Region of Interest
The Region of Interest (ROI) is used to remove points outside a user-defined region of interest. The ROI can either be a box in 3D, a range of z-values from the camera, or both.
A ROI is helpful if the application only requires a portion of the field of view and not the entire scene. If you, for example, want to detect parts in a bin, your detection algorithms may benefit from the reduced search space inside the bin rather than the whole scene.
Note
The ROI does not reduce the capture time. It is applied post-process and will increase capture time by a couple of milliseconds. It is, however, applied directly on the GPU and is likely faster than a third-party implementation.
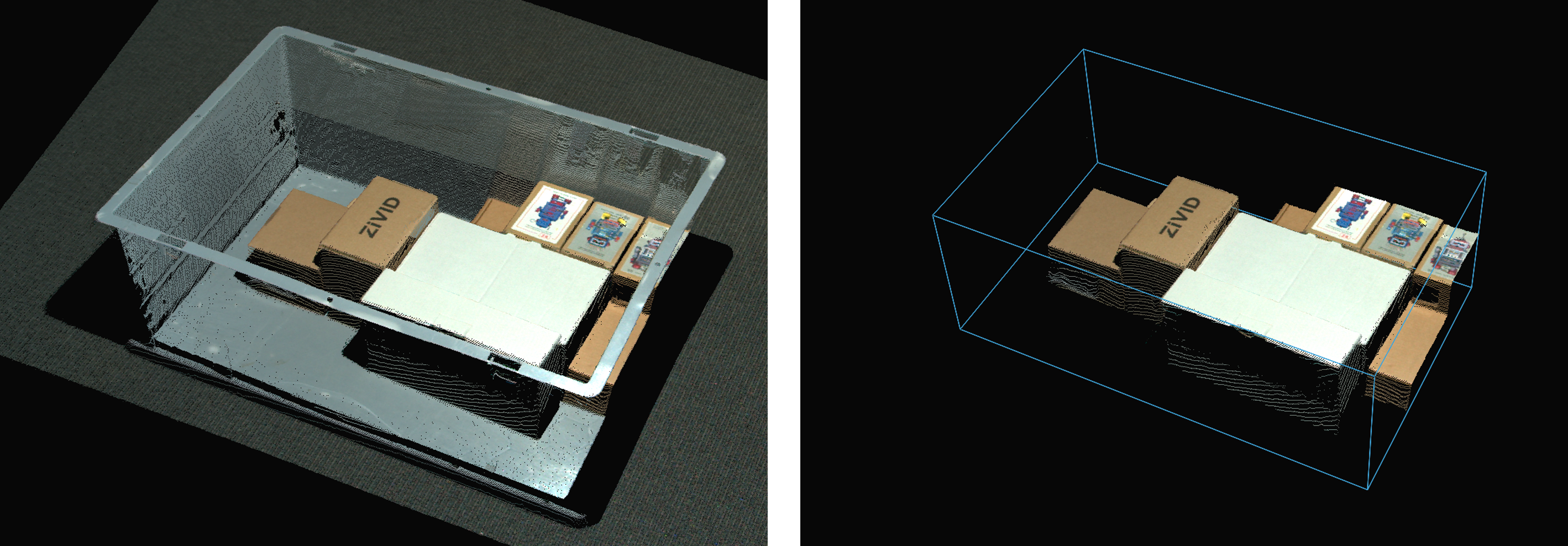
ROI as a Box
Three points define the base plane of the box and two extents define the height:
The three points are given in the camera frame of reference in 3D and define the base plane of the box. A fourth point is automatically found to bind the base plane into a frame and complete the rectangle. The three points constitute two vectors in order:
Point O is the origin of the vectors.
Point A spans the first vector from the origin.
Point B spans the second vector from the origin.
The two extents extrude the base frame into a box. The cross-product of vectors OA and OB defined by Point O, Point A and Point B gives the direction of the extents. A negative extent will therefore extrude in the opposite direction of the cross-product.
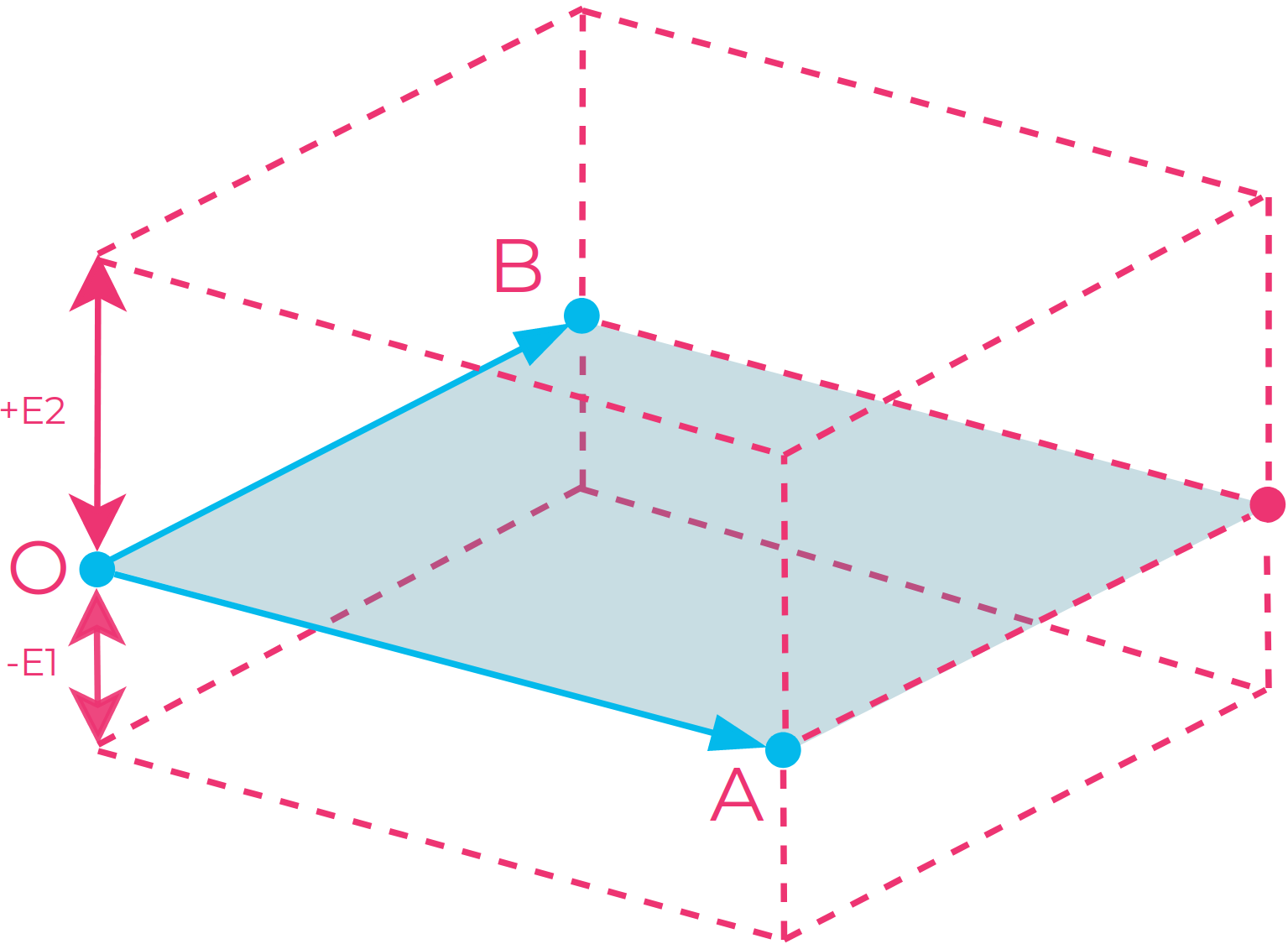
Illustration of the ROI box: Three points (O, A, and B) are given to define the box’s bottom plane, and a fourth point is automatically chosen to complete the rectangle. The bounded plane defined by the four points can then be extruded both upwards (+E2) and downwards (-E1) to complete the box.
Note
The base frame of the box is not constrained to a rectangle with perpendicular corners. It is therefore possible to make a parallelogram as the base, and a parallelepiped as the box.
Tip
Use the following steps when selecting the three points as a rule of thumb:
Select Point O in an arbitrary corner.
Select Point A such that Point B lies in a position counter-clockwise to Point A.
Select Point B in a position counter-clockwise to Point A.
This way the extents will have a positive direction towards the camera.
ROI as a Depth Range
The ROI can also be defined as a range of z-values from the camera, where points within a minimum depth threshold and a maximum depth threshold are kept. This is useful if you have points in the foreground or background of the scene that you want to filter out. Note that the z-values are given in the camera frame of reference and will therefore filter perpendicularly to the camera. This will thus work best if the camera is mounted perpendicularly to the objects you want to capture.
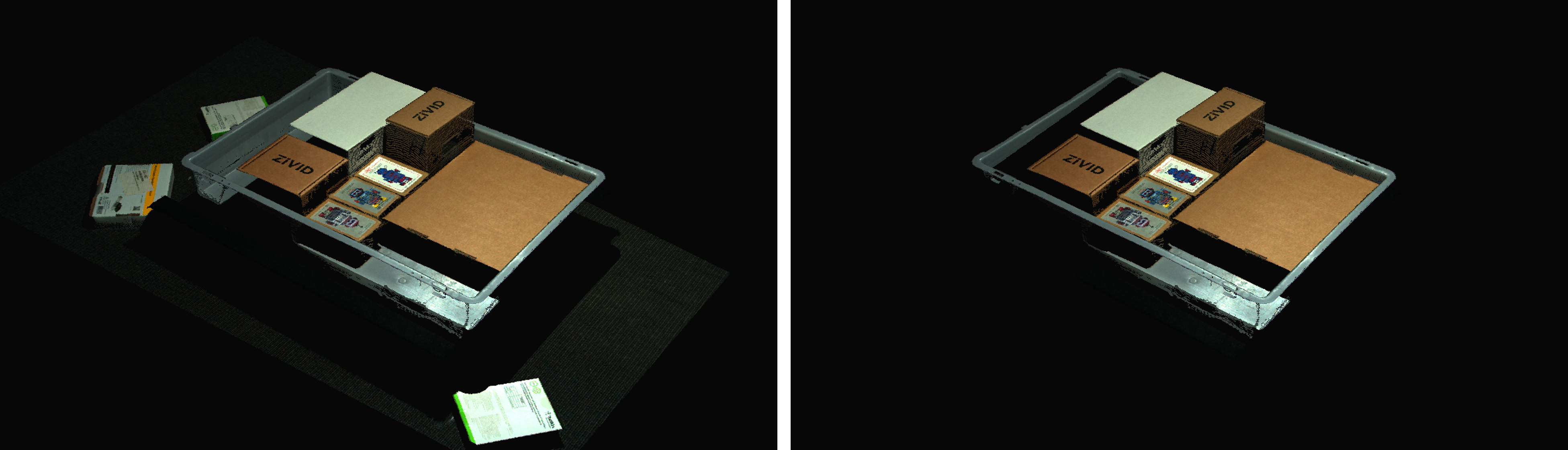
Performance
Note
ROI adds the following processing time per 3D capture:
Filter |
Zivid One+ |
Zivid Two |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Intel UHD 750 |
Intel UHD G1 |
NVIDIA 3070 |
Intel UHD 750 |
Intel UHD G1 |
NVIDIA 3070 |
|
High-end [1] |
Low-end [2] |
High-end [3] |
High-end [1] |
Low-end [2] |
High-end [3] |
|
RegionOfInterest - Box |
2 (±2) ms |
4 (±2) ms |
0 (±0.9) ms |
2 (±2) ms |
4 (±441) ms |
0 (±0.8) ms |
RegionOfInterest - Depth |
1 (±2) ms |
2 (±2) ms |
0 (±0.9) ms |
1 (±1) ms |
2 (±440) ms |
0 (±0.8) ms |
Check out Region of Interest Tutorial for a more in-depth tutorial on using ROI for your application.
Version History
SDK |
Changes |
|---|---|
2.9.0 |
ROI API is added. |