基于棋盘格的坐标转换
本教程展示了如何估计棋盘格的位姿并使用4x4齐次变换矩阵将点云转换到棋盘格坐标系。此示例还使用了转换矩阵来保存YAML文件。
本教程中使用的棋盘点云如下图所示。

我们可以在Zivid Studio中打开 原始点云 并进行检查。
备注
原始点云在 Sample Data(示例数据) 中。
现在,我们可以将深度视图中的Z范围设置为540毫米至735毫米。这使我们可以看到相机和棋盘格坐标系之间存在一个角度。
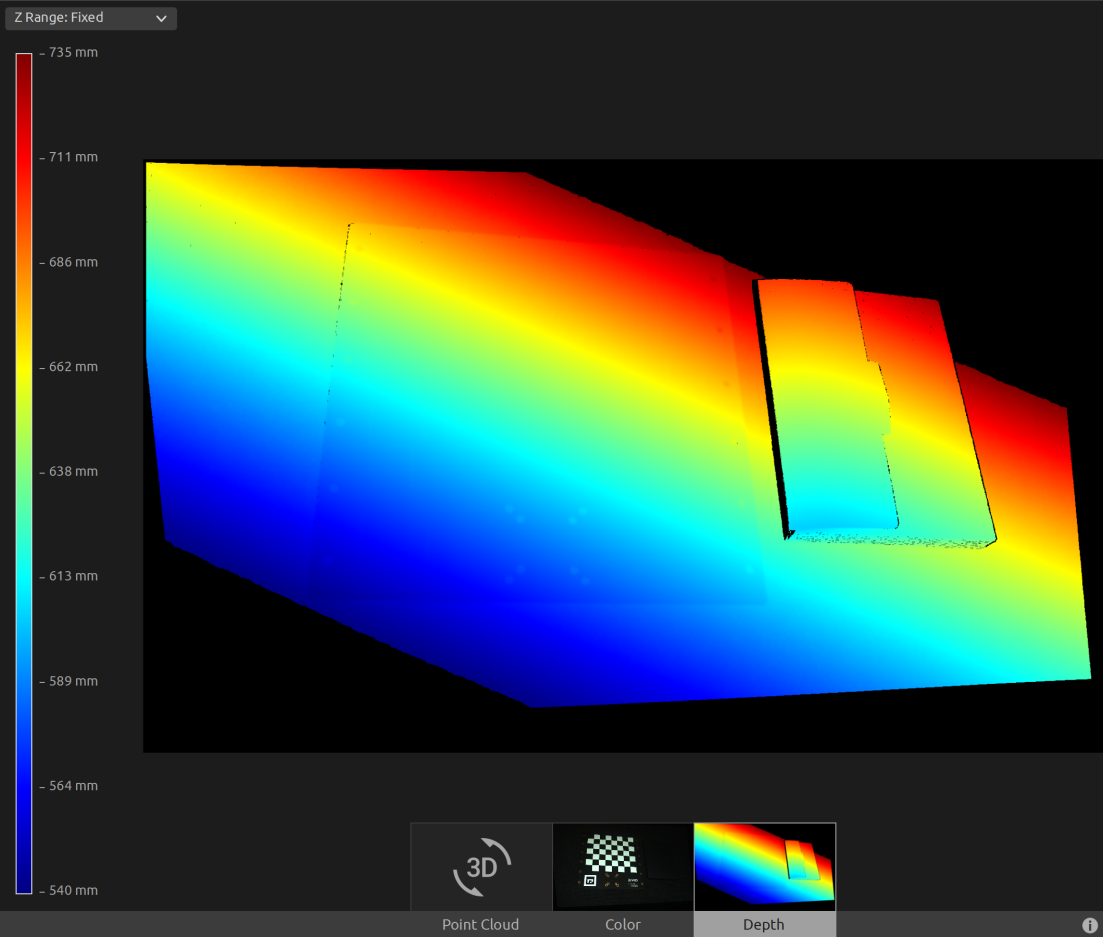
首先,我们加载一个棋盘格的点云。
const auto calibrationBoardFile = std::string(ZIVID_SAMPLE_DATA_DIR) + "/CalibrationBoardInCameraOrigin.zdf";
std::cout << "Reading ZDF frame from file: " << calibrationBoardFile << std::endl;
const auto frame = Zivid::Frame(calibrationBoardFile);
auto pointCloud = frame.pointCloud();
然后我们需要估计棋盘格的位姿。
std::cout << "Detecting and estimating pose of the Zivid checkerboard in the camera frame" << std::endl;
const auto detectionResult = Zivid::Calibration::detectCalibrationBoard(frame);
const auto cameraToCheckerboardTransform = detectionResult.pose().toMatrix();
Console.WriteLine("Detecting and estimating pose of the Zivid checkerboard in the camera frame");
var detectionResult = Detector.DetectCalibrationBoard(frame);
var cameraToCheckerboardTransform = new Zivid.NET.Matrix4x4(detectionResult.Pose().ToMatrix());
print("Detecting and estimating pose of the Zivid checkerboard in the camera frame")
detection_result = zivid.calibration.detect_calibration_board(frame)
if not detection_result.valid():
raise RuntimeError(f"No Checkerboard detected. {detection_result.status_description()}")
camera_to_checkerboard_transform = detection_result.pose().to_matrix()
在转换点云之前,我们将变换矩阵求逆,以便得到相机在棋盘格坐标系中的位姿。
std::cout << "Camera pose in checkerboard frame:" << std::endl;
const auto checkerboardToCameraTransform = cameraToCheckerboardTransform.inverse();
转换后,我们将位姿保存到YAML文件中。
const auto transformFile = "CheckerboardToCameraTransform.yaml";
std::cout << "Saving camera pose in checkerboard frame to file: " << transformFile << std::endl;
checkerboardToCameraTransform.save(transformFile);
这是YAML文件的内容:
__version__:
serializer: 1
data: 1
FloatMatrix:
Data: [
[0.9791644, 0.04366289, 0.1983198, 17.74656],
[0.0502592, 0.8941201, -0.444998, 431.1943],
[-0.1967516, 0.4456936, 0.8732962, -547.7883],
[0, 0, 0, 1]]
之后,我们将点云转换到棋盘格坐标系。
std::cout << "Transforming point cloud from camera frame to checkerboard frame" << std::endl;
pointCloud.transform(checkerboardToCameraTransform);
提示
了解更多关于 位置、方向和坐标变换。
在保存转换后的点云之前,我们可以将其转换为OpenCV 2D图像格式并绘制坐标系。
std::cout << "Converting to OpenCV image format" << std::endl;
const auto bgraImage = pointCloudToColorBGRA_SRGB(pointCloud);
std::cout << "Visualizing checkerboard with coordinate system" << std::endl;
drawCoordinateSystem(frame, cameraToCheckerboardTransform, bgraImage);
displayBGRA(bgraImage, "Checkerboard transformation frame");
在这里我们可以看到将要显示的图像,我们可以观察到棋盘格的坐标系在哪里。
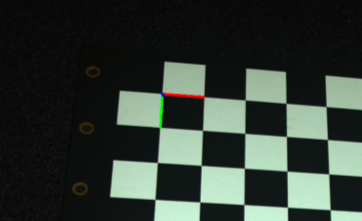
最后,我们将转换后的点云保存到磁盘。
const auto checkerboardTransformedFile = "CalibrationBoardInCheckerboardOrigin.zdf";
std::cout << "Saving transformed point cloud to file: " << checkerboardTransformedFile << std::endl;
frame.save(checkerboardTransformedFile);
提示
了解更多关于 位置、方向和坐标变换。
现在我们可以在Zivid Studio中打开 转换后的点云 并进行检查。
备注
在Zivid Studio中缩小图像来查找数据,因为视点原点不适用于转换后的点云。
我们现在可以在深度视图中手动将Z范围设置为-35mm至1mm,这样我们就可以过滤掉除了标定板和它旁边的物体之外的所有数据。这使我们可以看到我们在标定板上具有相同的Z值,并且从颜色渐变中我们可以检查该值是否为0。这意味着点云的原点位于棋盘格上。
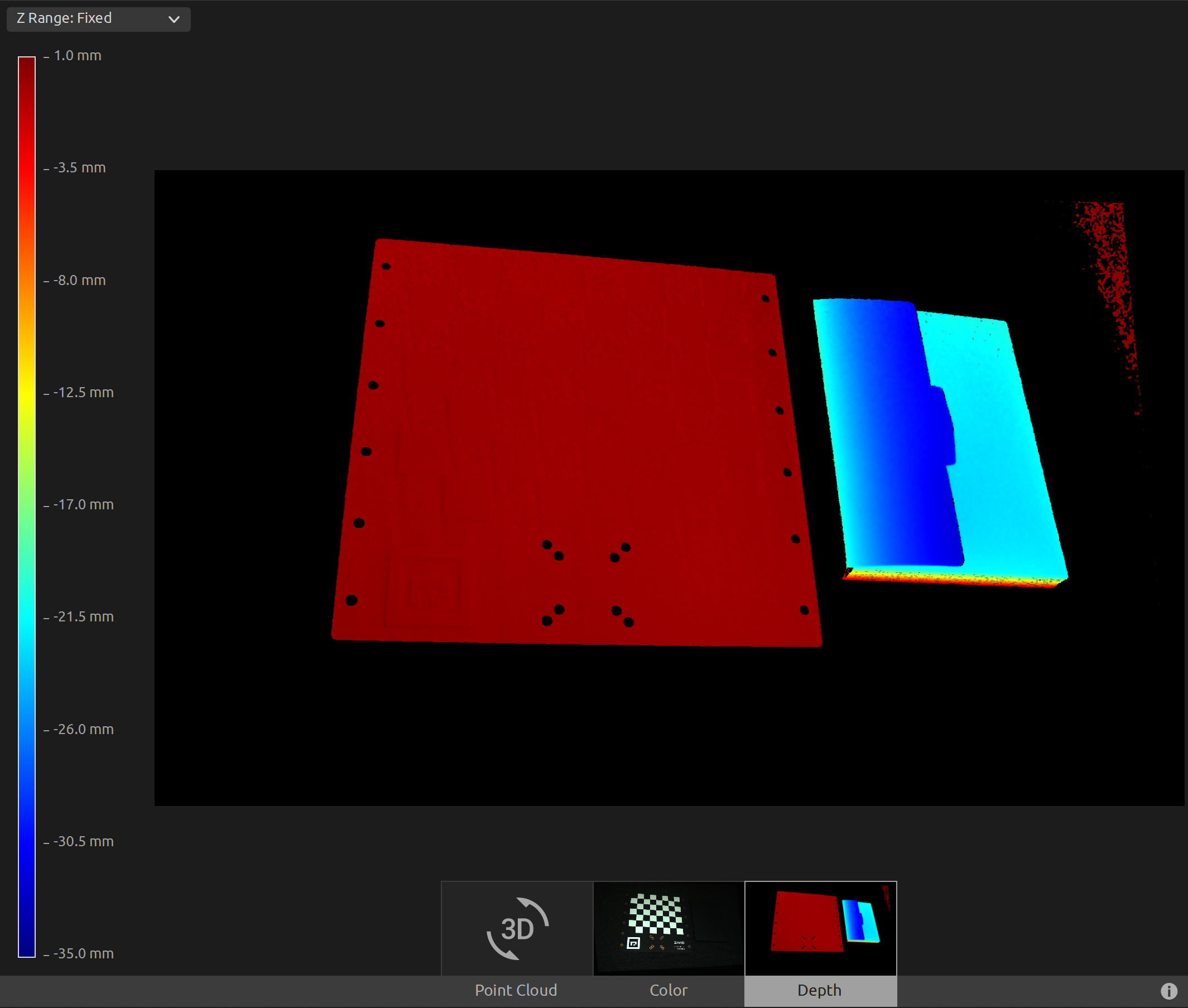
要将点云转换至标定板坐标系,您可以运行我们的代码示例。
示例: TransformPointCloudViaCheckerboard.cpp
./TransformPointCloudViaCheckerboard
示例: TransformPointCloudViaCheckerboard.cs
./TransformPointCloudViaCheckerboard
示例: transform_point_cloud_via_checkerboard.py
python transform_point_cloud_via_checkerboard.py
小技巧
如果您希望在自己的设置中使用它,请修改代码示例:
用您的实际相机和设置替换 ZDF 文件。
将棋盘格标定板放置在场景中。
运行示例!