Aperture
Introduction

카메라 조리개는 렌즈 창의 개구부입니다. 일부 카메라는 고정된 조리개를 가지고 있고, 다른 카메라는 조절 가능합니다. 조리개 크기는 일반적으로 \(f\) 숫자로 표현되는데, \(f\) 숫자가 감소할수록 개구부의 면적이 증가하기 때문에 직관적이지 않을 수 있습니다. \(f\) 숫자 \(N\) 은 다음과 같습니다.
여기서 \(f\) 는 초점 거리이고 \(D\) 입사 동공의 지름입니다. 초점 거리는 렌즈에서 카메라 내부 초점 F까지의 거리입니다. 대부분의 최신 렌즈는 표준 \(f\) 값을 사용합니다. 이는 2의 제곱근의 거듭제곱에 해당하는 기하급수에 기반합니다. \(\frac{f}{\sqrt{2^n}}\) 는 이렇게 하면 이 기하급수가 감소할 때마다 동공의 면적이 절반으로 줄어듭니다. 따라서 이 값을 증가 또는 감소시키는 것은 조리개를 더하거나 빼는 것과 같습니다.
Aperture in Zivid cameras
The following table summarizes which Zivid camera families have adjustable (dynamic) aperture and which have a fixed aperture.
Camera Family |
Aperture Type |
|---|---|
Zivid 3 |
Fixed |
Zivid 2+ |
Dynamic |
Zivid 2 |
Dynamic |
The relevant models have an integrated electro-mechanical iris that can be rapidly adjusted. A completely open pupil corresponds to an \(f\)-number of \(\frac{f}{1.4}\) and a completely closed pupil to an \(\frac{f}{32}\). To use the stop method, it is recommended to use the following f-number values:
\(f\)-number |
\(\frac{f}{1.4}\) |
\(\frac{f}{2}\) |
\(\frac{f}{2.8}\) |
\(\frac{f}{4}\) |
\(\frac{f}{5.6}\) |
\(\frac{f}{8}\) |
\(\frac{f}{11}\) |
\(\frac{f}{16}\) |
\(\frac{f}{22}\) |
\(\frac{f}{32}\) |
Stops |
+4 |
+3 |
+2 |
+1 |
0 |
-1 |
-2 |
-3 |
-4 |
-5 |
Aperture and Depth-of-Field
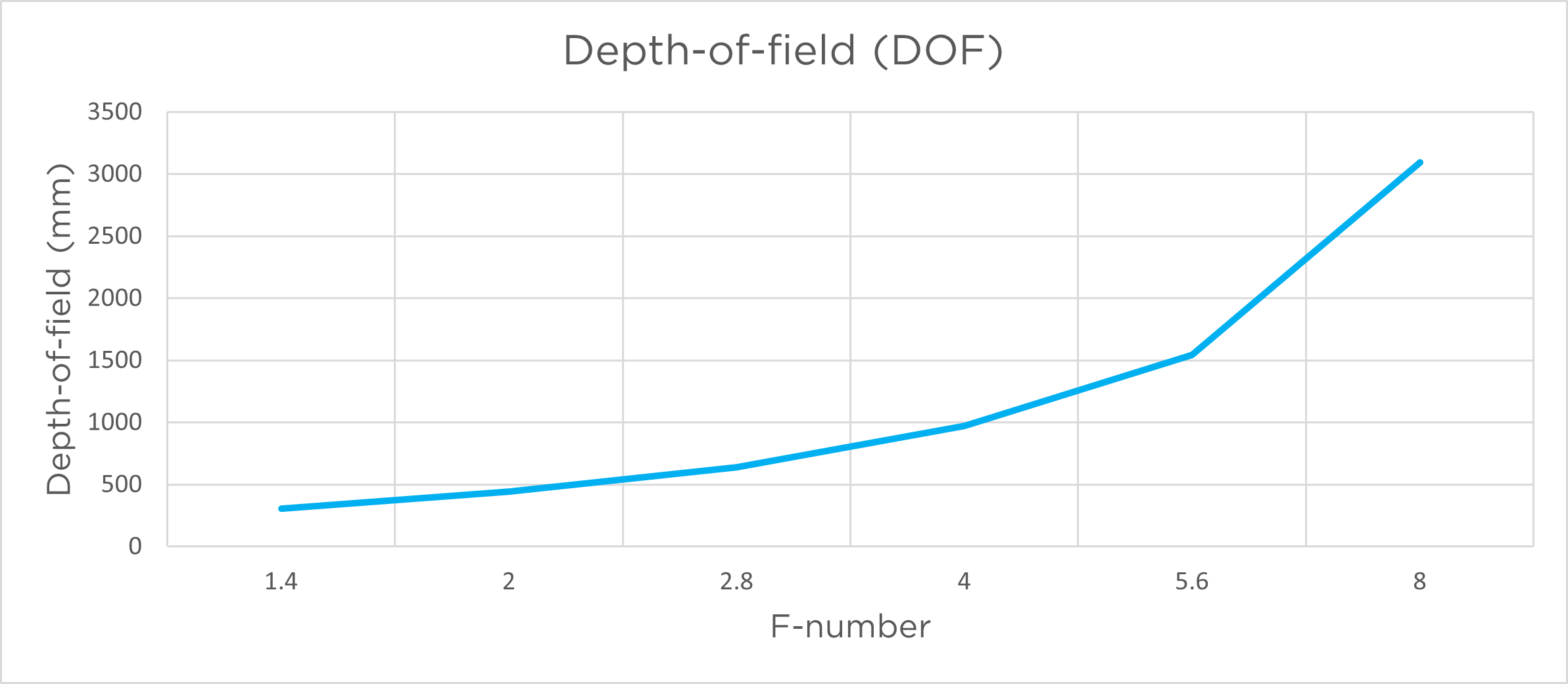
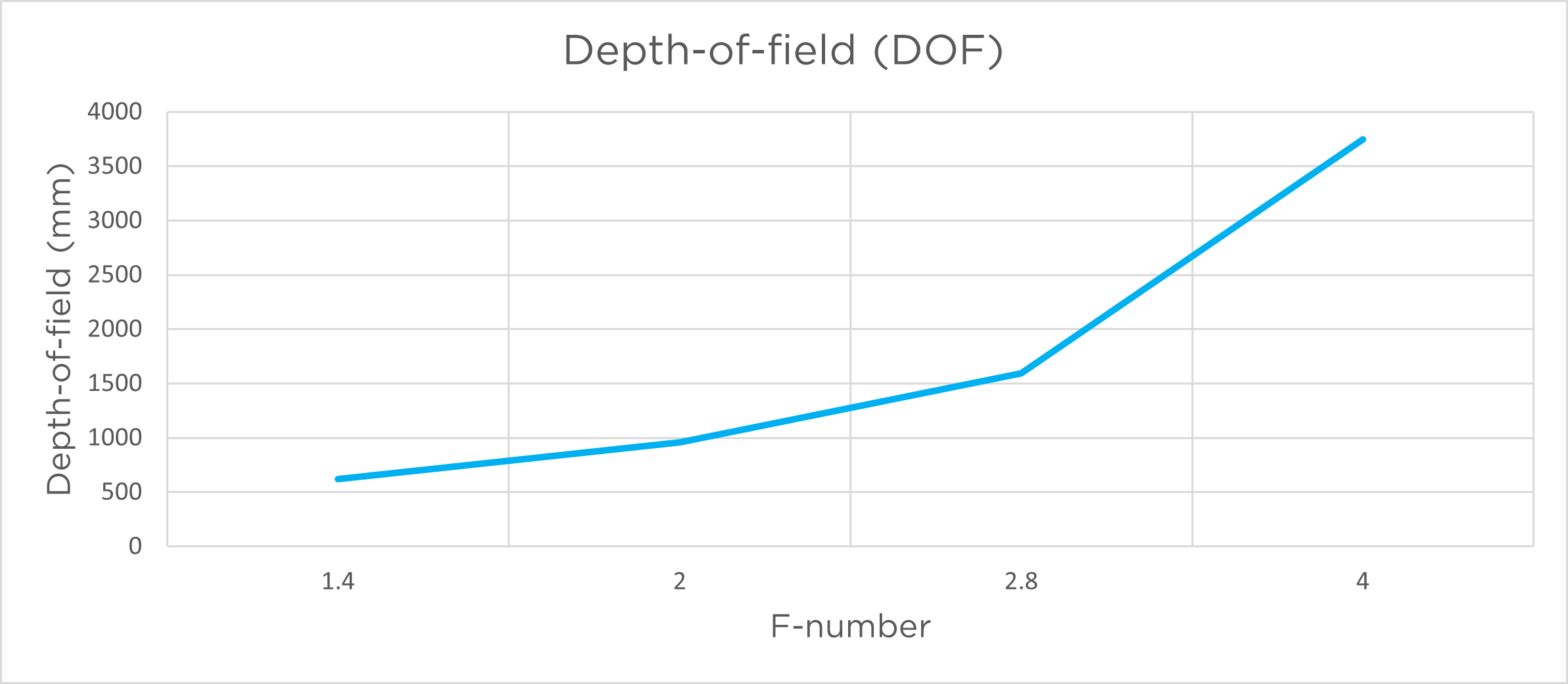
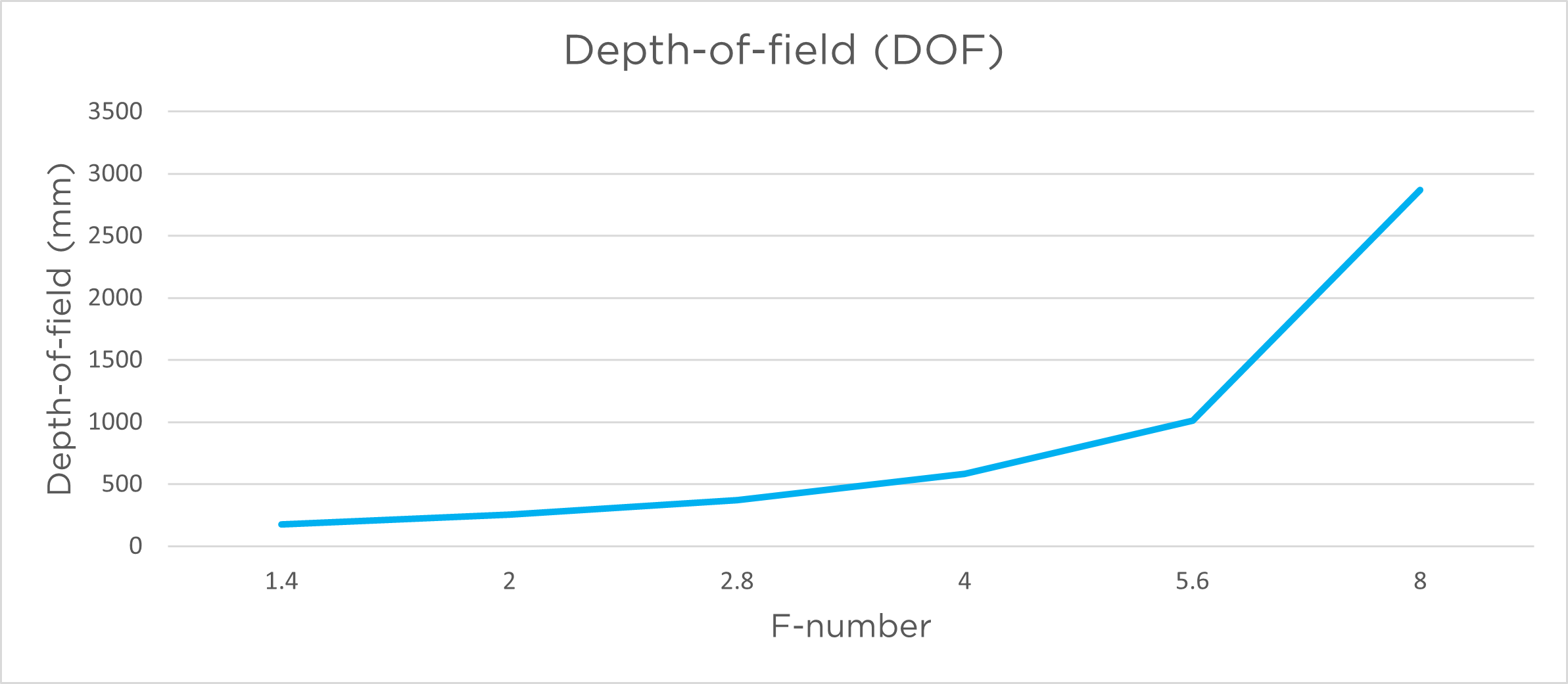
피사계 심도는 주어진 조리개 값에 대해 허용 가능한 정도로 선명한 초점이 맞춰진 이미지 범위입니다. 넓은 조리개/조리개(낮은 f-값)는 좁은 피사계 심도(초점 범위가 좁아짐)를 제공합니다. 좁은 조리개/조리개(높은 f-값)는 더 깊은 피사계 심도(초점 범위가 길어짐)를 제공합니다. 피사계 심도는 초점 지점 앞 약 1/3, 뒤 약 2/3 지점에 위치합니다.

The graphs below show the depth of field as a function of aperture for the relevant models.
Zivid 3 XL250 cameras have a fixed aperture with an f-number of 3 and a non-variable depth of field.
Further reading
Depth of Focus 에 대해 자세히 알아보세요.
Version History
SDK |
Changes |
|---|---|
2.17 |
Added support for Zivid 3 XL250. |
2.0.0 |
Aperture API가 Iris에서 Aperture로 변경되었습니다. 자세한 내용은 Porting guide 를 참조하세요. |