw std::runtime_error("Registration did not converge...");
}
const auto pointCloud1ToPointCloud2Transform = localPointCloudRegistrationResult.transform();
const auto unorganizedPointCloud2Transformed =
unorganizedPointCloud2.transformed(pointCloud1ToPointCloud2Transform.toMatrix());
std::cout << "Stitching and displaying painted point clouds to evaluate stitching quality" << std::endl;
Zivid::UnorganizedPointCloud finalPointCloud;
finalPointCloud.extend(unorganizedPointCloud1);
finalPointCloud.extend(unorganizedPointCloud2Transformed);
Zivid::UnorganizedPointCloud paintedFinalPointCloud;
paintedFinalPointCloud.extend(unorganizedPointCloud1.paintedUniformColor(Zivid::ColorRGBA{ 255, 0, 0, 255 }));
paintedFinalPointCloud.extend(
unorganizedPointCloud2Transformed.paintedUniformColor(Zivid::ColorRGBA{ 0, 255, 0, 255 }));
visualizePointCloud(paintedFinalPointCloud);
std::cout << "Voxel-downsampling the stitched point cloud" << std::endl;
finalPointCloud = finalPointCloud.voxelDownsampled(2.0, 1);
std::cout << "Visualize the overlapped point clouds" << std::endl;
visualizePointCloud(finalPointCloud);
Console.WriteLine("Estimating transformation between point clouds");
var unorganizedPointCloud1LPCR = unorganizedPointCloud1.VoxelDownsampled(1.0f, 3);
var unorganizedPointCloud2LPCR = unorganizedPointCloud2.VoxelDownsampled(1.0f, 3);
var registrationParams = new Zivid.NET.Experimental.LocalPointCloudRegistrationParameters();
var identityPose = new Pose(Zivid.NET.Matrix4x4.Identity());
var localPointCloudRegistrationResult = PointCloudRegistration.LocalPointCloudRegistration(
unorganizedPointCloud1LPCR,
unorganizedPointCloud2LPCR,
registrationParams,
identityPose);
if (!localPointCloudRegistrationResult.Converged)
{
throw new Exception("Registration did not converge...");
}
var pointCloud1ToPointCloud2Transform = localPointCloudRegistrationResult.Transform;
var unorganizedPointCloud2Transformed =
unorganizedPointCloud2.Transform(pointCloud1ToPointCloud2Transform.ToMatrix());
Console.WriteLine("Stitching and displaying painted point clouds to evaluate stitching quality");
var finalPointCloud = new Zivid.NET.UnorganizedPointCloud();
finalPointCloud.Extend(unorganizedPointCloud1);
finalPointCloud.Extend(unorganizedPointCloud2Transformed);
var paintedFinalPointCloud = new Zivid.NET.UnorganizedPointCloud();
paintedFinalPointCloud.Extend(unorganizedPointCloud1.PaintedUniformColor(new Zivid.NET.ColorRGBA { r = 255, g = 0, b = 0, a = 255 }));
paintedFinalPointCloud.Extend(unorganizedPointCloud2Transformed.PaintedUniformColor(new Zivid.NET.ColorRGBA { r = 0, g = 255, b = 0, a = 255 }));
VisualizePointCloud(paintedFinalPointCloud);
Console.WriteLine("Voxel-downsampling the stitched point cloud");
finalPointCloud = finalPointCloud.VoxelDownsampled(2.0f, 1);
Console.WriteLine("Visualize the overlapped point clouds");
VisualizePointCloud(finalPointCloud);
print("Estimating transformation between point clouds")
unorganized_point_cloud_1_lpcr = unorganized_point_cloud_1.voxel_downsampled(voxel_size=1.0, min_points_per_voxel=3)
unorganized_point_cloud_2_lpcr = unorganized_point_cloud_2.voxel_downsampled(voxel_size=1.0, min_points_per_voxel=3)
registration_params = LocalPointCloudRegistrationParameters()
local_point_cloud_registration_result = local_point_cloud_registration(
target=unorganized_point_cloud_1_lpcr, source=unorganized_point_cloud_2_lpcr, parameters=registration_params
)
assert local_point_cloud_registration_result.converged(), "Registration did not converge..."
point_cloud_1_to_point_cloud_2_transform = local_point_cloud_registration_result.transform()
unorganized_point_cloud_2_transformed = unorganized_point_cloud_2.transformed(
point_cloud_1_to_point_cloud_2_transform.to_matrix()
)
print("Stitching and displaying painted point clouds to evaluate stitching quality")
final_point_cloud = zivid.UnorganizedPointCloud()
final_point_cloud.extend(unorganized_point_cloud_1)
final_point_cloud.extend(unorganized_point_cloud_2_transformed)
painted_final_point_cloud = zivid.UnorganizedPointCloud()
painted_final_point_cloud.extend(unorganized_point_cloud_1.painted_uniform_color([255, 0, 0, 255]))
painted_final_point_cloud.extend(unorganized_point_cloud_2_transformed.painted_uniform_color([0, 255, 0, 255]))
display_pointcloud(painted_final_point_cloud)
print("Voxel-downsampling the stitched point cloud")
final_point_cloud = final_point_cloud.voxel_downsampled(voxel_size=2.0, min_points_per_voxel=1)
display_pointcloud(final_point_cloud)
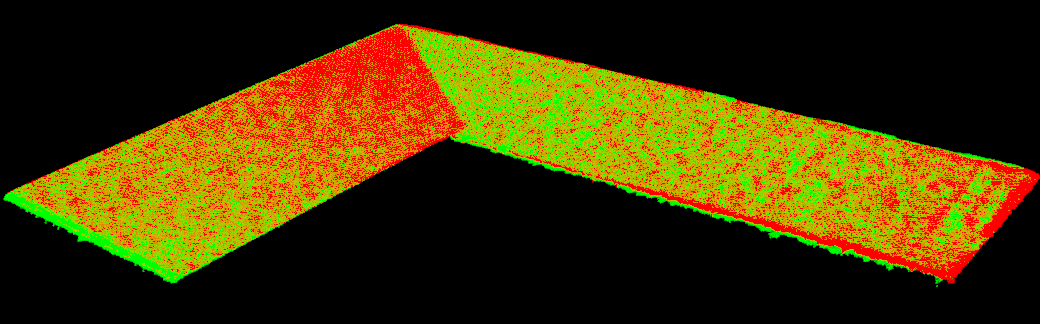
스티칭하기 전에 개별 포인트 클라우드에 균일한 색상을 칠해 정렬 품질을 시각화할 수 있습니다.
Stitching with a rotary table
이 예제는 회전 테이블에 놓인 물체의 점군을 스티칭하는 방법을 보여줍니다. 이 방법을 사용하여 스티칭하려면 다음이 필요합니다.
Zivid 카메라에 연결하세요.
관심 영역(ROI)을 사용하여 카메라 설정을 로드합니다.
객체가 회전하면서 여러 개의 포인트 클라우드를 캡처합니다.
각 캡처를 정리되지 않은 포인트 클라우드로 변환하고 다운샘플링합니다.
기존 모델에 맞춰 새로운 프레임을 등록합니다.
기존 모델을 새로운 프레임에 스티칭합니다.
다운샘플링, 표시 및 최종 결과를 폴리곤 파일 형식(.ply)으로 내보냅니다.
참고
이 예시에서 회전 테이블은 약 25초 만에 360도 회전을 완료합니다. 각 사이클은 250ms 이상(캡처, 전송, 처리 및 스티칭 포함)이 걸리므로, 캡처 사이에 1초의 지연 시간을 추가했습니다. 그 결과, 물체 주변에 고르게 분포된 각도에서 약 20개의 캡처가 이루어졌습니다.
먼저 카메라에 연결하고 정의된 ROI를 사용하여 캡처 설정을 불러옵니다. 앞서 언급했듯이 ROI는 회전 테이블 위의 물체를 포함하도록 정의됩니다. 테이블 자체의 포인트는 캡처하지 않는 것이 이상적이지만, 물체가 충분히 크다면 테이블의 일부 포인트를 포함하는 것이 일반적으로 허용됩니다.
std::cout << "Connecting to camera" << std::endl;
auto camera = app.connectCamera();
std::cout << "Loading settings from file: " << settingsPath << std::endl;
const auto settings = Zivid::Settings(settingsPath);
다음으로, 회전하는 물체의 포인트 클라우드를 캡처하고 로컬 포인트 클라우드 등록(Local Point Cloud Registration)을 적용하여 정렬합니다. 새로 캡처된 각 포인트 클라우드는 기준 프레임이 되고, 이전에 스티칭된 모델은 해당 프레임으로 변환됩니다.
왜 최신 캡처 대신 스티칭된 모델을 변환해야 할까요? 최신 캡처를 고정된 세계 프레임으로 변환하려면 이전의 모든 변환을 적용해야 하므로 오류가 누적되기 때문입니다. 기존 모델을 항상 최신 프레임으로 변환하면 오류가 국한되어 관리하기 더 쉬워집니다.
Zivid::UnorganizedPointCloud unorganizedStitchedPointCloud;
auto registrationParams = Zivid::Experimental::LocalPointCloudRegistrationParameters{};
auto previousToCurrentPointCloudTransform = Zivid::Matrix4x4::identity();
for(int numberOfCaptures = 0; numberOfCaptures < 20; ++numberOfCaptures)
{
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(1));
auto frame = camera.capture2D3D(settings);
const auto unorganizedPointCloud = frame.pointCloud().toUnorganizedPointCloud().voxelDownsampled(1.0, 2);
if(numberOfCaptures != 0)
{
if(unorganizedStitchedPointCloud.size() < 4 || unorganizedPointCloud.size() < 4)
{
std::cout << "Not enough points for registration, skipping stitching..." << std::endl;
continue;
}
const auto registrationResult = Zivid::Experimental::Toolbox::localPointCloudRegistration(
unorganizedStitchedPointCloud,
unorganizedPointCloud,
registrationParams,
previousToCurrentPointCloudTransform);
if(!registrationResult.converged())
{
std::cout << "Registration did not converge..." << std::endl;
continue;
}
previousToCurrentPointCloudTransform = registrationResult.transform().toMatrix();
unorganizedStitchedPointCloud.transform(previousToCurrentPointCloudTransform.inverse());
}
unorganizedStitchedPointCloud.extend(unorganizedPointCloud);
std::cout << "Captures done: " << numberOfCaptures << std::endl;
}
std::cout << "Voxel-downsampling the stitched point cloud" << std::endl;
unorganizedStitchedPointCloud = unorganizedStitchedPointCloud.voxelDownsampled(0.75, 2);
visualizePointCloud(unorganizedStitchedPointCloud);
var unorganizedStitchedPointCloud = new Zivid.NET.UnorganizedPointCloud();
var registrationParams = new Zivid.NET.Experimental.LocalPointCloudRegistrationParameters();
var previousToCurrentPointCloudTransform = new Pose(Zivid.NET.Matrix4x4.Identity());
var captureCount = 20;
for (int numberOfCaptures = 0; numberOfCaptures < captureCount; ++numberOfCaptures)
{
Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(1));
using (var frame = camera.Capture2D3D(settings))
{
var unorganizedPointCloud = frame.PointCloud.ToUnorganizedPointCloud().VoxelDownsampled(1.0f, 2);
if (numberOfCaptures != 0)
{
if (unorganizedStitchedPointCloud.Size < 4 || unorganizedPointCloud.Size < 4)
{
Console.WriteLine("Not enough points for registration, skipping stitching...");
continue;
}
var registrationResult = PointCloudRegistration.LocalPointCloudRegistration(
unorganizedStitchedPointCloud,
unorganizedPointCloud,
registrationParams,
previousToCurrentPointCloudTransform);
if (!registrationResult.Converged)
{
Console.WriteLine("Registration did not converge, skipping this frame...");
continue;
}
previousToCurrentPointCloudTransform = registrationResult.Transform;
var previousToCurrentMatrix = new Zivid.NET.Matrix4x4(previousToCurrentPointCloudTransform.ToMatrix());
unorganizedStitchedPointCloud.Transform(previousToCurrentMatrix.Inverse());
}
unorganizedStitchedPointCloud.Extend(unorganizedPointCloud);
Console.WriteLine("Captures done: " + (numberOfCaptures + 1));
}
}
Console.WriteLine("Voxel-downsampling the stitched point cloud");
unorganizedStitchedPointCloud = unorganizedStitchedPointCloud.VoxelDownsampled(0.75f, 2);
VisualizePointCloud(unorganizedStitchedPointCloud);
previous_to_current_point_cloud_transform = np.eye(4)
unorganized_stitched_point_cloud = zivid.UnorganizedPointCloud()
registration_params = LocalPointCloudRegistrationParameters()
for number_of_captures in range(20):
time.sleep(1)
frame = camera.capture_2d_3d(settings)
unorganized_point_cloud = (
frame.point_cloud().to_unorganized_point_cloud().voxel_downsampled(voxel_size=1.0, min_points_per_voxel=2)
)
if number_of_captures != 0:
local_point_cloud_registration_result = local_point_cloud_registration(
target=unorganized_stitched_point_cloud,
source=unorganized_point_cloud,
parameters=registration_params,
initial_transform=previous_to_current_point_cloud_transform,
)
if not local_point_cloud_registration_result.converged():
print("Registration did not converge...")
continue
previous_to_current_point_cloud_transform = local_point_cloud_registration_result.transform().to_matrix()
unorganized_stitched_point_cloud.transform(np.linalg.inv(previous_to_current_point_cloud_transform))
unorganized_stitched_point_cloud.extend(unorganized_point_cloud)
print(f"Captures done: {number_of_captures}")
print("Voxel-downsampling the stitched point cloud")
unorganized_stitched_point_cloud = unorganized_stitched_point_cloud.voxel_downsampled(
voxel_size=0.75, min_points_per_voxel=2
)
display_pointcloud(unorganized_stitched_point_cloud)
참고
회전 테이블이 일정한 각속도로 회전하므로, 연속된 점군 간의 변환은 유사해야 합니다. 따라서 이전 변환을 다음 정합의 초기 추측값으로 사용할 수 있습니다.
마지막으로, 스티칭된 결과는 복셀 다운샘플링되어 표시됩니다. 아래에서 스티칭된 포인트 클라우드 결과를 확인하세요.
로봇 팔을 사용하여 사전 정렬을 통해 포인트 클라우드 스티칭
이 문서에서는 핸드-아이 칼리브레이션 데이터와 로컬 포인트 클라우드 등록을 사용하여 다양한 로봇 장착 카메라 위치에서 수집한 포인트 클라우드를 스티칭하는 프로세스를 설명합니다.
Overview and Requirements
이 스티칭 방식을 사용하면 로봇 팔로 카메라를 움직여 객체의 완전한 3D 포인트 클라우드를 생성할 수 있습니다. 특히 다음과 같은 경우에 유용합니다.
해당 물체가 카메라의 시야보다 큽니다.
검사, 모델링 또는 조작을 위해서는 여러 각도에서 객체를 캡처하는 것이 필요합니다.
이 방법을 사용하려면 유효한 hand-eye calibration 가 결과가 필요합니다. 이 결과는 일반적으로 hand_eye_transform.yaml 형식으로 제공되며, 로봇의 엔드 이펙터 좌표계와 카메라 좌표계 간의 변환을 정의합니다. 이 변환은 서로 다른 카메라 포즈에서 촬영한 이미지들을 연관시키는 데 사용되며, 포인트 클라우드를 공통 좌표계로 변환하여 여러 뷰에서 정확한 정렬을 구현할 수 있습니다.
필요한 것:
캡처된 Zivid 포인트 클라우드 세트 (
capture_*.zdf)로봇 포즈의 해당 세트 (
robot_pose_*.yaml) - 캡처당 하나성공적인 핸드-아이 칼리브레이션 절차에서 얻은
hand_eye_transform.yaml
이러한 요소를 함께 사용하면 개별 캡처를 공통 좌표계에 미리 정렬할 수 있습니다.
Stitching Workflow
스티칭 과정은 다음과 같은 주요 단계로 진행됩니다.
다양한 로봇 포즈에서 캡처한 여러 개의 포인트 클라우드를 로드합니다.
각 포즈 (
robot_pose_*.yaml) 와 핸드-아이 칼리브레이션 (hand_eye_transform.yaml) 을 로드합니다.핸드-아이 변환을 사용하여 각 로봇 포즈를 카메라 포즈로 변환합니다.
카메라 좌표계에서 로봇의 기본 좌표계로 변환하여 포인트 클라우드를 미리 정렬합니다.
각 포인트 클라우드(voxel 그리드)를 다운샘플링하여 처리 속도를 높이고 노이즈를 줄입니다.
로컬 포인트 클라우드 등록을 사용하여 확장되는 스티칭된 포인트 클라우드와 각각의 새로운 포인트 클라우드 간의 정렬을 세부적으로 조정합니다.
선택적으로 원래의 전체 해상도 클라우드를 다시 로드하고 추정된 변환을 적용하여 전체 해상도로 스티칭합니다.
최종 결과를 스티치된 .ply 포인트 클라우드로 내보냅니다.
[Robot Arm (Pose A)] -> capture_1.zdf
[Robot Arm (Pose B)] -> capture_2.zdf
...
[Robot Arm (Pose N)] -> capture_N.zdf
Each capture is paired with:
- robot_pose_*.yaml
- hand_eye_transform.yaml
Apply:
- Pre-alignment using robot pose and hand-eye calibration
- Local point cloud registration for refinement
Output:
- Combined and visualized point cloud
- Optionally reload original captures for full-resolution stitching
Export:
- Final stitched point cloud as a PLY file
How Local Registration Works
로봇과 핸드-아이 포즈를 이용한 초기 사전 정렬 후, 사소한 포즈 부정확성을 보정하기 위해 추가적인 미세 조정이 필요합니다. 로컬 포인트 클라우드 등록은 다운샘플링된 각 포인트 클라우드를 성장하는 포인트 클라우드(이전에 스티칭된 포인트 클라우드)와 정렬하여 정확도를 향상시킵니다.
정합을 적용하기 전에 모든 포인트 클라우드는 복셀 다운샘플링됩니다. 이 단계는 스티칭 프로세스에 중요한데, 그 이유는 다음과 같습니다.
센서 노이즈를 줄여 더욱 안정적인 정렬을 가능하게 합니다.
등록을 방해할 수 있는 이상치를 제거하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
구조적 세부 사항을 희생하지 않고 포인트 수를 줄여 처리 속도를 높입니다.
사용자는 프로세스 시작 전에 스티칭 전략을 선택합니다. 그러나 실제 스티칭은 모든 변환이 추정된 후에만 수행됩니다.
저해상도 스티칭: 정렬 중에 준비된 다운샘플링된 포인트 클라우드를 사용합니다.
고해상도 스티칭: 원래의 전체 해상도 포인트 클라우드를 다시 로드하고 추정된 변환을 적용하여 세부적인 최종 포인트 클라우드를 만듭니다.
참고
Voxel 다운샘플링 없이 스티칭하면 (--full-resolution) 더 높은 세부 정보가 생성되지만 더 많은 메모리와 계산 시간이 필요합니다.
참고
로컬 정합을 수행할 때, 사전 정렬 단계부터 포인트 클라우드가 상당히 잘 정렬되어 있는 것이 중요합니다. 초기 정렬 오차가 너무 크면 알고리즘이 수렴하지 못하거나 부정확한 결과를 생성할 수 있습니다.
max_correspondence_distance 매개변수는 소스 클라우드와 타겟 클라우드 사이의 대응점을 찾기 위한 검색 반경을 정의합니다. 다음과 같아야 합니다.
일반적인 포인트 간격보다 더 큼(올바른 일치를 허용하기 위해)
그러나 정렬 품질을 저하시킬 수 있는 잘못된 대응을 포함할 정도로 크지는 않습니다.
auto registrationParameters = Zivid::Experimental::LocalPointCloudRegistrationParameters{
Zivid::Experimental::LocalPointCloudRegistrationParameters::MaxCorrespondenceDistance{ 2 }
};
아래는 카메라의 시야보다 크기 때문에 여러 번 촬영해야 하는 객체에 대한 스티칭된 포인트 클라우드 결과입니다.
Zivid SDK Examples
로봇에 장착된 카메라를 사용하여 스티칭하는 전체 예제 코드를 살펴보세요.
View Python sample on GitHub Python 샘플을 참조하세요.
Version History
SDK |
Changes |
|---|---|
2.17.0 |
Added support for local point cloud registration in C#. |