焦深
介绍
焦深描述了是物体聚焦的距离范围。超出此范围的物体会显得模糊。
在本文中,我们将解释焦深的基本原理以及如何将这些原理应用于 Zivid 相机。
什么是焦点?
焦点通常由所谓的*Circle of Confusion*(弥散圆)或简称 CoC 定义。 CoC是指光线在通过相机镜头后撞击成像传感器时,其所覆盖的半径或面积。通常,当CoC大到会覆盖一个以上像素时,就会认为对象失焦。这会导致信号丢失和噪声。当光圈足够大时,距离太近的物体会聚焦在图像传感器的前方,而距离镜头太远的物体会聚焦在传感器后方,两者都会导致模糊。请参见下图。
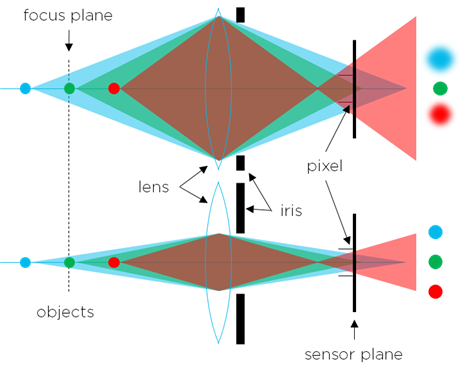
景深
景深是物体能够被正常聚焦的前后距离范围。其边界由近焦距 ( \(d_{near}\) ) 和远焦距 ( \(d_{far}\) ) 定义。在这些边界之外,CoC 会增大,导致光线扩散到相邻像素中。
镜头折射光线的角度会随着光圈大小而增大。对于 Zivid 3D 相机,大光圈会导致物体失焦,从而降低信噪比 (SNR) 并使点云更加嘈杂。因此,选择适合相机工作距离的光圈对于获得最佳图像质量至关重要。
焦点如何影响我的点云?
随着图像越来越模糊,噪声和 对比度失真 等伪影将会增加。当我们谈论噪声时,我们谈论的是点云的点精度。这意味着给定像素的捕获间变化将会增加,并且给定捕获内的像素间变化将会增加。重要的是要注意,噪声的轻微增加可能仍然是可以接受的。根据所使用的处理算法,噪声的轻微增加可能是可以接受的。因此,在许多情况下,未聚焦的图像仍然是可以接受的。
备注
Zivid 相机具有很强的防失焦能力!
还需要注意的是,只有图像的失焦区域才会受到影响。考虑相机在给定应用中的工作距离,以获得具有最佳精度的良好点云。
Zivid 相机的焦深
下表显示了 Zivid 相机的焦深。
Zivid 2+ M130/MR130 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
\(f\) -值 |
\(f/2\) |
\(f/2.8\) |
\(f/4\) |
\(f/5.6\) |
\(f/8\) |
\(f/11\) |
\(f/16\) |
\(f/22\) |
\(f/32\) |
Stops |
+3 |
+2 |
+1 |
0 |
-1 |
-2 |
-3 |
-4 |
-5 |
近焦点 (mm) |
1115 |
1055 |
975 |
885 |
780 |
680 |
560 |
460 |
355 |
远焦点(mm) |
1560 |
1695 |
1945 |
2430 |
3880 |
15120 |
Inf [1] |
Inf [1] |
Inf [1] |
景深 (mm) |
445 |
640 |
970 |
1545 |
3095 |
14440 |
Inf [1] |
Inf [1] |
Inf [1] |
Zivid 2+ L110/LR110 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
\(f\) -值 |
\(f/2\) |
\(f/2.8\) |
\(f/4\) |
\(f/5.6\) |
\(f/8\) |
\(f/11\) |
\(f/16\) |
\(f/22\) |
\(f/32\) |
Stops |
+3 |
+2 |
+1 |
0 |
-1 |
-2 |
-3 |
-4 |
-5 |
近焦点 (mm) |
800 |
720 |
630 |
535 |
440 |
360 |
275 |
215 |
155 |
远焦点(mm) |
1769 |
2310 |
4375 |
Inf [1] |
Inf [1] |
Inf [1] |
Inf [1] |
Inf [1] |
Inf [1] |
景深 (mm) |
960 |
1590 |
3745 |
Inf [1] |
Inf [1] |
Inf [1] |
Inf [1] |
Inf [1] |
Inf [1] |
Zivid 2+ M60/MR60 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
\(f\) -值 |
\(f/2\) |
\(f/2.8\) |
\(f/4\) |
\(f/5.6\) |
\(f/8\) |
\(f/11\) |
\(f/16\) |
\(f/22\) |
\(f/32\) |
Stops |
+3 |
+2 |
+1 |
0 |
-1 |
-2 |
-3 |
-4 |
-5 |
近焦点 (mm) |
500 |
465 |
425 |
380 |
330 |
285 |
230 |
185 |
140 |
远焦点(mm) |
755 |
840 |
1010 |
1390 |
3200 |
Inf [1] |
Inf [1] |
Inf [1] |
Inf [1] |
景深 (mm) |
255 |
370 |
585 |
1010 |
2870 |
Inf [1] |
Inf [1] |
Inf [1] |
Inf [1] |
Zivid 2 M70 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
\(f\) -值 |
\(f/2\) |
\(f/2.8\) |
\(f/4\) |
\(f/5.6\) |
\(f/8\) |
\(f/11\) |
\(f/16\) |
\(f/22\) |
\(f/32\) |
Stops |
+3 |
+2 |
+1 |
0 |
-1 |
-2 |
-3 |
-4 |
-5 |
近焦点 (mm) |
530 |
480 |
420 |
370 |
300 |
250 |
190 |
150 |
110 |
远焦点(mm) |
1040 |
1280 |
1990 |
7630 |
Inf [1] |
Inf [1] |
Inf [1] |
Inf [1] |
Inf [1] |
景深 (mm) |
510 |
800 |
1570 |
7260 |
Inf [1] |
Inf [1] |
Inf [1] |
Inf [1] |
Inf [1] |
Zivid 2 L100 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
\(f\) -值 |
\(f/2\) |
\(f/2.8\) |
\(f/4\) |
\(f/5.6\) |
\(f/8\) |
\(f/11\) |
\(f/16\) |
\(f/22\) |
\(f/32\) |
Stops |
+3 |
+2 |
+1 |
0 |
-1 |
-2 |
-3 |
-4 |
-5 |
近焦点 (mm) |
680 |
605 |
520 |
430 |
350 |
280 |
210 |
160 |
120 |
远焦点(mm) |
1870 |
2870 |
14290 |
Inf [1] |
Inf [1] |
Inf [1] |
Inf [1] |
Inf [1] |
Inf [1] |
景深 (mm) |
1190 |
2260 |
13770 |
Inf [1] |
Inf [1] |
Inf [1] |
Inf [1] |
Inf [1] |
Inf [1] |
警告
Zivid 3 采用固定光圈,不具备光圈调节功能。
焦深计算器
通过使用Zivid的 焦深计算器,可以根据工作距离和可接受的模糊半径找到推荐的最大光圈。请记住,在感兴趣的区域获得清晰的图像是获得最佳点云质量所需的许多条件之一,但这不是硬性限制。如上所述,Zivid 3D技术具有非常强的抗模糊和散焦能力。即使图像看起来失焦,它仍然能够提供良好的点云,尽管它们可能会看起来有点嘈杂。
版本历史记录
SDK |
变更 |
|---|---|
2.17.0 |
新增对 Zivid 3 XL250 的支持。 |