Static IP Network Configuration - PC
Caution
The correct instructions for network configuration will depend on your SDK version. Choose your SDK version in the top left drop-down.
This guides you through how to set the static IP of the network card that interfaces your camera. You can configure it to match the default configuration of the camera, or to a custom static IP.
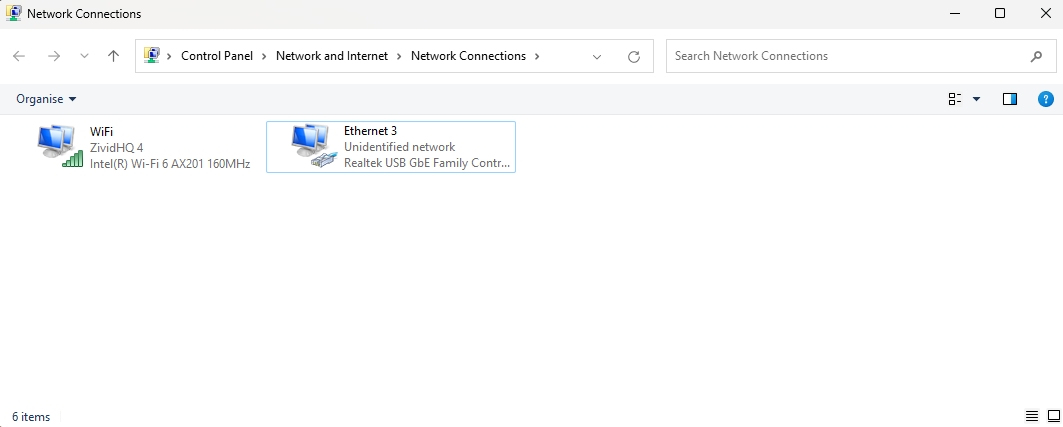
Navigate to:
Control Panel → Network and Internet → Network and Sharing Center → Change adapter settings
Right click on your network connection and choose Properties.
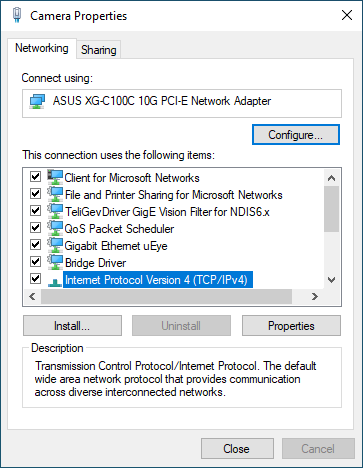
Then, find Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and open its Properties.
Select Use the following IP address and configure your network interface (card/adapter), and choose an IP address that is in the same subnet as the camera. For a camera with default configuration, this would be:
IP address:
172.28.60.2Subnet mask:
255.255.255.0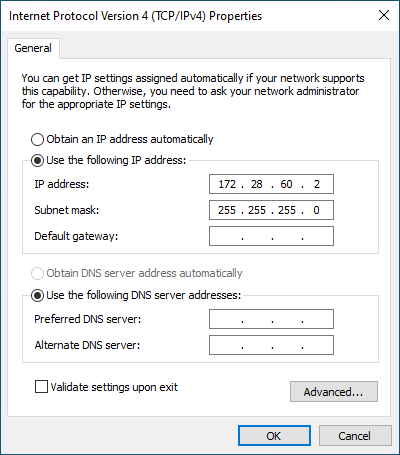
Caution
Capture time on Windows can occasionally be longer (about 1 second longer than normal) due to ethernet packet loss leading to data re-transmits. You can reduce the occurrence of packet loss by increasing receive and transmit buffers.
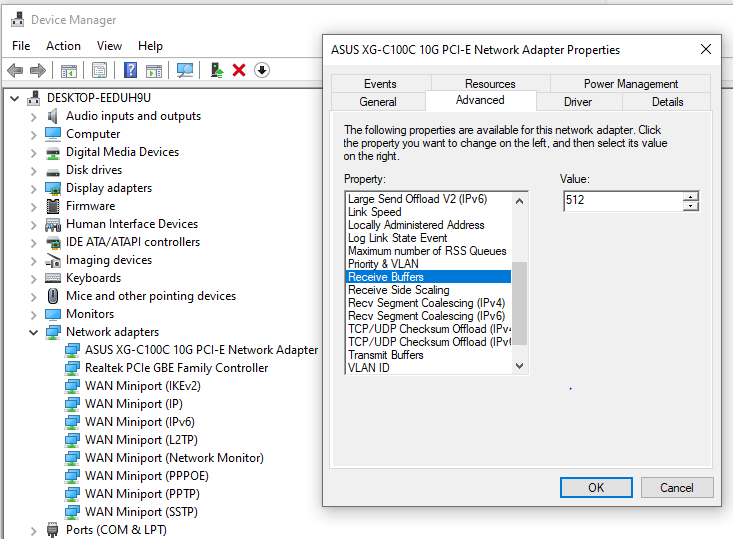
Navigate to Device Manager → Network adapters. Right click on your network adapter and press Properties. Under Advanced, increase Receive Buffers and Transmit Buffers.
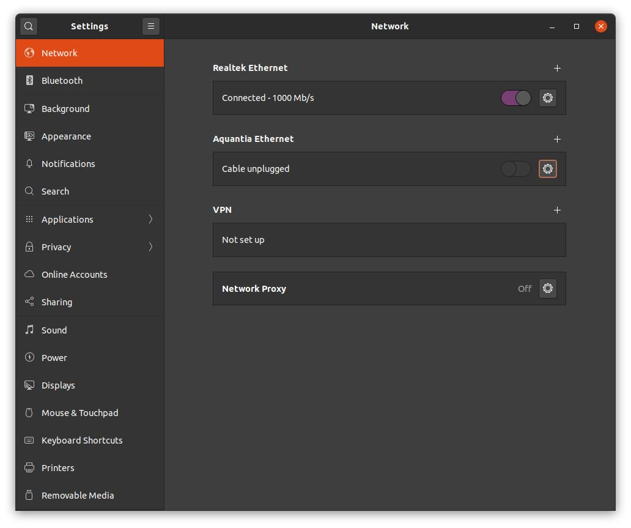
Navigate to your network settings and then click on the cogwheel for the unconnected network interface (card/adapter). This should look approximately like the screenshot below if you are using Ubuntu 20.04.
Set up the network configuration in the IPv4 tab. Set IPv4 Method to manual, and choose an IP address that is in the same subnet as the camera. For a camera with default configuration, this would be:
Address to:
172.28.60.2Netmask to:
255.255.255.0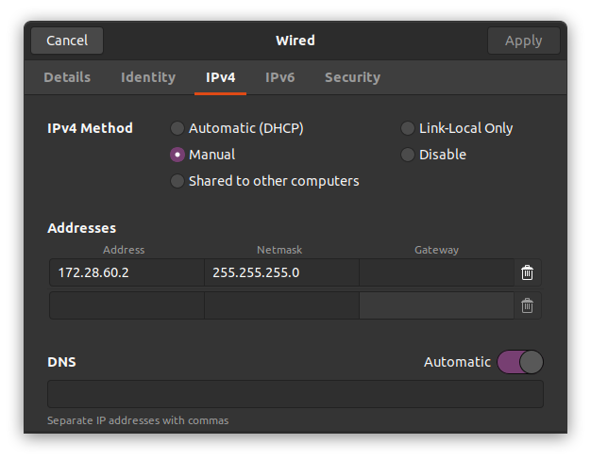
Caution
You might need to bring down and up your network interface after this step (set the first toggle button from the first screenshot to on and off).
Find current interfaces and configuration
ip addrExample output for ip addrzivid@se-zivid-xps15:~$ ip addr 1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000 link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00 inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 ::1/128 scope host valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever 8: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000 link/ether 48:65:ee:1c:12:ba brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet 172.21.96.50/24 brd 172.28.60.255 scope global noprefixroute eth0 valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 fe80::4a65:eeff:fe1c:12ba/64 scope link valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
The current IP address is
172.21.96.50/24. That will not work if the IP address of the camera is not in the same subnet. For a camera with default configuration, the IP should be in the same subnet as172.28.60.5.We will use netplan to update the IP address for this interface. First, find your current configuration.
ls /etc/netplanBy default, you should see a .yaml file named something like 01-network-manager-all.yaml. Then list its contents, e.g.:
cat /etc/netplan/01-netcfg.yaml # Let NetworkManager manage all devices on this system network: version: 2 renderer: NetworkManager
For safety, copy the file before you update the configuration as follows:
sudo nano /etc/netplan/01-netcfg.yaml network: version: 2 renderer: networkd ethernets: eth0: dhcp4: no addresses: - 172.28.60.2/24 gateway4: 172.28.60.1
Apply changes
sudo netplan apply
Verify that the IP address has been correctly updated
Example output for ip addrzivid@se-zivid-xps15:~$ ip addr 1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000 link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00 inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 ::1/128 scope host valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever 8: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000 link/ether 48:65:ee:1c:12:ba brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet 172.28.60.2/24 brd 172.28.60.255 scope global noprefixroute eth0 valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 fe80::4a65:eeff:fe1c:12ba/64 scope link valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
Once you have configured the static IP of your PC to be in the same subnet as your camera, go back to Connecting to the camera.
Multiple cameras
There are two cases in the multiple camera setup:
Multiple cameras connected to multiple network cards
Multiple cameras connected to the same network card via a switch
In both cases, you also have to do a custom configuration of the cameras.
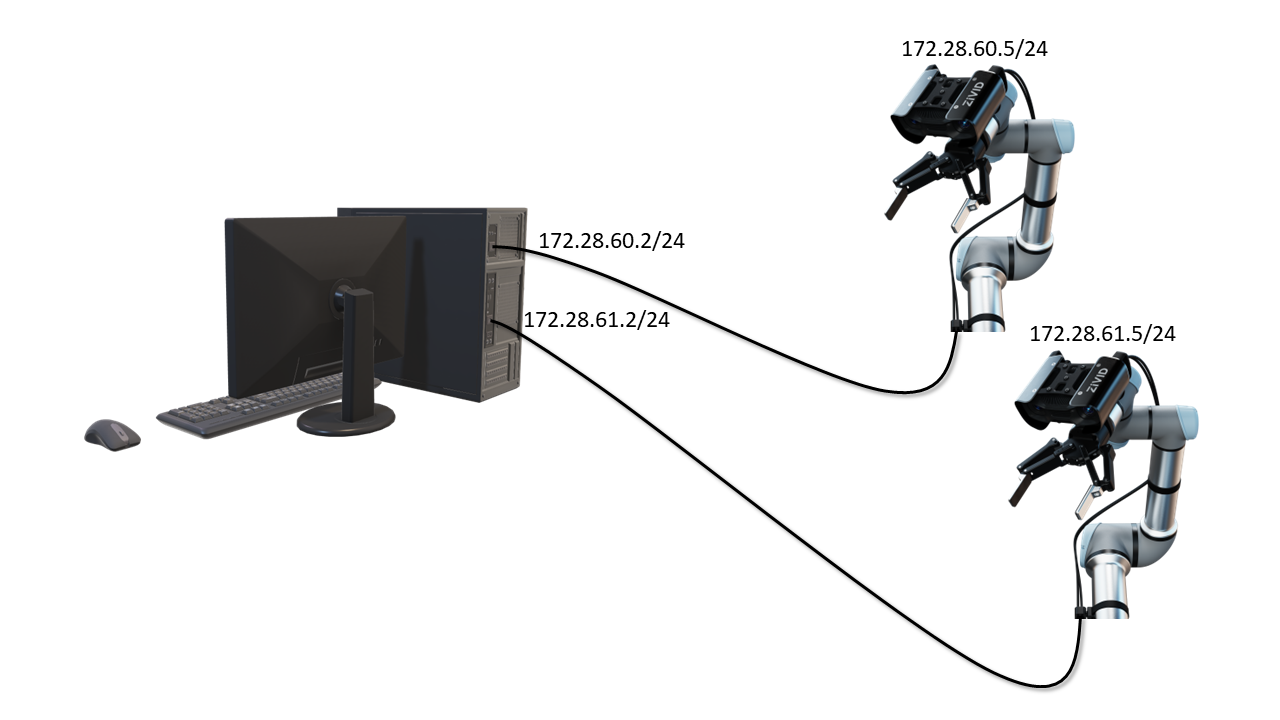
If you use multiple cameras connected to multiple network interface cards then they should not exist on the same subnet.
For example, if the subnet mask is 255.255.255.0, at least one bit in the first 24 bits must be different.
Using the default configuration as an example, the network card configurations would be:
Network interface card one:
Address to:
172.28.60.2Netmask to:
255.255.255.0
Network interface card two:
Address to:
172.28.61.2Netmask to:
255.255.255.0
For network interface card two, you must also configure the IP of the camera to be in the subnet range. Follow Static IP Network Configuration - Camera to do this.
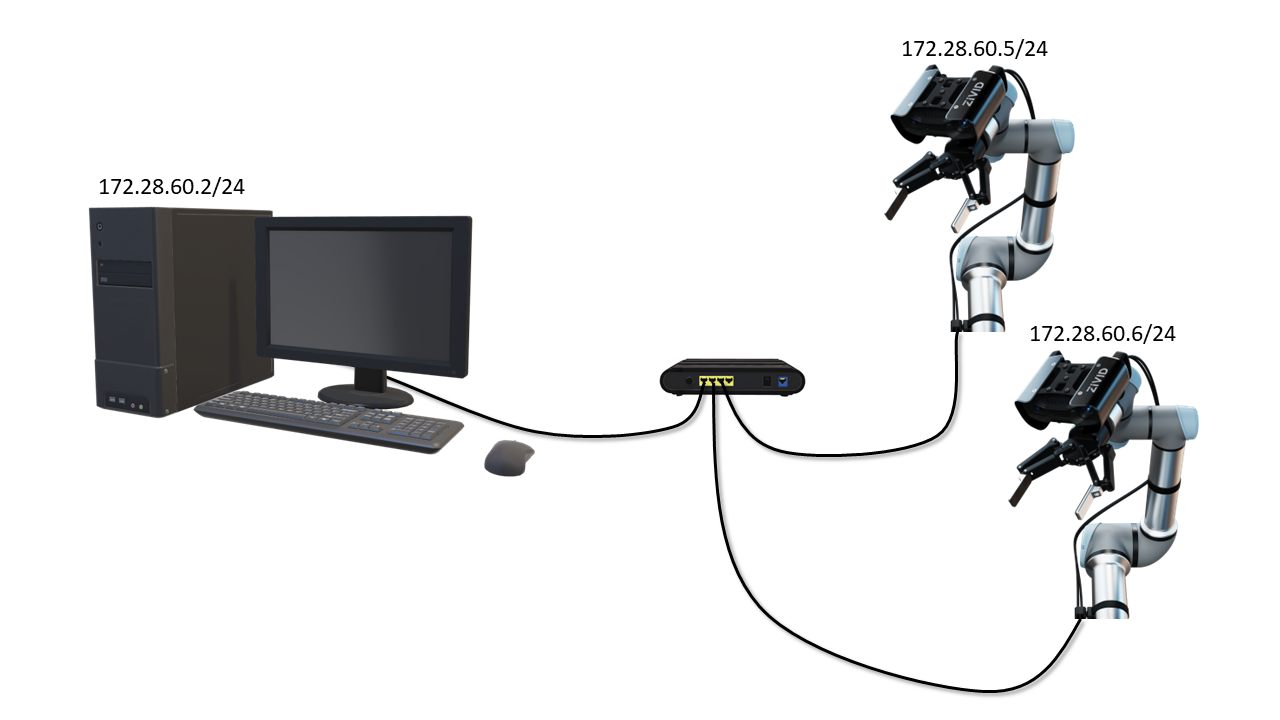
If you use multiple cameras connected to the same network card via a switch, you have to configure the cameras to different IPs in the same subnet as the network card. Using the default configuration as an example, you would have to configure the cameras as:
Camera one:
Address to
172.28.60.5(already set by default)
Camera two:
Address to e.g.
172.28.60.6
This can be repeated for camera three, four, etc. Follow Static IP Network Configuration - Camera to do this.
Note
Multiple network interface cards can potentially provide higher speed than a switch. This is because they will not have to share network bandwidth.
Once you have configured the static IP of your PC to be in the same subnet as your camera(s), go back to Connecting to the camera.