ROI Box via ArUco Marker
This tutorial demonstrates how to find the ROI box parameters using an ArUco marker and how to filter the contents of a bin using it. We are here using the ArUco marker on the Zivid calibration board, and assume the calibration board is placed in the bottom right corner of the bin. The bin size is also assumed known and is used to set the dimensions of the ROI box. This way you can automatically find the ROI parameters in the camera frame.
Note
This tutorial uses a file camera for the scene in the image below for demonstration.
First, we capture a point cloud of the ArUco marker.
const auto fileCamera = std::string(ZIVID_SAMPLE_DATA_DIR) + "/BinWithCalibrationBoard.zfc";
std::cout << "Creating virtual camera using file: " << fileCamera << std::endl;
auto camera = zivid.createFileCamera(fileCamera);
Zivid::Settings2D settings2D{ Zivid::Settings2D::Acquisitions{ Zivid::Settings2D::Acquisition{} } };
Zivid::Settings settings{ Zivid::Settings::Acquisitions{ Zivid::Settings::Acquisition{} },
Zivid::Settings::Color{ settings2D } };
const auto originalFrame = camera.capture2D3D(settings);
auto pointCloud = originalFrame.pointCloud();
string fileCamera = Environment.GetFolderPath(Environment.SpecialFolder.CommonApplicationData) + "/Zivid/BinWithCalibrationBoard.zfc";
Console.WriteLine("Creating virtual camera using file: " + fileCamera);
var camera = zivid.CreateFileCamera(fileCamera);
var settings2D = new Zivid.NET.Settings2D
{
Acquisitions = { new Zivid.NET.Settings2D.Acquisition { } }
};
var settings = new Zivid.NET.Settings
{
Acquisitions = { new Zivid.NET.Settings.Acquisition { } }
};
settings.Color = settings2D;
using (var originalFrame = camera.Capture2D3D(settings))
{
var pointCloud = originalFrame.PointCloud;
file_camera = get_sample_data_path() / "BinWithCalibrationBoard.zfc"
print(f"Creating virtual camera using file: {file_camera}")
camera = app.create_file_camera(file_camera)
settings = zivid.Settings([zivid.Settings.Acquisition()])
settings.color = zivid.Settings2D(acquisitions=[zivid.Settings2D.Acquisition()])
original_frame = camera.capture_2d_3d(settings)
point_cloud = original_frame.point_cloud()
The ArUco marker frame has its origin in the center of the ArUco marker.
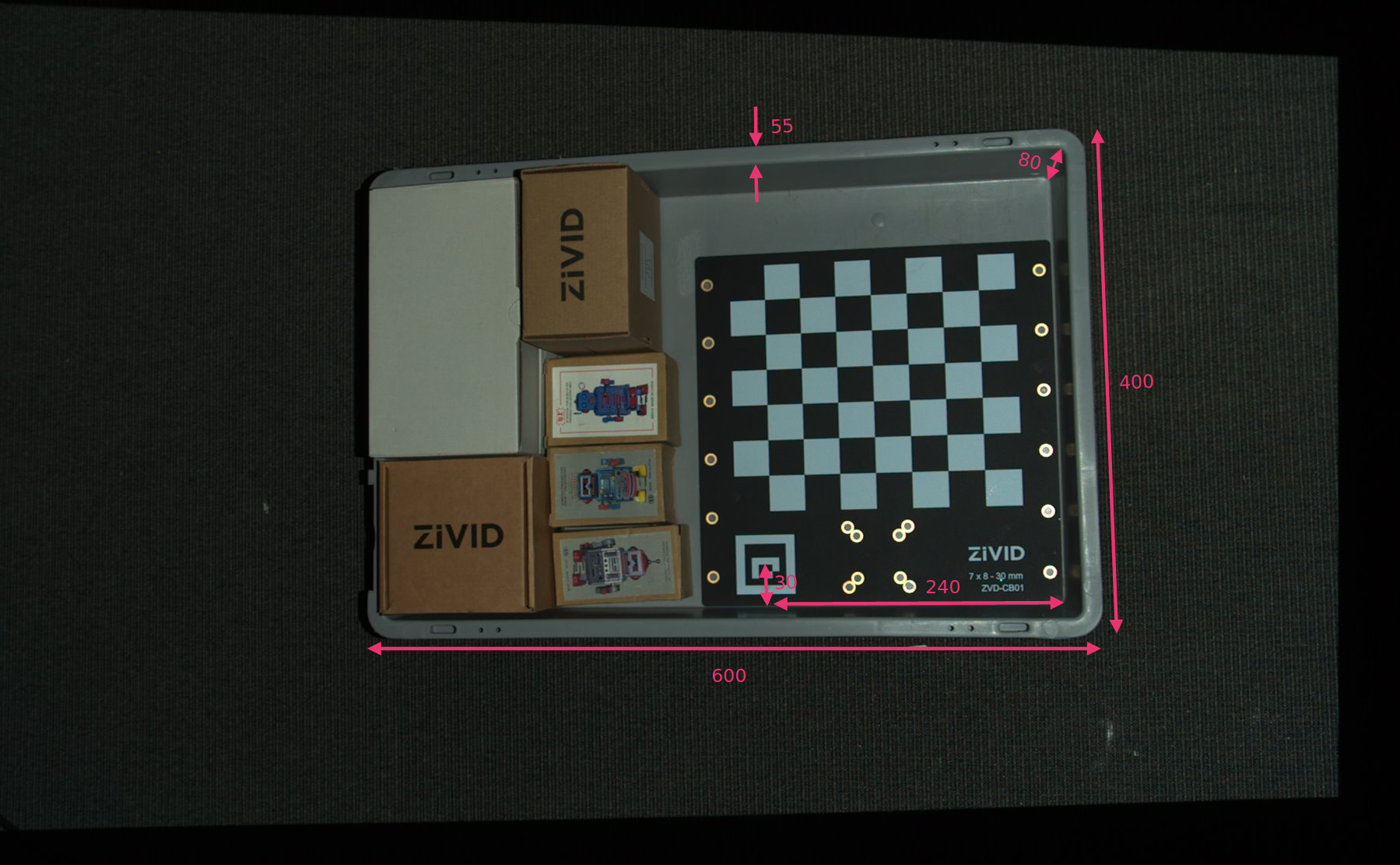
We define the position of the bottom-right corner of the ROI box relative to the ArUco marker frame, and the ROI box size. Then we subtract the width of the bin edge from the length and width to remove the bin walls.
const float roiBoxLength = 545.F;
const float roiBoxWidth = 345.F;
const float roiBoxHeight = 150.F;
// Coordinates are relative to the ArUco marker origin which lies in the center of the ArUco marker.
// Positive x-axis is "East", y-axis is "South" and z-axis is "Down".
const Zivid::PointXYZ roiBoxLowerRightCornerInArUcoFrame{ 240.F, 30.F, 5.F };
const Zivid::PointXYZ roiBoxUpperRightCornerInArUcoFrame{ roiBoxLowerRightCornerInArUcoFrame.x,
roiBoxLowerRightCornerInArUcoFrame.y - roiBoxWidth,
roiBoxLowerRightCornerInArUcoFrame.z };
const Zivid::PointXYZ roiBoxLowerLeftCornerInArUcoFrame{ roiBoxLowerRightCornerInArUcoFrame.x - roiBoxLength,
roiBoxLowerRightCornerInArUcoFrame.y,
roiBoxLowerRightCornerInArUcoFrame.z };
float roiBoxLength = 545F;
float roiBoxWidth = 345F;
float roiBoxHeight = 150F;
// Coordinates are relative to the checkerboard origin which lies in the intersection between the four checkers
// in the top-left corner of the checkerboard: Positive x-axis is "East", y-axis is "South" and z-axis is "Down"
var roiBoxLowerRightCornerInCheckerboardFrame = new Zivid.NET.PointXYZ
{
x = 240F,
y = 30F,
z = 5F
};
var roiBoxUpperRightCornerInCheckerboardFrame = new Zivid.NET.PointXYZ
{
x = roiBoxLowerRightCornerInCheckerboardFrame.x,
y = roiBoxLowerRightCornerInCheckerboardFrame.y - roiBoxWidth,
z = roiBoxLowerRightCornerInCheckerboardFrame.z
};
var roiBoxLowerLeftCornerInCheckerboardFrame = new Zivid.NET.PointXYZ
{
x = roiBoxLowerRightCornerInCheckerboardFrame.x - roiBoxLength,
y = roiBoxLowerRightCornerInCheckerboardFrame.y,
z = roiBoxLowerRightCornerInCheckerboardFrame.z
};
roi_box_length = 545
roi_box_width = 345
roi_box_height = 150
roi_box_lower_right_corner_in_aruco_frame = np.array([240, 30, 5])
roi_box_upper_right_corner_in_aruco_frame = np.array(
[
roi_box_lower_right_corner_in_aruco_frame[0],
roi_box_lower_right_corner_in_aruco_frame[1] - roi_box_width,
roi_box_lower_right_corner_in_aruco_frame[2],
]
)
roi_box_lower_left_corner_in_aruco_frame = np.array(
[
roi_box_lower_right_corner_in_aruco_frame[0] - roi_box_length,
roi_box_lower_right_corner_in_aruco_frame[1],
roi_box_lower_right_corner_in_aruco_frame[2],
]
)
The three points that define the base frame of the ROI box can then be set.
const Zivid::PointXYZ pointOInArUcoFrame = roiBoxLowerRightCornerInArUcoFrame;
const Zivid::PointXYZ pointAInArUcoFrame = roiBoxUpperRightCornerInArUcoFrame;
const Zivid::PointXYZ pointBInArUcoFrame = roiBoxLowerLeftCornerInArUcoFrame;
Then we configure the ArUco marker.
std::cout << "Configuring ArUco marker" << std::endl;
const auto markerDictionary = Zivid::Calibration::MarkerDictionary::aruco4x4_50;
std::vector<int> markerId = { 1 };
We then detect the ArUco marker.
std::cout << "Detecting ArUco marker" << std::endl;
const auto detectionResult = Zivid::Calibration::detectMarkers(originalFrame, markerId, markerDictionary);
Then we estimate the pose of the ArUco marker to transform the three points into the camera frame of reference.
std::cout << "Estimating pose of detected ArUco marker" << std::endl;
const auto cameraToMarkerTransform = detectionResult.detectedMarkers()[0].pose().toMatrix();
std::cout << "Transforming the ROI base frame points to the camera frame" << std::endl;
const auto roiPointsInCameraFrame = transformPoints(
std::vector<Zivid::PointXYZ>{ pointOInArUcoFrame, pointAInArUcoFrame, pointBInArUcoFrame },
cameraToMarkerTransform);
Console.WriteLine("Estimating pose of detected ArUco marker");
var cameraToMarkerTransform = new Zivid.NET.Matrix4x4(detectionResult.DetectedMarkers()[0].Pose().ToMatrix());
Console.WriteLine("Transforming the ROI base frame points to the camera frame");
var roiPointsInCameraFrame = TransformPoints(
new List<Zivid.NET.PointXYZ> { pointOInCheckerboardFrame, pointAInCheckerboardFrame, pointBInCheckerboardFrame },
cameraToMarkerTransform);
print("Estimating pose of detected ArUco marker")
camera_to_marker_transform = detection_result.detected_markers()[0].pose.to_matrix()
print("Transforming the ROI base frame points to the camera frame")
roi_points_in_camera_frame = _transform_points(
[point_o_in_aruco_frame, point_a_in_aruco_frame, point_b_in_aruco_frame],
camera_to_marker_transform,
)
Hint
Learn more about Position, Orientation and Coordinate Transformations to understand how this works.
Now we can filter the point cloud based on the size and position of the ROI box. The first extent is set to a small negative value to include the floor, and the second extent is set to the desired height of the box.
settings.set(
Zivid::Settings::RegionOfInterest{
Zivid::Settings::RegionOfInterest::Box::Enabled::yes,
Zivid::Settings::RegionOfInterest::Box::PointO{ roiPointsInCameraFrame[0] },
Zivid::Settings::RegionOfInterest::Box::PointA{ roiPointsInCameraFrame[1] },
Zivid::Settings::RegionOfInterest::Box::PointB{ roiPointsInCameraFrame[2] },
Zivid::Settings::RegionOfInterest::Box::Extents{ -10, roiBoxHeight } });
settings.RegionOfInterest.Box.Enabled = true;
settings.RegionOfInterest.Box.PointO = roiPointsInCameraFrame[0];
settings.RegionOfInterest.Box.PointA = roiPointsInCameraFrame[1];
settings.RegionOfInterest.Box.PointB = roiPointsInCameraFrame[2];
settings.RegionOfInterest.Box.Extents = new Zivid.NET.Range<double>(-10, roiBoxHeight);
settings.region_of_interest.box.enabled = True
settings.region_of_interest.box.point_o = roi_points_in_camera_frame[0]
settings.region_of_interest.box.point_a = roi_points_in_camera_frame[1]
settings.region_of_interest.box.point_b = roi_points_in_camera_frame[2]
settings.region_of_interest.box.extents = (-10, roi_box_height)
Finally, we take a new capture and visualize the filtered point cloud.
const auto roiFrame = camera.capture2D3D(settings);
std::cout << "Displaying the ROI-filtered point cloud" << std::endl;
visualizeZividPointCloud(roiFrame);
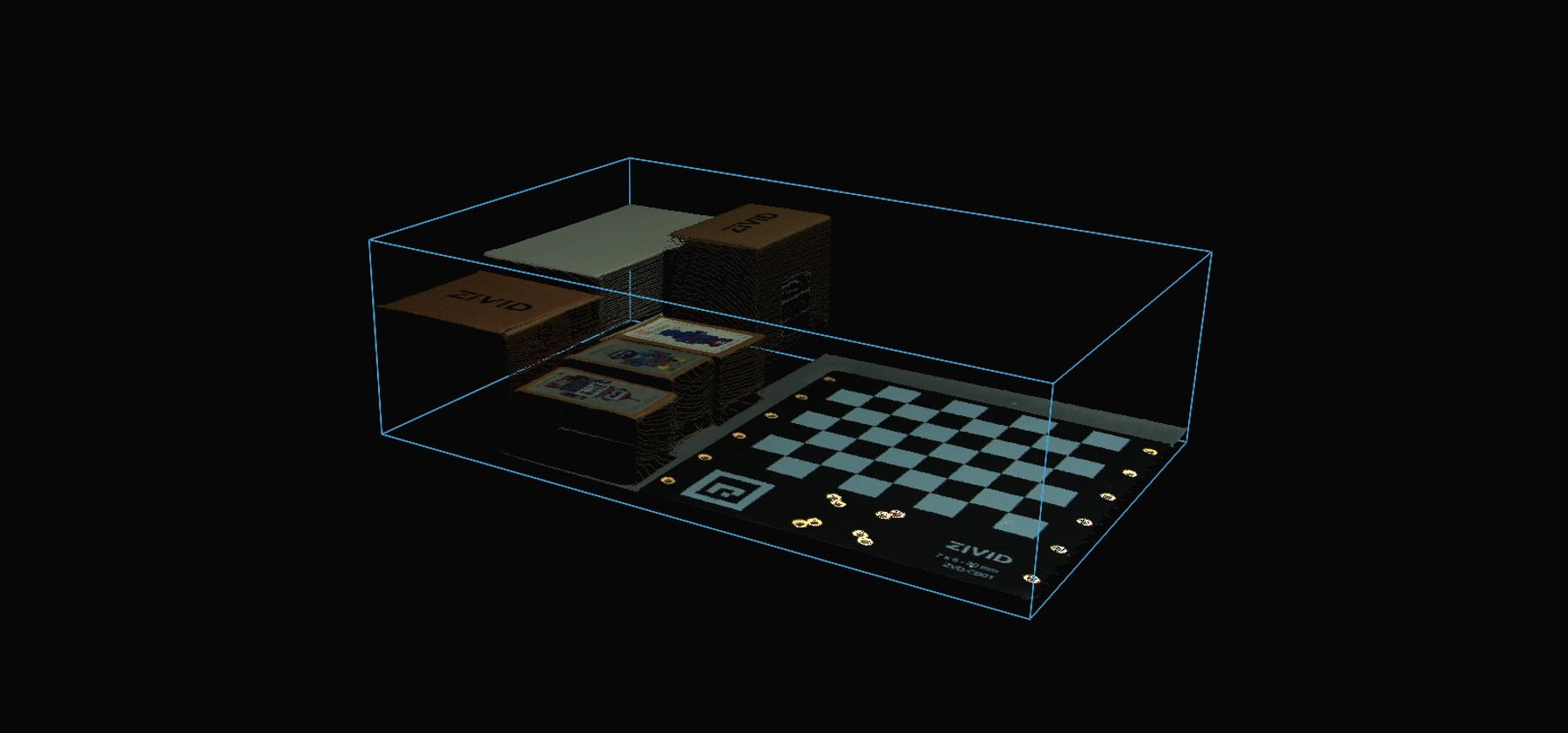
To filter the point cloud based on a ROI box, you can run our code sample.
Sample: ROIBoxViaArucoMarker.cpp
./ROIBoxViaArucoMarker
Sample: ROIBoxViaArucoMarker.cs
./ROIBoxViaArucoMarker
Sample: roi_box_via_aruco_marker.py
python roi_box_via_aruco_marker.py
Tip
Modify the code sample if you wish to use this in your own setup:
Replace the file camera with your actual camera and settings.
Place the calibration board in the bottom right corner of your bin.
Modify the ROI box size to your bin size.
Run sample!
You can now save the capture settings with the ROI parameters, remove the calibration board and use the settings on the whole bin.