Network Configuration
Caution
The correct instructions for network configuration will depend on your SDK version. Choose your SDK version in the top left drop-down.
Default configuration
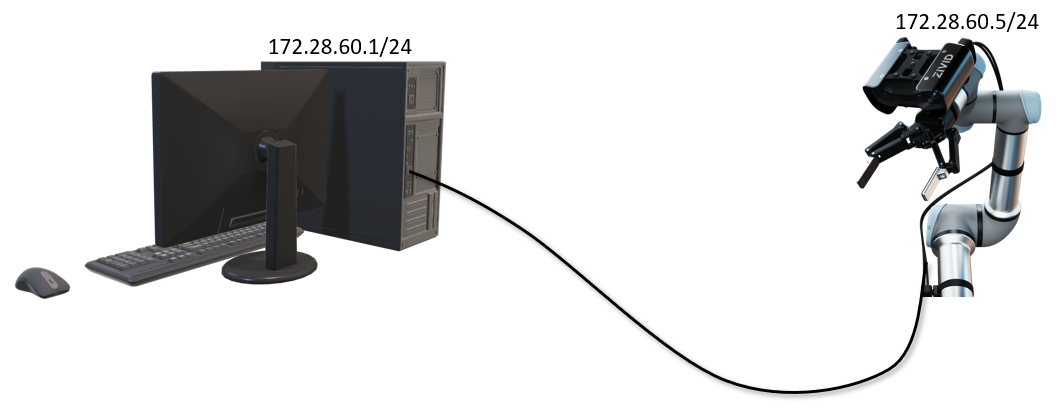
Ethernet-based Zivid cameras are shipped with the default static IP as listed in the table below. To connect to a camera, the interfacing network card must have an IP in the same subnet range as the camera.
Suppose you have not configured the camera in any way before this tutorial, or you know that the camera is still in its default configuration. In that case, you may connect to it after configuring the interfacing network card of your PC. Go to Static IP Network Configuration - PC to do this.
IP |
Subnet mask |
Gateway |
Hostname |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
Zivid camera |
|
|
|
|
Possible PC |
|
|
|
Custom configuration
A custom configuration is necessary if, for example:
You want to change the IP or hostname of the camera
The camera is not in its default configuration
You want to connect to multiple cameras
You want to restrict which cameras Zivid SDK can connect to
This can involve changing the static IP of the camera and PC, but also configuring them to dynamic modes. The custom configuration is divided into static IP and dynamic IP configuration.
This is the default configuration for the camera, which comes with static IP 172.28.60.5.
The following guides describe how to change and configure static IP for both the camera and PC:
The camera also supports automatic IP configuration using either DHCP or link-local. When configured to use an automatic IP, the camera will first try to obtain an IP address using DHCP (within ~45 seconds). Getting an IP address from a DHCP server requires a DHCP server running either on a router on the network or locally on the PC.
The following guides describe how to configure dynamic IP for both the PC and camera, either using DHCP or link-local:
Connecting to the camera
Assuming you have followed either Default configuration or Custom configuration, you should now be able to connect to the camera. Be aware that the first time a camera is connected to in a process, it can take 10-20 seconds before it connects. There are two recommended ways to discover and connect to the camera.
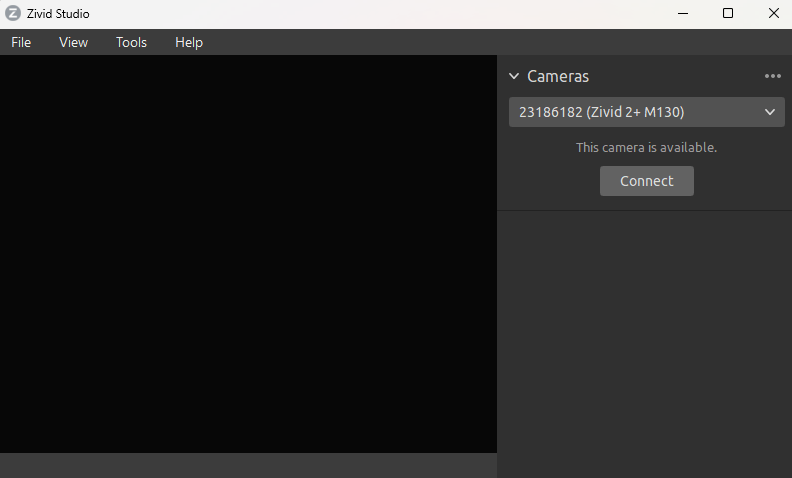
Open Zivid Studio and check that it can discover and connect to the camera.
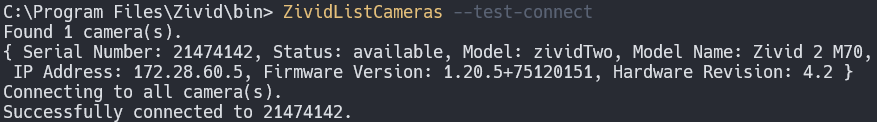
Use the ZividListCameras CLI tool to test the connection.
This tool is installed alongside the Zivid SDK on Windows, and with the Zivid Tools package on Ubuntu.
ZividListCameras --test-connect
If you are still not able to discover or connect to the camera, check out the troubleshooting article No cameras found in Zivid Studio.
Performance
The capture time will, among others, depend on the connection speed between the camera and the network interface and the capture settings used. For optimal performance, the camera needs 10 Gbps. Your computer may not have a port for 10 Gigabit Ethernet, but in that case, you can connect to it using a Thunderbolt 3 to 10GbE Adapter. At a reduced performance you can also use 5GbE, 2.5GbE, or 1GbE.
To check the maximum bandwidth of a specific capture setting (including presets), go to the Capture Speed Calculator.
Hint
The status LEDs at the back of the camera show the current link capacity.
Performance |
Network |
Interface |
Connection |
|---|---|---|---|
Optimal (recommended) |
10GbE (10Gbps) |
PCIe card |
Direct |
Very good |
10GbE |
Thunderbolt Adapter |
Direct |
Good |
5GbE or 2.5GbE |
PCIe/USB/Thunderbolt Adapter |
Direct/Switch |
Minimum |
1GbE (1Gbps) |
PCIe/USB Adapter |
Direct/Switch |
Caution
USB-based network adapters have reduced and more variable capture speed, and can occasionally give errors when using the camera.
Cameras.yml and how to restrict discoverable cameras
A configuration file Cameras.yml can be used to restrict which IP addresses and hostnames Zivid SDK can connect to.
Use the drop-down below for more information about how Zivid SDK discovers cameras and how Cameras.yml can be used.
Cameras.yml and how Zivid SDK discovers cameras
How does Zivid SDK find cameras?
Zivid SDK uses Multicast DNS (mDNS) for auto-discovering cameras on the network.
In SDK 2.7 and earlier, cameras with non-default IPs had to be listed in the Cameras.yml file in the Zivid configuration folder, which the SDK searched through to discover cameras.
Even though mDNS removes the requirement of Cameras.yml, this file may still be used to override which cameras the SDK can connect to.
Cameras.yml therefore has the function of restricting which cameras the PC can connect to, if provided.
Cameras.yml
If you wish to restrict the IPs Zivid SDK searches for, download Cameras.yml and place it in the Zivid configuration folder, as shown below.
mkdir %LOCALAPPDATA%\Zivid\API
move %HOMEPATH%\Downloads\Cameras.yml %LOCALAPPDATA%\Zivid\API\
mkdir --parents "${XDG_CONFIG_HOME-$HOME/.config}"/Zivid/API
mv ~/Downloads/Cameras.yml "${XDG_CONFIG_HOME-$HOME/.config}"/Zivid/API/
Caution
Any existing Config file will be overwritten.
Caution
Zivid configuration files must use .yml file extension ( not .yaml).
Some examples of how Cameras.yml can look like are shown below, either using hostnames or IP addresses.
__version__: 1
Cameras:
NetworkCameras:
- NetworkCamera:
Host: zivid-2152D404.local
- NetworkCamera:
Host: zivid-20205M19.local
- NetworkCamera:
Host: zivid-21389K63.local
__version__: 1
Cameras:
NetworkCameras:
- NetworkCamera:
Host: 172.28.60.5
- NetworkCamera:
Host: 172.28.60.6
- NetworkCamera:
Host: 172.28.60.7
Version History
SDK |
Changes |
|---|---|
2.13.0 |
Added support for network configuration in Zivid Studio and SDK. |
2.11.0 |
Improved network discovery for listing and configuring all cameras, both available and unavailable. |
2.8.0 |
Added support for auto-discovery using Multicast DNS, removing the requirement of |
2.7.0 |
Added support for name queries ending with the |