Sampling (3D)
Pixel
The Settings::Sampling::Pixel parameter is used to choose the light color of the projected patterns and sampled pixels.
Depending on camera model the setting will have different options.
Zivid 2/2+ |
Zivid 2+R/3 |
|
|---|---|---|
|
✓ |
✓ |
|
✓ |
|
|
✓ |
|
|
✓ |
|
|
✓ |
|
|
✓ |
|
|
✓ |
The respective resolutions, given camera, are as follows:
3D capture |
Zivid 3 |
Zivid 2+/2+R |
Zivid 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
Full resolution [1] |
2816 x 2816 |
2448 x 2048 |
1944 x 1200 |
2x2 [1] |
1408 x 1408 |
1224 x 1024 |
972 x 600 |
4x4 [1] |
704 x 704 |
612 x 512 |
Not available |
When set to all, all pixels sampled, the point cloud has full resolution.
The following illustration shows the sensor grid and associated indices.
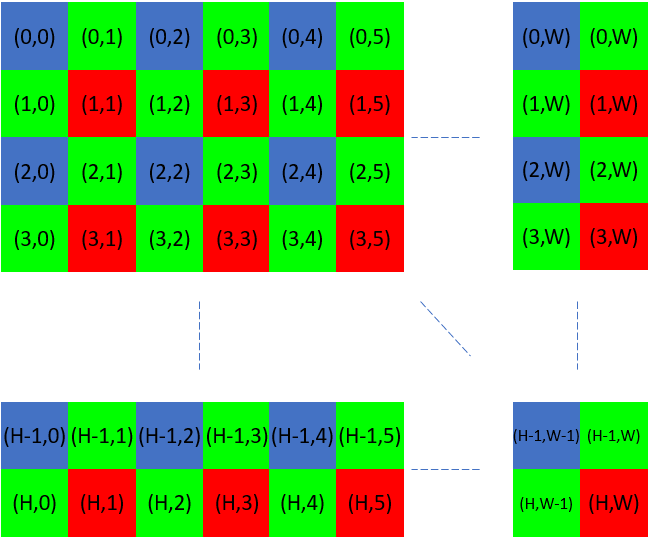
When we sub-/downsample (2x2) we get 1/4 of the original number of points.
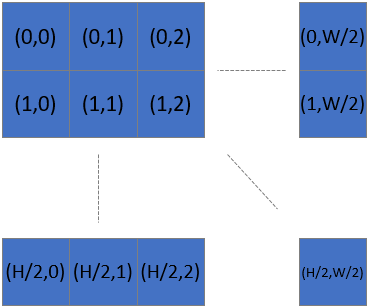
This means that, after subsampling or downsampling 2x2, the number of points along x and y axis is divided by 2. For subsample or downsample 4x4 the number of points along x and y axis is divided by 4.
For example, for Zivid 2+ M130 the spatial distance between two pixels is 0.32 mm @ 1300 mm working distance. With 2x2 subsampling, this distance is doubled to 0.64 mm at the same working distance.
This does not affect the resolution in depth; the point precision determines this.
Subsampling decreases the acquisition and capture time, as less data will be captured and processed. Additionally, it eliminates the need to downsample the data to transform it to a more manageable size and thus reduces the storage and post-processing requirements. With a quarter of the data, Zivid post-processing (such as Normals and Transform) and user post-processing (e.g., CAD matching) become faster.
Picking a specific color channel can also help reduce noise and effects of ambient light. Projecting blue light will in most cases give better data than red light. On 2+ MR60/MR130/LR110, we always prefer to project blue light.
Version History
SDK |
Changes |
|---|---|
2.17.0 |
Added support for Zivid 3. |
2.14.0 |
Added support for 2+ MR60/MR130/LR110 with the |
2.11.0 |
Added support for |

